Last updated on November 22, 2025
Amazon SNS Cheat Sheet
- A web service that makes it easy to set up, operate, and send notifications from the cloud. SNS follows the “publish-subscribe” (pub-sub) messaging paradigm, with notifications being delivered to clients using a “push” mechanism rather than to periodically check or “poll” for new information and updates.
Features
- SNS is an event-driven computing hub that has native integration with a wide variety of AWS event sources (including EC2, S3, and RDS) and AWS event destinations (including SQS, and Lambda).
- Event-driven computing is a model in which subscriber services automatically perform work in response to events triggered by publisher services. It can automate workflows while decoupling the services that collectively and independently work to fulfill these workflows.
- Message filtering allows a subscriber to create a filter policy so that it only gets the notifications it is interested in.
- Message fanout occurs when a message is sent to a topic and then replicated and pushed to multiple endpoints. Fanout provides asynchronous event notifications, which in turn allows for parallel processing.
- SNS mobile notifications allow you to fanout mobile push notifications to iOS, Android, Fire OS, Windows, and Baidu-based devices. You can also use SNS to fanout text messages (SMS) to 200+ countries and fanout email messages (SMTP).
- Application and system alerts are notifications, triggered by predefined thresholds, sent to specified users by SMS and/or email.
- Push email and text messaging are two ways to transmit messages to individuals or groups via email and/or SMS.
- SNS provides durable storage of all messages that it receives. When SNS receives your Publish request, it stores multiple copies of your message to disk. Before SNS confirms to you that it received your request, it stores the message in multiple Availability Zones within your chosen AWS Region.
- SNS allows you to set a TTL (Time to Live) value for each message. When the TTL expires for a given message that was not delivered and read by an end user, the message is deleted.
- Amazon SNS integrates with various AWS services such as EC2, S3, RDS, Lambda, SQS, and Kinesis Data Firehose to enable event-driven workflows.
- SNS provides durable storage by replicating messages across multiple Availability Zones.
- You can set a Time-to-Live (TTL) for messages so that undelivered messages are automatically deleted after a certain period.
- SNS supports message fanout, allowing a single message to be delivered in parallel to multiple endpoints.
- Messages can include attributes such as timestamps, geospatial data, and identifiers to provide structured metadata.
- Subscribers can use filter policies to receive only the messages that match specific criteria.
- SNS offers a raw message delivery option, which sends the message payload without any JSON wrapping.
- It supports mobile push notifications for iOS, Android, Fire OS, Windows, and Baidu devices.
- SNS can send SMS and email notifications, with the ability to mark SMS as transactional or promotional.
- Delivery status tracking is available for SMS, email, and mobile push messages.
- FIFO topics support message deduplication to prevent duplicate deliveries.
- Messages can be published across AWS regions or to different AWS accounts.
- HTTP/S endpoints can be configured with retry policies that use linear or exponential backoff.
- SNS allows direct addressing to send targeted notifications to specific endpoints.
- Subscription filter policies now support numeric ranges, prefix matching, and “anything-but” rules for more precise message selection.
- Failed messages can be routed to Dead Letter Queues (DLQs) for error handling.
- The SNS API provides simple integration for publishing messages, subscribing endpoints, and managing topics.
- Topics and messages can be tagged for management, automation, and cost allocation.
- SNS supports encryption and detailed access control policies to secure messages.
- CloudWatch and CloudTrail can be used to monitor SNS topics and log API calls.
SNS provides simple APIs and easy integration with applications.
Publishers and Subscribers
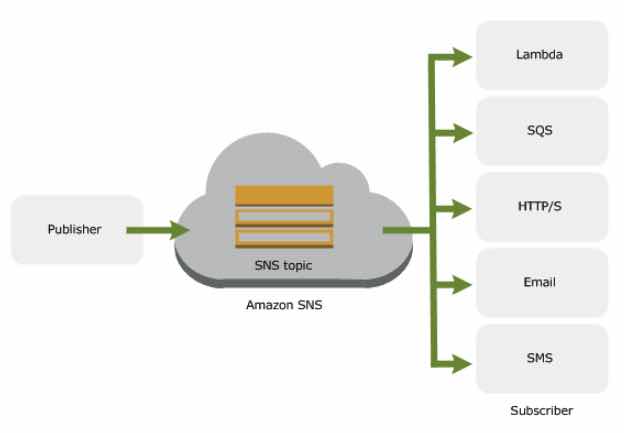
- Publishers communicate asynchronously with subscribers by producing and sending a message to a topic, which is a logical access point and communication channel.
- Subscribers consume or receive the message or notification over one of the supported protocols when they are subscribed to the topic.
- Publishers create topics to send messages, while subscribers subscribe to topics to receive messages.
- SNS FIFO topics support the forwarding of messages to SQS FIFO queues. You can also use SNS to forward messages to standard queues.
SNS Topics
- Instead of including a specific destination address in each message, a publisher sends a message to a topic. SNS matches the topic to a list of subscribers who have subscribed to that topic and delivers the message to each of those subscribers.
- Each topic has a unique name that identifies the SNS endpoint for publishers to post messages and subscribers to register for notifications.
- A topic can support subscriptions and notification deliveries over multiple transports.
The SNS service will attempt to deliver messages from the publisher in the order they were published into the topic, so no guarantee.
SNS also logs the delivery status of notification messages sent to topics with the following SNS endpoints:
- Application
- HTTP
- Lambda
- SQS
- Amazon Data Firehose
Message Attributes
- Amazon SNS supports the delivery of message attributes. Message attributes allow you to provide structured metadata items (such as time stamps, geospatial data, signatures, and identifiers) about the message. Message attributes are optional and separate from, but sent along with the message body.
- You can use message attributes to help structure the push notification message for mobile endpoints. The attributes are not delivered to the mobile endpoint, as they are when sending messages with message attributes to SQS endpoints.
- You can also use message attributes to make your messages filterable with subscription filter policies. You apply filter policies to topic subscriptions.
- Message attributes contain a name, type, and value that must not be empty or null. The message body should not be empty or null also.
Message Filtering
- A filter policy is a simple JSON object.
- By default, a subscriber of an SNS topic receives every message published to the topic. The filter policy contains attributes that define which messages the subscriber receives.
Raw Message Delivery
- By default, messages are delivered encoded in JSON that provides metadata about the message and topic.
- You can send large payload messages using AWS SDK that supports AWS Signature Version 4 signing.
- You can also enable raw message delivery for messages delivered to either SQS endpoints or HTTP/S endpoints.
System to System Messaging
- When a message is published to an SNS topic that has a Lambda function subscribed to it, the Lambda function is invoked with the payload of the published message. The Lambda function receives the message payload as an input parameter and can manipulate the information in the message, publish the message to other SNS topics, or send the message to other AWS services.
- When you subscribe a SQS queue to a SNS topic, you can publish a message to the topic and SNS sends a SQS message to the subscribed queue. The SQS message contains the subject and message that were published to the topic along with metadata about the message in a JSON document.
- When you subscribe an HTTP/s endpoint to a topic, you can publish a notification to the topic and SNS sends an HTTP POST request delivering the contents of the notification to the subscribed endpoint. When you subscribe to the endpoint, you select whether SNS uses HTTP or HTTPS to send the POST request to the endpoint.
User Notifications
- You have the ability to send push notification messages directly to apps on mobile devices. Push notification messages sent to a mobile endpoint can appear in the mobile app as message alerts, badge updates, or even sound alerts.
- Direct addressing allows you to deliver notifications directly to a single endpoint, rather than sending identical messages to all subscribers of a topic. This is useful if you want to deliver precisely targeted messages to each recipient.
- You can use SNS to send text messages, or SMS messages, to SMS-enabled devices. You can send a message directly to a phone number, or you can send a message to multiple phone numbers at once by subscribing those phone numbers to a topic and sending your message to the topic.
- You can use the Delivery Status feature to get information on the final disposition of your SMS message.
- SMS messages that are of high priority to your business should be marked as Transactional. This ensures that messages such as those that contain one-time passwords or PINs get delivered over routes with the highest delivery reliability.
- SMS messages that carry marketing messaging should be marked Promotional. Amazon SNS ensures that such messages are sent over routes that have reasonable delivery reliability but are substantially cheaper than the most reliable routes.
SNS Delivery Retries
- All messages sent to SNS are processed and delivered immediately. If a message cannot be successfully delivered on the first attempt, SNS implements a 4-phase retry policy:
1) retries with no delay in between attempts
2) retries with some minimum delay between attempts
3) retries with some back-off model (linear or exponential)
4) retries with some maximum delay between attempts
Amazon SNS Monitoring
- Monitoring SNS topics using CloudWatch
- Logging SNS API calls using CloudTrail
Amazon SNS Security
- SNS provides encrypted topics to protect your messages from unauthorized and anonymous access. The encryption takes place on the server side.
- SNS supports VPC Endpoints via AWS PrivateLink. You can use VPC Endpoints to privately publish messages to SNS topics, from a VPC, without traversing the public internet.
- Using access control policies, you have detailed control over which endpoints a topic allows, who is able to publish to a topic, and under what conditions.
- You can enable AWS X-Ray for your messages passing through Amazon SNS, making it easier to trace and analyze messages as they travel through to the downstream services.
Amazon SNS Pricing
- SNS has no upfront cost; you pay only for what you use.
- You are charged per message published and delivered. Each 64 KB chunk of data counts as one message.
- Endpoint delivery costs vary: SMS, email, mobile push, Lambda, and SQS may have different charges.
- FIFO topics have separate pricing based on published messages and payload size.
- Message filtering using attributes is free. Payload-based filtering may incur small charges.
- Data transfer in to SNS is free; data transfer out may incur charges at large scale.
- Server-side encryption (KMS) adds extra cost if enabled.
- SMS messaging costs vary by country and carrier; using dedicated short codes or toll-free numbers may have extra fees.
- SNS offers a Free Tier: 1M requests, 100K HTTP notifications, 1K email notifications, and 1M mobile push messages per month.
Amazon SNS Limits
- By default, SNS offers 10 million subscriptions per topic and 100,000 topics per account.
- A single SMS message can contain a maximum of 140 bytes of information.
- With the exception of SMS messages, SNS messages can contain up to 256 KB of text data.
Amazon SNS Cheat Sheet References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sns/latest/dg
https://aws.amazon.com/sns/features/
https://aws.amazon.com/sns/pricing/
https://aws.amazon.com/sns/faqs/