Last updated on July 26, 2023
Amazon ElastiCache Cheat Sheet
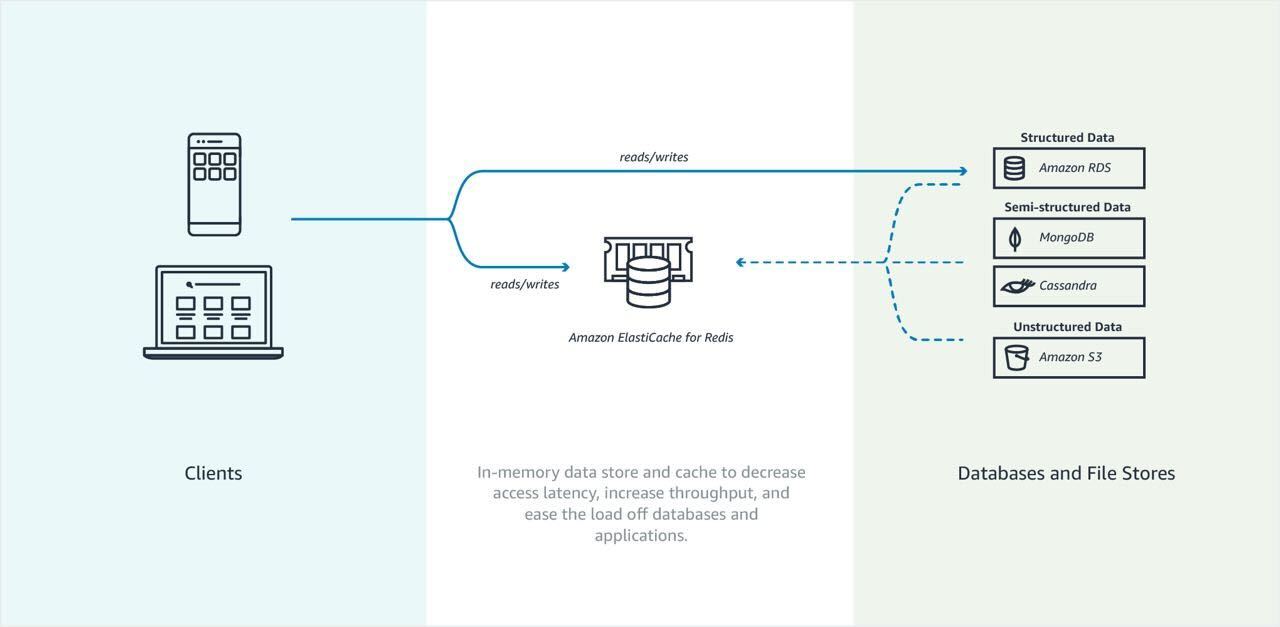
- ElastiCache is a distributed in-memory cache environment in the AWS Cloud.
- ElastiCache works with both the Redis and Memcached engines.
Components
- ElastiCache Nodes
- A node is a fixed-size chunk of secure, network-attached RAM. A node can exist in isolation from or in some relationship to other nodes.
- Every node within a cluster is the same instance type and runs the same cache engine. Each cache node has its own Domain Name Service (DNS) name and port.
- If a maintenance event is scheduled for a given week, it will be initiated and completed at some point during the 60 minute maintenance window you specify.
- Elasticache can be used for storing session state.
- ElastiCache Redis
- Existing applications that use Redis can use ElastiCache with almost no modification.
- Features
- Automatic detection and recovery from cache node failures.
- Multi-AZ with automatic failover of a failed primary cluster to a read replica in Redis clusters that support replication.
- Redis (cluster mode enabled) supports partitioning your data across up to 250 shards.
- The node or shard limit can be increased to a maximum of 500 per cluster if the Redis engine version is 5.0.6 or higher.
- Redis supports in-transit and at-rest encryption with authentication so you can build HIPAA-compliant applications.
- Flexible Availability Zone placement of nodes and clusters for increased fault tolerance.
- Data is persistent.
- Can be used as a datastore.
- Not multi-threaded.
- Amazon ElastiCache for Redis supports self-service updates, which allows you to apply service updates at the time of your choosing and track the progress in real-time.
- Cache data if:
- It is slow or expensive to acquire when compared to cache retrieval.
- It is accessed with sufficient frequency.
- It is relatively static, or if rapidly changing, staleness is not a significant issue.
- Redis sorted sets guarantee both uniqueness and element ordering. Each time a new element is added to the sorted set it’s reranked in real time. It’s then added to the set in its appropriate numeric position.
- In the Redis publish/subscribe paradigm, you send a message to a specific channel not knowing who, if anyone, receives it. Recipients of the message are those who are subscribed to the channel.
- Redis hashes are hashes that map string names to string values.
- Components
- Redis Shard – a grouping of one to six related nodes. A Redis (cluster mode disabled) cluster always has one shard. A Redis (cluster mode enabled) cluster can have 1–90 shards.
- A multiple node shard implements replication by have one read/write primary node and 1–5 replica nodes.
- If there is more than one node in a shard, the shard supports replication with one node being the read/write primary node and the others read-only replica nodes.
- Redis Cluster – a logical grouping of one or more ElastiCache for Redis Shards. Data is partitioned across the shards in a Redis (cluster mode enabled) cluster.
- Redis Shard – a grouping of one to six related nodes. A Redis (cluster mode disabled) cluster always has one shard. A Redis (cluster mode enabled) cluster can have 1–90 shards.
- For improved fault tolerance, have at least two nodes in a Redis cluster and enabling Multi-AZ with automatic failover.
- Replica nodes use asynchronous replication mechanisms to keep synchronized with the primary node.
- If any primary has no replicas and the primary fails, you lose all that primary’s data.
- You can use backup and restore to migrate to Redis (cluster mode enabled) and resize your Redis (cluster mode enabled).
- Redis (cluster mode disabled) vs Redis (cluster mode enabled)
|
Redis |
Redis |
|
|
Shards (node groups) |
1 |
1-90 |
|
Replicas for each shard |
0-5 |
0-5 |
|
Data partitioning |
No |
Yes |
|
Add/Delete replicas |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Add/Delete node groups |
No |
No |
|
Supports scale up |
Yes |
No |
|
Supports engine upgrades |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Promote replica to primary |
Yes |
No |
|
Multi-AZ with automatic failover |
Yes, with at least a replica. |
Required |
|
Backup / Restore |
Yes |
Yes |
-
- You can vertically scale up or scale down your sharded Redis Cluster on demand. Amazon ElastiCache resizes your cluster by changing the node type, while the cluster continues to stay online and serve incoming requests.
- You can set up automatic snapshots or initiate manual backups, and then seed new ElastiCache for Redis clusters. You can also export your snapshots to an S3 bucket of your choice for disaster recovery, analysis or cross-region backup and restore.
- Endpoints
- Single Node Redis (cluster mode disabled) Endpoints – used to connect to the cluster for both reads and writes.
- Multi-Node Redis (cluster mode disabled) Endpoints – use the primary endpoint for all writes to the cluster. The read endpoint points to your read replicas.
- Redis (cluster mode enabled) Endpoints – has a single configuration endpoint. By connecting to the configuration endpoint, your application is able to discover the primary and read endpoints for each shard in the cluster.
- Parameter Groups
- Cache parameter group is a named collection of engine-specific parameters that you can apply to a cluster.
- Parameters are used to control memory usage, eviction policies, item sizes, and more.
- Redis Security
- ElastiCache for Redis node access is restricted to applications running on whitelisted EC2 instances. You can control access of your cluster by using subnet groups or security groups. By default, network access to your clusters is turned off.
- By default, all new ElastiCache for Redis clusters are launched in a VPC environment. Use subnet groups to grant cluster access from Amazon EC2 instances running on specific subnets.
- ElastiCache for Redis supports TLS and in-place encryption for nodes running specified versions of the ElastiCache for Redis engine.
- You can use your own customer managed customer master keys (CMKs) in AWS Key Management Service to encrypt data at rest in ElastiCache for Redis.
- Redis Backups
- A point-in-time copy of a Redis cluster.
- Backups consist of all the data in a cluster plus some metadata.
- Global Datastore
- A new feature that provides fully managed, secure cross-region replication. You can now write to your ElastiCache for Redis cluster in one region and have the data available for reading in two other cross-region replica clusters.
- In the unlikely event of regional degradation, one of the healthy cross-region replica clusters can be promoted to become the primary cluster with full read/write capabilities.
ElastiCache Memcached
-
Features
- Automatic detection and recovery from cache node failures.
- Automatic discovery of nodes within a cluster enabled for automatic discovery, so that no changes need to be made to your application when you add or remove nodes.
- Flexible Availability Zone placement of nodes and clusters.
- ElastiCache Auto Discovery feature for Memcached lets your applications identify all of the nodes in a cache cluster and connect to them.
- ElastiCache node access is restricted to applications running on whitelisted EC2 instances. You can control the instances that can access your cluster by using subnet groups or security groups.
- It is not persistent.
- Supports large nodes with multiple cores or threads.
- Does not support multi-AZ failover or replication
- Does not support snapshots
-
Components
- Memcached cluster – a logical grouping of one or more ElastiCache Nodes. Data is partitioned across the nodes in a Memcached cluster.
- Memcached supports up to 100 nodes per customer for each Region with each cluster having 1–20 nodes.
- When you partition your data, use consistent hashing.
- Endpoint – the unique address your application uses to connect to an ElastiCache node or cluster.
- Each node in a Memcached cluster has its own endpoint.
- The cluster also has an endpoint called the configuration endpoint.
- ElastiCache parameter group – a named collection of engine-specific parameters that you can apply to a cluster. Parameters are used to control memory usage, eviction policies, item sizes, and more.
- ElastiCache allows you to control access to your clusters using security groups. By default, network access to your clusters is turned off.
- A subnet group is a collection of subnets that you can designate for your clusters running in a VPC environment. If you create a cluster in a VPC, then you must specify a cache subnet group. ElastiCache uses that cache subnet group to choose a subnet and IP addresses within that subnet to associate with your cache nodes.
- Memcached cluster – a logical grouping of one or more ElastiCache Nodes. Data is partitioned across the nodes in a Memcached cluster.
-
Mitigating Failures
- Node Failures
- Spread your cached data over more nodes. Because Memcached does not support replication, a node failure will always result in some data loss from your cluster.
- Availability Zone Failure
- Locate your nodes in as many Availability Zones as possible. In the unlikely event of an AZ failure, you will lose the data cached in that AZ, not the data cached in the other AZs.
- Node Failures
- ElastiCache uses DNS entries to allow client applications to locate servers (nodes). The DNS name for a node remains constant, but the IP address of a node can change over time.
Caching Strategies
- Lazy Loading – a caching strategy that loads data into the cache only when necessary.
- Only requested data is cached.
- Node failures are not fatal.
- There is a cache miss penalty.
- Stale data.
- Write Through – adds data or updates data in the cache whenever data is written to the database.
- Data in the cache is never stale.
- Write penalty vs. Read penalty. Every write involves two trips: A write to the cache and a write to the database.
- Missing data.
- Cache churn.
- By adding a time to live (TTL) value to each write, we are able to enjoy the advantages of each strategy and largely avoid cluttering up the cache with superfluous data.
Scaling ElastiCache for Memcached Clusters
- Scaling Memcached Horizontally
- The Memcached engine supports partitioning your data across multiple nodes. Because of this, Memcached clusters scale horizontally easily. A Memcached cluster can have 1 to 20 nodes. To horizontally scale your Memcached cluster, just add or remove nodes.
- Scaling Memcached Vertically
- When you scale your Memcached cluster up or down, you must create a new cluster. Memcached clusters always start out empty unless your application populates it.
Amazon ElastiCache Monitoring
- The service continuously monitors the health of your instances. In case a node experiences failure or a prolonged degradation in performance, ElastiCache will automatically restart the node and associated processes.
- ElastiCache provides both host-level metrics and metrics that are specific to the cache engine software. These metrics are measured and published for each Cache node in 60-second intervals.
- Monitor events with ElastiCache Events. When significant events happen on a cache cluster, including failure to add a node, success in adding a node, the modification of a security group, and others, ElastiCache sends a notification to a specific SNS topic.
- Monitor costs with tags.
Redis VS Memcached
- Memcached is designed for simplicity while Redis offers a rich set of features that make it effective for a wide range of use cases.
|
Redis (cluster mode enabled) |
Redis (cluster mode disabled) |
Memcached |
|
|
Data Types |
string, sets, sorted sets, lists, hashes, bitmaps, hyperloglog, geospatial indexes |
string, sets, sorted sets, lists, hashes, bitmaps, hyperloglog, geospatial indexes |
string, objects, (like databases) |
|
Data Partitioning (distribute your data among multiple nodes) |
Supported |
Unsupported |
Supported |
|
Modifiable cluster |
Only versions 3.2.10 and later |
Yes |
|
|
Online resharding |
Only versions 3.2.10 and later |
No |
|
|
Encryption |
3.2.6,4.0.10 and later |
Unsupported |
|
|
Sub-millisecond latency |
Yes |
||
|
FedRAMP, PCI DSS and HIPAA compliant |
3.2.6,4.0.10 and later |
No |
|
|
Multi-threaded (make use of multiple processing cores) |
No |
Yes |
|
|
Node type upgrading |
No |
Yes |
No |
|
Engine upgrading |
Yes |
||
|
Cluster replication (create multiple copies of a primary cluster) |
Supported |
Unsupported |
|
|
Multi-AZ for automatic failover |
Required |
Optional |
Unsupported |
|
Transaction (execute a group of commands as an isolated and automatic operation) |
Supported |
Unsupported |
|
|
Pub/Sub capability |
Yes |
No |
|
|
Backup and restore (keep your data on disk with a point in time snapshot) |
Supported |
Unsupported |
|
|
Lua Scripting (execute transactional Lua scripts) |
Supported |
Unsupported |
|
|
Use Case |
|
|
|
Amazon ElastiCache Pricing
- With on-demand nodes you pay only for the resources you consume by the hour without any long-term commitments.
- With Reserved Nodes, you can make a low, one-time, up-front payment for each node you wish to reserve for a 1 or 3 year term. In return, you receive a significant discount off the ongoing hourly usage rate for the Node(s) you reserve.
- ElastiCache provides storage space for one snapshot free of charge for each active ElastiCache for Redis cluster. Additional backup storage is charged.
- EC2 Regional Data Transfer charges apply when transferring data between an EC2 instance and an ElastiCache Node in different Availability Zones of the same Region.
Free Amazon ElastiCache Tutorials on YouTube:
https://www.youtube.com/user/AmazonWebServices/search?query=elasticache
Amazon ElastiCache-related Cheat Sheets:
Note: If you are studying for the AWS Certified Database Specialty exam, we highly recommend that you take our AWS Certified Database – Specialty Practice Exams and read our Database Specialty exam study guide.
Validate Your Knowledge
Question 1
A startup is developing a distributed cache for session management using Amazon ElastiCache for Redis with cluster mode enabled. The cache layer will be used by various applications running in AWS. The cluster shall use the default port for Redis connection.
Which combination of steps should the Database Specialist do to protect the ElastiCache cluster from unauthorized access? (Select TWO.)
- Enable Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) in the ElastiCache cluster.
- Set the associated security group to allow inbound traffic on TCP port 6379 from trusted clients only.
- Enable encryption in-transit and encryption at-rest on the ElastiCache cluster including Redis AUTH. Configure the clients to use the
auth-tokenparameter when connecting to the Redis cluster. - Ensure that the associated security group allows inbound traffic on TCP port 11211 from trusted clients only.
- Integrate AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF) with the ElastiCache Redis cluster.
Question 2
A developer is moving a legacy web application from their on-premises data center to AWS. The application is used simultaneously by thousands of users, and their session states are stored in memory. The on-premises server usually reaches 100% CPU Utilization every time there is a surge in the number of people accessing the application.
Which of the following is the best way to re-factor the performance and availability of the application’s session management once it is migrated to AWS?
- Use an ElastiCache for Redis cluster to store the user session state of the application.
- Store the user session state of the application using CloudFront.
- Use an ElastiCache for Memcached cluster to store the user session state of the application.
- Use Sticky Sessions with Local Session Caching.
For more AWS practice exam questions with detailed explanations, visit the Tutorials Dojo Portal:
Amazon ElastiCache References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonElastiCache/latest/red-ug/
https://aws.amazon.com/elasticache/redis-details/
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonElastiCache/latest/mem-ug/
https://aws.amazon.com/elasticache/redis-vs-memcached/
https://aws.amazon.com/elasticache/features/
https://aws.amazon.com/elasticache/pricing/