Last updated on February 17, 2023
- A task placement strategy is an algorithm for selecting instances for task placement or tasks for termination. When a task that uses the EC2 launch type is launched, Amazon ECS must determine where to place the task based on the requirements specified in the task definition, such as CPU and memory. Similarly, when you scale down the task count, Amazon ECS must determine which tasks to terminate.
- A task placement constraint is a rule that is considered during task placement.
- You can use constraints to place tasks based on Availability Zone or instance type.
- You can also associate attributes, which are name/value pairs, with your container instances and then use a constraint to place tasks based on attribute.
- Task placement strategy types:
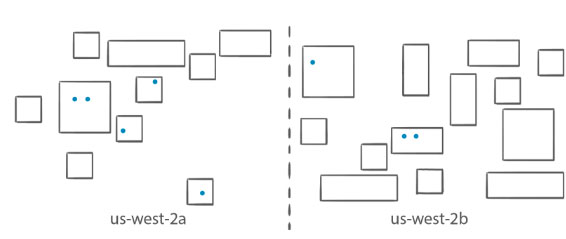
- Binpack – Place tasks based on the least available amount of CPU or memory. This minimizes the number of instances in use and allow you to be cost-efficient. For example, you have running tasks in c5.2xlarge instances that are known to be CPU intensive but are not memory consuming. You can maximize your instances’ memory allocation by launching tasks in them instead of spawning a new instance.
-
- Random – Place tasks randomly. You use this strategy when task placement or termination does not matter.
-
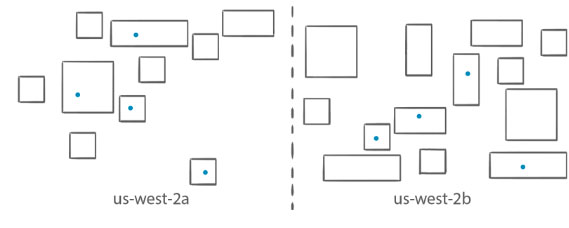
- Spread – Place tasks evenly based on the specified value. Accepted values are attribute key-value pairs, instanceId, or host. Spread is typically used to achieve high availability by making sure that multiple copies of a task are scheduled across multiple instances. Spread across Availability Zones is the default placement strategy used for services.
- You can combine different strategy types to suit your application needs.
- Task placement strategies are a best effort.
- By default, Fargate tasks are spread across Availability Zones.
- By default, ECS uses the following placement strategies:
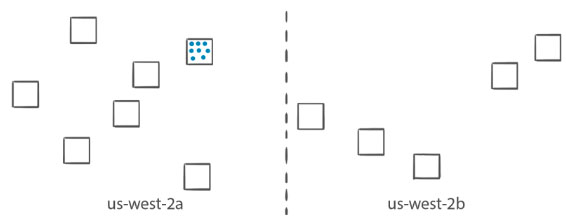
- When you run tasks with the RunTask API action, tasks are placed randomly in a cluster.
- When you launch and terminate tasks with the CreateService API action, the service scheduler spreads the tasks across the Availability Zones (and the instances within the zones) in a cluster.
Sources:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/task-placement.html
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/amazon-ecs-task-placement/