Last updated on December 26, 2025
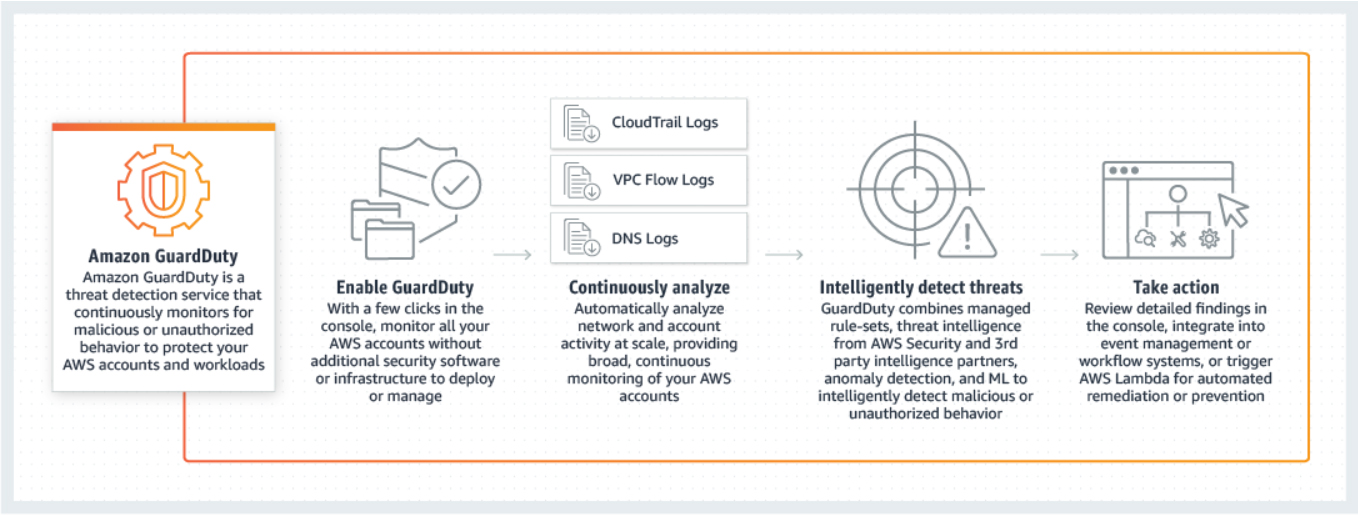
Amazon GuardDuty Cheat Sheet
- Amazon GuardDuty is an intelligent threat detection service that analyzes billions of events across your AWS accounts from:
- AWS CloudTrail (user and API activity)
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs (network traffic)
- DNS Logs (name query patterns)
Features
- UnauthorizedAccess: Detects API calls from external hosts using Lambda-created temporary credentials.
- Extended Threat Detection: Detects multi-stage attacks (EC2/ECS/EKS sequences).
- Runtime Monitoring Updates: Monitors latest agent versions for EC2, ECS, EKS-Fargate.
- Malware Protection for Backup: Scans EBS snapshots, EC2 AMIs, and Recovery Points.
- S3 Malware Protection: Scans objects up to 100 GB; on-demand scanning via API.
- Suppression Rules Enhancement: Supports wildcards (*, ?).
- CloudWatch Usage Metrics: Monitor GuardDuty usage by protection plan.
- AI Workloads Protection: Detects threats in AI workloads via Lambda.
- Regional Expansion: Supports multiple Asia Pacific, Canada, Middle East, and Mexico regions.
- EC2/ECS attack sequence finding types (Expanded Extended Threat Detection)
- Default automatic enablement of Extended Threat Detection
- Integrations with AWS services (Detective, Security Hub, EventBridge)
How It Works
- Backdoor: Compromised resource contacting a C&C server.
- Cryptocurrency: Mining software detected.
- Trojan: Silent malicious activity.
- Stealth: Attempting to hide actions/tracks.
- PenTest: Intentional testing tools or vulnerability scanners.
Service-specific Protection:
- EKS Protection: Monitors Kubernetes audit logs and runtime events inside pods/nodes.
- Lambda Protection: Monitors network logs to detect malicious code or crypto-mining.
- RDS Protection: Analyzes Amazon Aurora login attempts for credential compromise or brute-force attacks.
- S3 Protection: Monitors S3 data events for anomalous access patterns or exfiltration.
Malware Protection:
- EC2: Scans EBS volumes when suspicious activity is detected.
- S3: Scans new objects in specific buckets.
- Zero Performance Impact: Scans occur on snapshots or separate environments.
Other Threat Categories:
- Persistence: Unusual permission/configuration changes.
- Reconnaissance: Attacker scoping activity.
- Instance Compromise: Signs of compromised EC2 instances.
- Account Compromise: Indicators of IAM credential compromise.
- Bucket Compromise: Suspicious S3 activity.
- Runtime Security: Threats inside OS or containers.
Data Sources & Event Analysis
- AWS CloudTrail Management Events – API calls and user activity.
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs – IP traffic data.
- DNS Logs – Query patterns.
- CloudTrail Data Events (S3) – Object-level activity.
- Kubernetes Audit Logs – Control plane activity.
- RDS Login Activity – Aurora login attempts.
- Runtime Monitoring – OS-level events via lightweight agent.
Threat Detection Categories
- Reconnaissance: Scoping out environment.
- Instance Compromise: EC2 compromised indicators.
- Account Compromise: IAM credential compromise indicators.
- Bucket Compromise: Suspicious S3 access or exfiltration.
- Malware: Malware on EBS or S3.
- Runtime Security: OS/container threats.
GuardDuty Findings
GuardDuty generates findings when it detects unexpected and potentially malicious activity. These are viewable via Console, CLI, or API.
A Finding’s summary includes:
-
Finding type: A concise yet readable description of the potential security issue.
-
Severity: Assigned severity level (High, Medium, or Low).
-
Region: The AWS region where the finding was generated.
-
Count: Number of times this finding was generated.
-
Account ID / Resource ID: Identifiers for the affected account and resource.
-
Threat list name: Name of the threat list (if applicable).
-
Last seen: Time the activity took place.
Detailed Finding Sections:
-
Resource Affected: Includes Resource role (Target), Resource type (AccessKey, Instance, S3Bucket, etc.), Instance ID, Port, Access Key ID, Principal ID, User type/name.
-
Action: Describes the activity type (
NETWORK_CONNECTION,AWS_API_CALL,PORT_PROBE,DNS_REQUEST), API name, Connection direction (INBOUND,OUTBOUND), and Protocol. -
Actor: Location (IP geolocation), Organization (ISP/ASN), IP address, Port, and Domain.
Threat Purpose Definitions (The “Why”):
-
Backdoor: Compromised resource contacting a C&C server.
-
Behavior: Activity patterns differing from the established baseline.
-
Cryptocurrency: Mining software detected.
-
PenTest: Intentional testing tools (vulnerability scanners) detected.
-
Persistence: Unusual changes to permissions/network configs to maintain access.
-
Policy: Behavior violating security best practices.
-
PrivilegeEscalation: Principal trying to gain higher privileges indicatively.
-
Recon: Scoping out vulnerabilities (port probing, listing users).
-
ResourceConsumption: Unusual launch of resources (e.g., launching many EC2 instances).
-
Stealth: Attempting to hide actions/tracks (e.g., disabling logs).
-
Trojan: Silent malicious software carrying out attacks.
-
UnauthorizedAccess: Suspicious activity by an unauthorized individual.
Managing Findings
- Filters: View specific findings.
- Suppression Rules: Automatically archive matching findings.
- Trusted IP Lists: Whitelist secure IPs (1 per region).
- Threat Lists: Custom malicious IP lists (6 per region).
- Exporting: Findings automatically exported to EventBridge or S3 within 5 minutes.
Amazon GuardDuty Pricing
- Foundational: Charged based on the volume of CloudTrail events, VPC Flow Logs, and DNS Logs analyzed.
- EKS Protection: Charged per vCPU per hour for Runtime Monitoring and per million audit logs.
- Lambda Protection: Charged per GB of network activity logs scanned.
- Malware Protection: Charged per GB of data scanned (EBS volumes or S3 objects).
- RDS Protection: Charged per million login events analyzed.
- Free Trial: New accounts (and new features enabled on existing accounts) typically receive a 30-day free trial.
- Note: If you are studying for the AWS Certified Security Specialty exam, we highly recommend that you take our AWS Certified Security – Specialty Practice Exams and read our Security Specialty exam study guide.
- Validate Your Knowledge
- Question 1
- A company is using Amazon GuardDuty to continuously monitor its AWS resources for malicious activity, unauthorized port scanning, and other security vulnerabilities. Whenever there are pre-approved port scanning activities from specific Amazon EC2 instances owned by the IT Security team, the Operations team still receives GuardDuty events via Amazon EventBridge. There is a new requirement to suppress alerts on these authorized security tests to prevent false positives. The Security team must ensure that the alerts are still sent for any unauthorized activity in AWS.
- Which of the following is the MOST suitable solution for this scenario?
- Exclude and filter out the IP addresses of the pre-approved EC2 instances owned by the Security team in AWS CloudTrail.
- Attach Elastic IP addresses to the EC2 instances and then add these addresses to the Trusted IP list in GuardDuty.
- Install the Amazon Inspector agent on the EC2 instances that execute the pre-approved port scanning activities. Configure Inspector to exclude the pre-approved port scanning activities from these instances.
- Use the
GuardDutyExcludedtag to prevent GuardDuty from generating alerts for pre-approved port scanning activities.
- For more AWS practice exam questions with detailed explanations, visit the Tutorials Dojo Portal:
- Amazon GuardDuty Cheat Sheet References:
- https://aws.amazon.com/guardduty/
https://aws.amazon.com/guardduty/faqs/
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/guardduty/latest/ug/what-is-guardduty.html
https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=7&v=o2YaIsps5LY