Last updated on May 29, 2024
Every application contains instructions made up of bytes and we want to make sure that these are kept safe in a secure storage system. When building applications on the cloud, it’s beneficial to know about the different types of storage systems to pick the right tool for the job. Welcome to part 2 of my 6-part series called Basics of the Basics to AWS, where I introduce you to AWS by breaking it down into smaller digestible concepts related to software development.
In this article, I will be talking about AWS Storage Options. Before we proceed with the services, we’ll be talking about File Storage, Object Storage, and Block Storage. The services included in this article are Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, and Amazon EFS. Let’s get started!

Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, and Amazon EFS
File Storage, Object Storage, and Block Storage
As ordinary computer users, we are all too familiar with File Storage. From the traditional way of storing files inside folders inside cabinets, File Storage allows us to store out data inside Files which are organized into Folders. Each Folder can also have sub-folders, creating a hierarchy for our files. We see this in the file systems of our computers as everything is stored in files, which are stored in folders. In AWS, we can see three main types of storage – File Storage, Object Storage, and Block Storage.
Object Storage stores data inside self-contained units at a flat level. Unlike the File Storage, there is no hierarchy in an Object Storage. Objects are found not through a path but through a unique key either in the form of a number or a prefix. Lastly, Block Storage is the default storage type for hard disk drives. In Block Storage, data is split into blocks, which are stored in fixed locations inside a storage. When one accesses files from a Block Storage, the processor finds all the blocks that are a part of that file and reassembles them to recreate the original file.
Amazon S3
Now that we know the different types of storage in AWS let’s move on to our first AWS storage service. Amazon S3, which stands for Simple Storage Service, is one of the core AWS services. It is an object storage service that allows us to store our files as objects inside buckets. We can mimic the hierarchy of a file system by creating “folders” inside buckets, but these are actually just prefixes, not actual folders. Amazon S3 is vital to our application as it allows us to store various multimedia assets. We can also control the visibility of our objects stored in S3 through Bucket Policies, which are JSON files that dictate who has access to which resources.
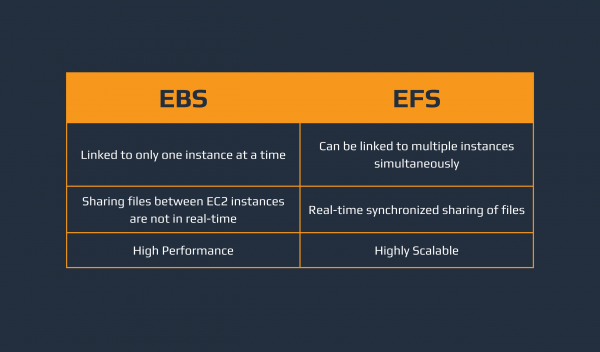
Amazon EBS and Amazon EFS
Our next 2 AWS storage services are all directly connected to AWS EC2. Amazon EBS stands for Elastic Block Store and is a Block Storage service for AWS. Through Amazon EBS, we can have EBS Volumes, which are network-attached blocks that we can connect to our EC2 Instances. By default, every instance we create has an attached EBS Volume, and we can easily add more if needed. The downside to EBS is that they can only be attached to one EC2 instance at a time (except for specific EBS Volume types). On the other hand, we have Amazon Elastic File System (EFS), which allows us to connect a File Storage to multiple EC2 Instances. The good thing about EFS is that it allows us to have centralized and synchronized storage for multiple EC2 Instances.
We are now done with the second part of our Basics of the Basics to AWS series. In this article, I talked about the differences between File Storage, Object Storage, and Block Storage. We also added 3 AWS Services to our toolkit, which are Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, and Amazon EFS. In the next article, we will be talking about databases with AWS.