This is the first part of a series of blogs about the platform management of a React Application infrastructure using Terraform. In the early phases of a software development project, it is mandatory to have the application reviewed by security way before the Beta release to ensure that the app adheres to the standards of a secure web application and is able to protect the sensitive data it handles. Most of the time, DevOps Engineers are tasked to deploy the web application in a private domain to allow the initial load testing, penetration testing, and other security-related testing while keeping the application secure from external attacks.
To be able to repeatedly deploy the infrastructure across different environments, we make use of an Infrastructure as Code tool, Terraform. When we use IaC, we are able to version the Infrastructure code and safely automate infrastructure tasks, including database changes. Learning Terraform is very easy, and is one of the reasons why it has remained one of the most popular Infrastructures as Code tools today.
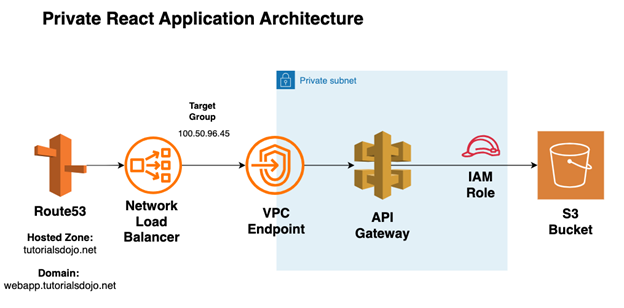
The Architecture
S3 is only one of the ways to host a React Application. It is a managed object storage service, and when used to host a web application, we maintain some level of control over how deployment is done as opposed to an alternative solution like AWS Amplify. S3 is a suitable solution for simple web applications and is what we’ll be using in this demo.
AWS S3 buckets are publicly resolvable. It does not have a native “private website” feature, but the S3 policy can be written such that the objects are only accessed by certain resources we define. In the architecture above, a private API Gateway is defined and is allowed access to the S3 bucket by assuming an IAM role that is added to the S3 bucket policy. The API Gateway can then be exposed using a VPC endpoint. The VPC Endpoint IP is configured as a target of the Network Load Balancer, which is the route destination of a private domain defined in Route 53.
In the solution, we assume that the S3 bucket is built separately as part of the permanent architecture when the web application is released. We will partially discuss the required S3 policy to limit access to the S3 objects.
Steps
1. Create an IAM role for S3 access
As best practice, all public access to an S3 bucket should be blocked. This is the principle of least privilege access. We will only allow access to the resource that needs it, in this case, the IAM role that the API Gateway will assume.
To assist in creating the S3 bucket policy statement, we can use the AWS Policy Generator provided here. We only need s3:ListBucket and s3:GetObject to access the files, but as this role will be re-used for the CI/CD pipeline, we will also add s3:PutObject permissions to it.
{
"Sid": "IAMRoleTemporaryAccess",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::123456789:role/react-app-iamrole"
},
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::s3-reactapp-bucket/*",
"arn:aws:s3:::s3-reactapp-bucket"
]
}
}
In the code above, the S3 bucket named s3-reactapp-bucket is added with a bucket policy named IAMRoleTemporaryAccess. The policy allows the iam role react-app-iamrole in account ID 12345678 the following actions: PutObject, ListBucket, and GetObject.
To build the Terraform code for this specific part of the infrastructure, we can define a logical group named IAM. This module will contain all the required parts of the IAM role resource. The IAM module will be a reusable component across environments. The variables will vary across environments, so it makes sense to create separate vars.tf files for each environment.
The IAM Module
There are three parts to the IAM module: aws_iam_role, aws_iam_policy, and aws_iam_policy_attachment (where we attach the iam policy to the iam role).
a. aws_iam_role
resource "aws_iam_role" "tutorialsdojo-iamrole" {
name = "${var.iamrolename}"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": ["apigateway.amazonaws.com"]
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
})
}
Note: In the code above, the IAM role name is an input named iamrolename and takes the value of the variable from the vars.tf file in the same location. This strategy is done to allow the module to use a name passed to it, allowing it to be re-used across environments.
b. aws_iam_policy
The aws_iam_policy contains the policy statement of the role. Since the IAM role is being built out, the resource defined can refer back to the terraform code of the previous resource (aws_iam_role.tutorialsdojo-iamrole.arn)
resource "aws_iam_policy" "tutorialsdojo-iampolicy" {
name = "${var.iampolicyname}"
description = "Tutorials Dojo IAM Role Policy"
policy = <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"s3:GetBucketLocation",
"s3:GetBucketTagging",
"s3:GetBucketVersioning",
"s3:GetBucketWebsite",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:GetObjectAcl",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:ListBucketMultipartUploads",
"s3:ListBucketVersions",
"s3:PutBucketCORS",
"s3:PutBucketTagging",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:PutObjectAcl"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": [
"${aws_iam_role.tutorialsdojo-iamrole.arn}"
]
}
]
}
EOF
}
c. aws_iam_policy_attachment
Lastly, we can associate the IAM policy with the IAM role by using aws_iam_policy_attachment.
resource "aws_iam_policy_attachment" "tutorialsdojo-iampolicyattachment" {
name = "tutorialsdojo-iamrole-attachment"
roles = [aws_iam_role.tutorialsdojo-iamrole.name]
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.tutorialsdojo-iampolicy.arn
}
This completes the IAM role resource needed for the architecture.
Putting it Together
In the main.tf file under the environments folder, we can invoke the modules by the code below. Take note that all the required variable inputs of the module should also be provided when invoking the module.
module "tutorialsdojo-iamrole" {
source = "../../modules/iam"
aws_profile = var.aws_profile
aws_region = var.aws_region
iamrolename = var.iamrolename
}
2. Create an ACM Certificate for the private domain
Since the ACM certificate rarely changes, we can skip creating a Terraform code for it and just request for a private certificate manually through the AWS management console. Note that the private certificate option will only be available for selection if you have already set up a private certificate authority in your AWS account.
Once available, you can get the certificate ARN of the private certificate and use it when building the Terraform code of the rest of the web application. Do note that a CNAME record has to be added in Route53 to prove to AWS that you own or control all the domain names that you request in ACM.
3. Build the Terraform Code of the Private Infrastructure
Folder Structure
To continue on the standard of folder structure, the rest of the application will be built out within the modules folder to allow code re-use when deploying the app to a different environment. Here, we logically grouped the modules into two: apigateway-internal and nlb.
Breaking down the apigateway-internal module
The first resource to build is the aws_api_gateway_rest_api resource. An API endpoint type can either be edge-optimized, regional, or private. Since the requirement for the web application is to be accessible in an internal network, we will configure the endpoint to be PRIVATE.
resource "aws_api_gateway_rest_api" "tutorialsdojo-restapi" {
name = "${var.apigwname}"
description = "TutorialsDojo Bucket Private API Gateway"
policy = "${data.aws_iam_policy_document.tutorialsdojo-resourcepolicy.json}"
endpoint_configuration {
types = ["PRIVATE"]
vpc_endpoint_ids = [ "${var.apigwvpce}" ]
}
binary_media_types = [ "*/*" ]
tags = local.common_tags
}
From the code above, we specify the policy to refer to a data document json code. This is a strategy to separate out code and keep the resources configurations clean and easy to follow. Below is the data code that is being referred to by the endpoint.
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "tutorialsdojo-resourcepolicy" {
statement {
effect = "Deny"
actions = [
"execute-api:Invoke"
]
principals {
type = "*"
identifiers = ["*"]
}
resources = [
"execute-api:/*",
]
condition {
test = "StringNotEquals"
variable = "aws:sourceVpc"
values = [
"${var.apigwvpcid}"
]
}
}
statement {
effect = "Allow"
actions = [
"execute-api:Invoke"
]
principals {
type = "*"
identifiers = ["*"]
}
resources = [
"execute-api:/*",
]
}
}
The root proxy is the root path for the web application and is a pass-through method in the api gateway module.
There are four resources to build out for the root proxy: aws_api_gateway_method, aws_api_gateway_integaration, aws_api_gateway_method_response, and aws_api_gateway_integration_response.
resource "aws_api_gateway_method" "tutorialsdojo-apigwmethod" {
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration" "tutorialsdojo-rootintegration" {
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_method_response" "tutorialsdojo-rootmethodresp" {
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration_response" "tutorialsdojo-rootintegrationresp" {
}
Below is the expanded Terraform code of these four resources.
resource "aws_api_gateway_method" "tutorialsdojo-apigwmethod" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id
resource_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.root_resource_id
http_method = "GET"
authorization = "NONE"
api_key_required = "false"
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration" "tutorialsdojo-rootintegration" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id
resource_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.root_resource_id
http_method = aws_api_gateway_method.tutorialsdojo-apigwmethod.http_method
integration_http_method = "GET"
type = "AWS"
uri = "arn:aws:apigateway:${var.aws_region}:s3:path/${var.s3name}${var.s3index}"
credentials = "${var.iamrole}"
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_method_response" "tutorialsdojo-rootmethodresp" {
rest_api_id = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id}"
resource_id = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.root_resource_id}"
http_method = "${aws_api_gateway_method.tutorialsdojo-apigwmethod.http_method}"
status_code = "200"
response_parameters = {
"method.response.header.Content-Type" = false
"method.response.header.Content-Length" = false
}
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration_response" "tutorialsdojo-rootintegrationresp" {
rest_api_id = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id}"
resource_id = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.root_resource_id}"
http_method = "${aws_api_gateway_method.tutorialsdojo-apigwmethod.http_method}"
status_code = "${aws_api_gateway_method_response.tutorialsdojo-rootmethodresp.status_code}"
response_parameters = {
"method.response.header.Content-Type" = "integration.response.header.Content-Type"
"method.response.header.Content-Length" = "integration.response.header.Content-Length"
}
selection_pattern = ""
}
For the rest of the methods, we will follow the following resource structure.
resource "aws_api_gateway_resource" "tutorialsdojo-resource" {
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_method" "tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall" {
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration" "tutorialsdojo-otherintegration" {
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_method_response" "tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall200" {
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_method_response" "tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall404" {
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration_response" "tutorialsdojo-otherintegrationresp200" {
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration_response" "tutorialsdojo-otherintegrationresp404" {
}
The expanded code is shown below:
resource "aws_api_gateway_resource" "tutorialsdojo-resource" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id
parent_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.root_resource_id
path_part = "{proxy+}"
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_method" "tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id
resource_id = aws_api_gateway_resource.tutorialsdojo-resource.id
http_method = "GET"
authorization = "NONE"
api_key_required = "false"
request_parameters = {
"method.request.path.proxy" = true
}
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration" "tutorialsdojo-otherintegration" {
rest_api_id = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id}"
resource_id = "${aws_api_gateway_resource.tutorialsdojo-resource.id}"
http_method = "${aws_api_gateway_method.tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall.http_method}"
integration_http_method = "GET"
type = "AWS"
uri = "arn:aws:apigateway:${var.aws_region}:s3:path/${var.s3name}${var.s3index}"
credentials = "${var.iamrole}"
request_parameters = {
"integration.request.path.proxy" = "method.request.path.proxy"
}
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_method_response" "tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall200" {
rest_api_id = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id}"
resource_id = "${aws_api_gateway_resource.tutorialsdojo-resource.id}"
http_method = "${aws_api_gateway_method.tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall.http_method}"
status_code = "200"
response_parameters = {
"method.response.header.Content-Type" = false
"method.response.header.Content-Length" = false
}
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_method_response" "tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall404" {
rest_api_id = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id}"
resource_id = "${aws_api_gateway_resource.tutorialsdojo-resource.id}"
http_method = "${aws_api_gateway_method.tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall.http_method}"
status_code = "404"
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration_response" "tutorialsdojo-otherintegrationresp200" {
rest_api_id = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id}"
resource_id = "${aws_api_gateway_resource.tutorialsdojo-resource.id}"
http_method = "${aws_api_gateway_method.tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall.http_method}"
status_code = "${aws_api_gateway_method_response.tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall200.status_code}"
response_parameters = {
"method.response.header.Content-Type" = "integration.response.header.Content-Type"
"method.response.header.Content-Length" = "integration.response.header.Content-Length"
}
selection_pattern = ""
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration_response" "tutorialsdojo-otherintegrationresp404" {
rest_api_id = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.tutorialsdojo-restapi.id}"
resource_id = "${aws_api_gateway_resource.tutorialsdojo-resource.id}"
http_method = "${aws_api_gateway_method.tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall.http_method}"
status_code = "${aws_api_gateway_method_response.tutorialsdojo-apigwmethodall404.status_code}"
response_parameters = {
"method.response.header.Content-Type" = "integration.response.header.Content-Type"
"method.response.header.Content-Length" = "integration.response.header.Content-Length"
}
selection_pattern = "404"
}
Breaking down the nlb module.
For the nlb module, we first build out the network load balancer resource and the target group.
resource "aws_lb" "tutorialsdojo-nlb" {
name = "${var.nlbname}"
internal = true
load_balancer_type = "network"
ip_address_type = "ipv4"
subnets = ["${var.subnet0}","${var.subnet1}","${var.subnet2}"]
enable_deletion_protection = false
tags = local.common_tags
}
resource "aws_lb_target_group" "tutorialsdojo-nlbtg" {
name = "${var.nlbtg}"
port = 443
protocol = "TLS"
vpc_id = "${var.vpcid}"
target_type = "ip"
health_check {
port = 443
protocol = "TCP"
}
tags = local.common_tags
}
The data can be separated as below:
data "aws_vpc_endpoint" "tutorialsdojo-apigwvpce" {
vpc_id = "${var.vpcid}"
service_name = "com.amazonaws.us-east-1.execute-api"
}
data "aws_network_interface" "tutorialsdojo-vpceeni0" {
id = "${var.eni0}"
}
data "aws_network_interface" "tutorialsdojo-vpceeni1" {
id = "${var.eni1}"
}
data "aws_network_interface" "tutorialsdojo-vpceeni2" {
id = "${var.eni2}"
}
Lastly, we build the load balancer target group attachments as well as the listener configuration of the load balancer.
resource "aws_lb_target_group_attachment" "tutorialsdojo-nlbattach0" {
target_group_arn = "${aws_lb_target_group.tutorialsdojo-nlbtg.arn}"
target_id = "${data.aws_network_interface.tutorialsdojo-vpceeni0.private_ip}"
port = 443
}
resource "aws_lb_target_group_attachment" "tutorialsdojo-nlbattach1" {
target_group_arn = "${aws_lb_target_group.tutorialsdojo-nlbtg.arn}"
target_id = "${data.aws_network_interface.tutorialsdojo-vpceeni1.private_ip}"
port = 443
}
resource "aws_lb_target_group_attachment" "tutorialsdojo-nlbattach2" {
target_group_arn = "${aws_lb_target_group.tutorialsdojo-nlbtg.arn}"
target_id = "${data.aws_network_interface.tutorialsdojo-vpceeni2.private_ip}"
port = 443
}
resource "aws_lb_listener" "nlb-listener" {
load_balancer_arn = "${aws_lb.tutorialsdojo-nlb.arn}"
port = "443"
protocol = "TLS"
ssl_policy = "${var.sslpolicy}"
certificate_arn = "${var.acmcertificatearn}"
default_action {
type = "forward"
target_group_arn = "${aws_lb_target_group.tutorialsdojo-nlbtg.arn}"
}
}
Similar to before, the modules can be invoked from the main.tf file by adding its path in the source.
module "tutorialsdojo-nlb" {
source = "../../modules/nlb"
aws_profile = var.aws_profile
aws_region = var.aws_region
}
module "tutorialsdojo-apigatewayinternal" {
source = "../../modules/apigateway-internal"
aws_profile = var.aws_profile
aws_region = var.aws_region
}
4. Add an A record pointing to the NLB record
Finally, we add an A record that points to the NLB endpoint to be able to access the web application via the private domain we defined.
Final Notes
As always, ensure that you destroy the infrastructure that you don’t need to avoid being charged unnecessarily. Building the infrastructure in Terraform allows you to easily do this by running terraform destroy, and it is a clean way to destroy all temporary resources created in AWS.
References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/latest/developerguide/api-gateway-api-endpoint-types.html