Last updated on January 27, 2026
Google Cloud Hybrid Connectivity Cheat Sheet
- There are several ways to extend your on-premises environment to the Google Cloud Platform.
- You can connect your infrastructure to Google Cloud Platform (GCP) on your terms, from anywhere based on your requirements.
Cloud Interconnect
- Provides low latency, highly available connections that enable you to reliably transfer data between your on-premises and Google Cloud VPCs.
- Cloud Interconnect connections provide internal IP address communication, which means internal IP addresses are directly accessible from both networks.
- Cloud Interconnect offers two options to extend your on-premises network to the Google Cloud Platform:
- Dedicated Interconnect
- Direct physical Connection to Google’s network.
- Partner Interconnect
- Provides connectivity through a supported service provider.
- You can use Cloud Interconnect in combination with Private Google Access for on-premises resources so that your on-premises resources can use internal IP addresses rather than external IP addresses to reach Google APIs and services.
- Dedicated Interconnect
Direct Peering
- Direct Peering connects your on-premises network to Google services, including Google Cloud products that can be exposed via one or more public IP addresses.
- Traffic from Google’s network to your on-premises network also takes that same connection, including traffic from VPC networks in your projects.
- Direct Peering exists outside of Google Cloud Platform. So, unless you need to access Google Workspace applications, the recommended methods of access to Google Cloud Platform are via Dedicated Interconnect or Partner Interconnect.
Carrier Peering
- Carrier Peering enables you to access Google applications, such as Google Workspace, by using a service provider to obtain enterprise-grade network services that connect your infrastructure to Google.
- When connecting to Google through a service provider, you can get connections with higher availability and lower latency, using one or more links.
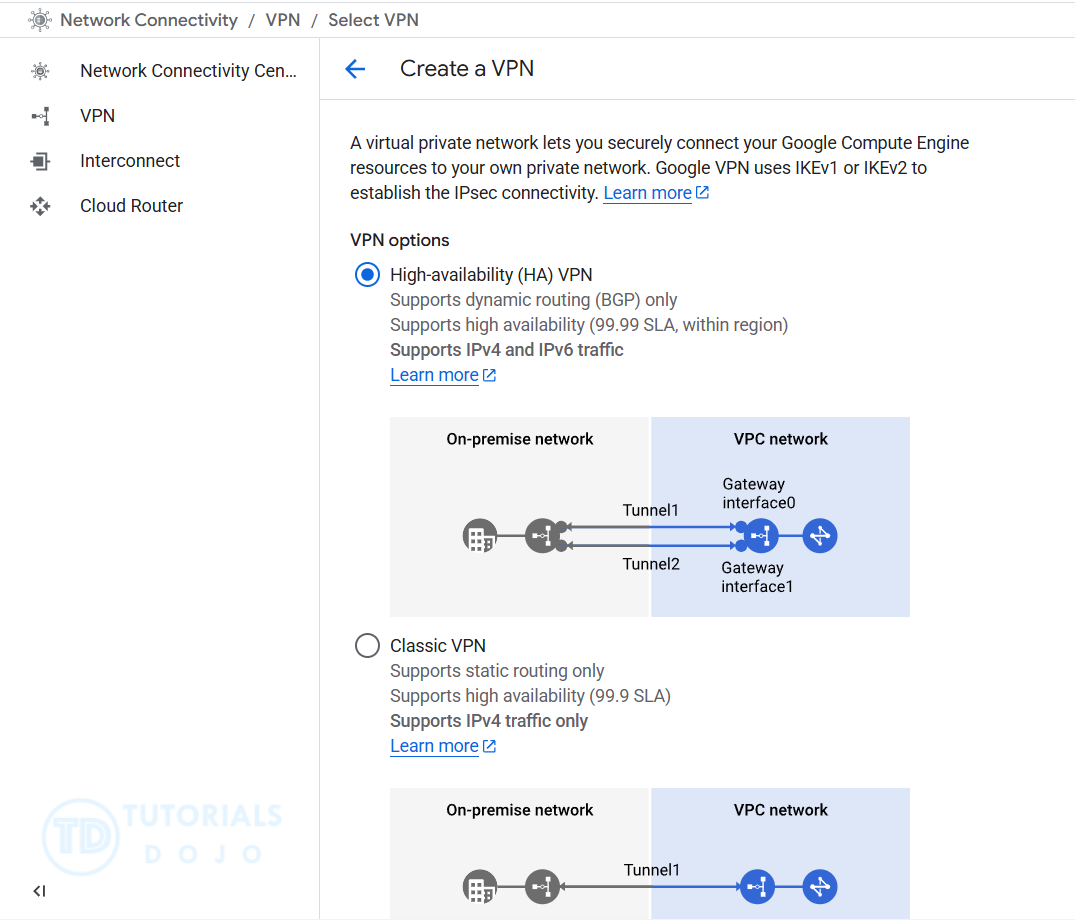
Cloud VPN
- Cloud VPN securely extends your peer network to Google’s network through an IPsec VPN tunnel.
- Ipsec VPN tunnels encrypt data by using industry-standard Ipsec protocols as traffic traverses the public Internet.
- It only requires a VPN device in your on-premises network, unlike Cloud Interconnect that comes with overhead and costs to set up a direct private connection.
- Cloud VPN pricing is based on the location of the Cloud VPN gateway and the number of tunnels per hour.
Validate Your Knowledge
Question 1
You are running VMs that are currently reaching the maximum capacity on your on-premises data center. You decided to extend your data center infrastructure to Google Cloud to accommodate new workloads. You have to ensure that the VMs that you provisioned in GCP can communicate directly with on-premises resources via a private IP range.
What should you do?
- Create a VPC on Google Cloud and configure it as a host for a Shared VPC.
- Build a custom-mode VPC. Set up VPC Network Peering between your on-premises network and your newly created VPC to establish a connection through a private IP range.
- Provision virtual machines on your on-premises and Google Cloud VPC networks that will serve as bastion hosts. Configure the VMs as proxy servers using public IP addresses.
- Set up Cloud VPN between your on-premises network to a VPC network through an IPsec VPN connection.
For more Google Cloud practice exam questions with detailed explanations, check out the Tutorials Dojo Portal:
Google Cloud Hybrid Connectivity Cheat Sheet References:
https://cloud.google.com/hybrid-connectivity
https://cloud.google.com/network-connectivity/docs/interconnect/concepts/overview
https://cloud.google.com/network-connectivity/docs/vpn/concepts/overview
https://cloud.google.com/network-connectivity/docs/direct-peering