Last updated on March 20, 2023
GCP Pricing Cheat Sheet
GCP’s customer-friendly pricing allows businesses to pay as you go, without termination fees, and no upfront costs.
Google Cloud Free Program
- New customers are given $300 free Cloud Billing credits valid for 90 days to explore and evaluate the Google Cloud Platform.
- Free Tier Limits are also available for all GCP customers on selected Google Cloud services – like GCE, GCS, and BigQuery. The free tier limit does not expire but is subject to change.
- You won’t be charged until you choose to upgrade your account from a free trial to a paid account through the GCP Console.
Cloud Billing Account
- In GCP, a project is linked to a Cloud Billing Account that enables customers to:
- connect a Payments Profile that includes a payment instrument to which costs are charged.
- pay for resource usage.
- A Cloud Billing Account can be linked to one or multiple projects.
- You can manage your Cloud Billing accounts using the Cloud Console.
- Cloud Billing accounts cannot be deleted.
- In case you close your Cloud Billing account, the Cloud Billing account information is retained for reporting and auditing purposes.
Pricing Factors
There are three basic pricing factors that influence your costs which are:
- Compute
- Storage
- Egress traffic
Pricing Innovations
Here are some pricing innovations introduced by GCP.
- Sustained-use Discounts
- Automatically get up to a 30% worth of discount on workloads that run for a significant portion of the billing month on Compute Engine and Cloud SQL.
- Preemptible instances
- Run instances at a lower price point than normal instances. Perfect for fault-tolerant applications that can withstand possible instance preemptions, which can help you save up to 79% on your costs significantly.
- Custom Machine Types
- Customize the type of CPU and memory you use for your instances and save up to 48% compared to fixed machine types from other clouds.
- Committed-use Discounts
- This pricing is ideal for workloads with predictable resource needs.
- When you purchase a committed use contract, you purchase a compute resource at a discounted price in return for committing to paying for those resources for 1 year or 3 years. Savings can be up to 57% without upfront cost or instance-type lock-in.
- Per-second billing
- Pay for services by the second with minimum consumption of one minute.
- Archival Storages
- Archival storage with the speed of disk at the cost of tape. Archival storages are ideal for data that you plan to be kept entirely for backup or archiving purposes.
- Rightsizing recommendations
- Compute Engine monitors the CPU and memory utilization for running VMs and automatically creates a rightsizing recommendation using the last 8 days of data.
- Unfortunately, sizing recommendations are currently not yet available for instances created using App Engine flexible environment, Dataflow, or GKE, or even for GCE instances with ephemeral disks, GPUs, or TPUs.
GCP Marketplace Pricing Model
The following are the pricing models when provisioning a solution from the GCP Marketplace:
- Free
- Customers only pay for the Google Cloud resources that they use, like the cost of running VM instances.
- Bring your own license (BYOL)
- Customers pay directly for the solution itself and are billed separately for the resources provisioned.
- Usage-based pricing
- Customers pay for software based on metrics that you choose.
- There are two pricing models for usage-based pricing namely:
- Fixed Pricing – charged based on the length of time the solution is used, in increments of minutes.
- Resource-based pricing – charged based on the number of vCPUs, size of the system’s memory, number of GPUs, or a combination of these options.
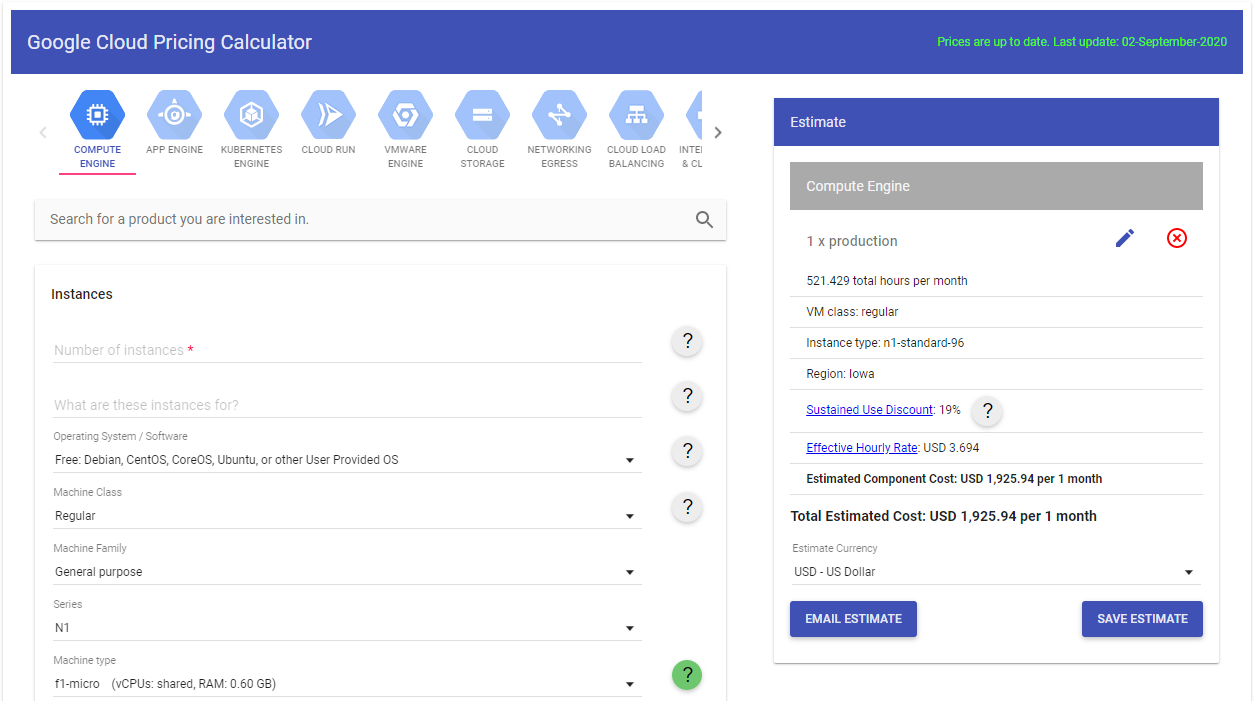
Pricing Calculator
You can estimate your cloud computing costs using the GCP Pricing Calculator.
Validate Your Knowledge
Question 1
You developed a decoupled application that is set to be deployed on a Kubernetes cluster on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). You need to be able to run on high IOPS for the application’s high-performance computing and you also need to use disk snapshots as part of your disaster recovery strategy. You used the GCP Pricing Calculator to generate a cost estimate and entered some information regarding your cluster, such as the number of nodes, average days, and average hours.
What should you do next?
- Enter the number of Local SSDs you want to use. Fill out Persistent Disk storage and snapshot storage fields.
- Enter the number of Local SSDs you want to use. Check the option to add the cost estimate for GKE cluster management.
- Request for quotation from the GCP Cloud Support Team.
- Tick the add GPUs option. Check the option to add the cost estimate for GKE cluster management.
Question 2
You have designed a cloud solution that uses a wide variety of Google Cloud Platform Services. Your company agreed to use these cloud services but asked you to provide an estimated cost of running this cloud solution. You need to submit an estimate to properly forecast future expenses.
What should you do?
- Deploy the solution on Google Cloud Platform. Leave the solution running for a week. Go to the GCP console and navigate to the Billing Report page. Multiply the 1-week cost by four to determine the monthly costs.
- Provide a list of GCP services of your cloud solution and check its pricing details on the GCP products pricing page. Create a Google Sheet with a monthly estimate of GCP services cost.
- Provide a list of GCP services of your cloud solution. Submit an email to GCP support with your GCP services list and ask them to estimate the monthly cost.
- Provide a list of GCP services of your cloud solution. Use the GCP Pricing Calculator and input the necessary details to get an estimated monthly cost for each GCP product.
For more Google Cloud practice exam questions with detailed explanations, check out the Tutorials Dojo Portal:
GCP Pricing Cheat Sheet References:
https://cloud.google.com/pricing
https://cloud.google.com/products/calculator
https://cloud.google.com/marketplace/docs/partners/vm/select-pricing