Last updated on December 23, 2025
Amazon CloudFront Cheat Sheet
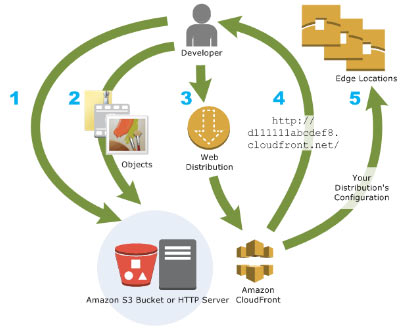
A global content delivery network (CDN) that speeds up the distribution of your static, dynamic, and streaming web content through a worldwide network of edge locations. CloudFront routes users to the edge location with the lowest latency for optimal performance.
Key Highlights
-
Speeds up static and dynamic content delivery
-
Supports HTTP, HTTPS, WebSocket, and gRPC
-
Regional edge caches for less-popular content
-
Integrates with Lambda@Edge, CloudFront Functions, MediaPackage, MediaStore, ALB, and custom origins
-
HIPAA eligible service
-
Supports TLS 1.2, TLS 1.3, TLSv1.2_2025, TLSv1.3_2025, mutual TLS, and post-quantum key exchange algorithms
-
Pay-per-use with free tier and flat-rate pricing plans
How CloudFront Delivers Content
-
Origin servers: S3 bucket, MediaPackage, MediaStore container, ALB, Lambda function URL, EC2, or custom HTTP server
-
Distributions: Define which origins CloudFront uses and how content is delivered
-
Edge locations: CloudFront caches content at global edge locations
-
Routing: User requests go to the lowest-latency edge location
Features
Content Delivery & Caching
-
Objects cached for 24 hours by default (configurable via TTLs)
-
Cache invalidation before expiration
-
Query string and header-based caching
-
Automatic gzip compression for supported file types
-
Origin Groups for primary/secondary failover
-
Preconfigured standard distribution settings
-
Multi-tenant distribution support for reusable configurations
Traffic & Access Management
-
Cache behaviors: Path pattern matching, origin selection, query string and header forwarding, HTTPS enforcement, signed URLs and cookies
-
Origin request policies: AWS-managed or custom policies, includes HostHeaderOnly
-
Networking & addressing: Anycast static IPs, dual-stack IPv4/IPv6, BYOIP via IPAM, IPv6 origin requests for custom origins, public CloudFront endpoints IPv6 support, VPC origin sharing across accounts
-
TLS & protocols: TLS 1.2, TLS 1.3, TLSv1.2_2025, TLSv1.3_2025, post-quantum (PQ) key exchange algorithms
Customization & Edge Compute
-
Lambda@Edge: Modify requests/responses, advanced logging controls, supports Node.js 22 and Python 3.13
-
CloudFront Functions: Lightweight edge logic; supports hostHeader, sni, allowedCertificateNames, originOverrides, CBOR Web Tokens (CWT), additional helper methods
-
Media Quality-Aware Resiliency (MQAR): Automatically selects the best-quality streaming origin
Amazon CloudFront Monitoring
-
Billing reports: High-level view of CloudFront activity across AWS
-
Usage reports: Aggregate by hour, day, or month with visual charts
-
CloudFront console reports: Cache Statistics, Popular Objects, Top Referrers, Usage, Viewers
-
AWS Config: Tracks configuration changes and evaluates compliance
-
Amazon CloudWatch: Requests, latency, error rates, CloudFront Function throttling
-
AWS CloudTrail: Captures CloudFront API calls (global service support required)
-
Server-Timing header: Measures performance from CloudFront to viewers
-
CloudFront-Viewer-TLS header: Shows TLS version and cipher used
-
Advanced access logging: Standard logging (v2), real-time logs, CMCD fields, connection-id for mutual TLS
-
CORS support: Wildcard access-control headers
-
Header-based identification: Configure header order and count to identify viewers
Amazon CloudFront Security
-
Layered protection: CloudFront + AWS Shield + AWS WAF + Route 53 (network & application-layer DDoS)
-
HTTPS / SSL/TLS: Enforced by default; advanced SSL features enabled
-
Geo-restriction: Allowlist or blocklist countries
-
Access controls: Custom HTTP headers for ALB restrictions, OAC for S3, MediaPackage, Lambda URLs, Field-Level Encryption for sensitive data
-
AWS-managed prefix lists: Restrict origin access to CloudFront IP ranges
-
Response headers policy: Remove or modify headers before sending to viewers
-
Mutual TLS (viewer): Viewer authentication with connection logging
Use Cases
-
Reduce operational overhead via centralized console and reusable distribution settings
-
Optimize performance with edge caching and dynamic routing
-
Protect content, APIs, and applications with layered security
-
Deliver high-quality media using MQAR, origin failover, and CloudFront Functions
-
Customize and monetize SaaS applications with Lambda@Edge and CloudFront Functions
Distributions & Origin Settings
-
Up to 25 origins per distribution
-
Supports:
-
Static and dynamic content
-
Video-on-demand
-
Live streaming
-
-
Configurable per-path cache behaviors
-
Custom domains with wildcard support (
*.example.com) -
Base path mappings for versioning and traffic migration
-
Custom error pages and error caching
-
Geographic restrictions per distribution
Amazon CloudFront Pricing
-
Charge for storage in an S3 bucket
-
Charge for serving objects from edge locations
-
Data Transfer Out: Charges apply for data transfer out to viewers
-
HTTP/HTTPS Requests
-
Invalidation Requests
-
Dedicated IP Custom SSL certificates associated with a CloudFront distribution
-
Additional surcharge for HTTPS requests with field-level encryption enabled
Compliance
-
PCI DSS validated
-
HIPAA eligible
-
SOC compliant
Free Amazon CloudFront Tutorials on YouTube:
https://www.youtube.com/user/AmazonWebServices/search?query=CloudFront
Amazon CloudFront-related Cheat Sheets:
- S3 Pre-signed URLs vs CloudFront Signed URLs vs Origin Access Identity (OAI)
- SNI Custom SSL vs Dedicated IP Custom SSL
Note: If you are studying for the AWS Certified Advanced Networking Specialty exam, we highly recommend that you take our AWS Certified Advanced Networking – Specialty Practice Exams and read our Advanced Networking Specialty exam study guide.
Validate Your Knowledge
Question 1
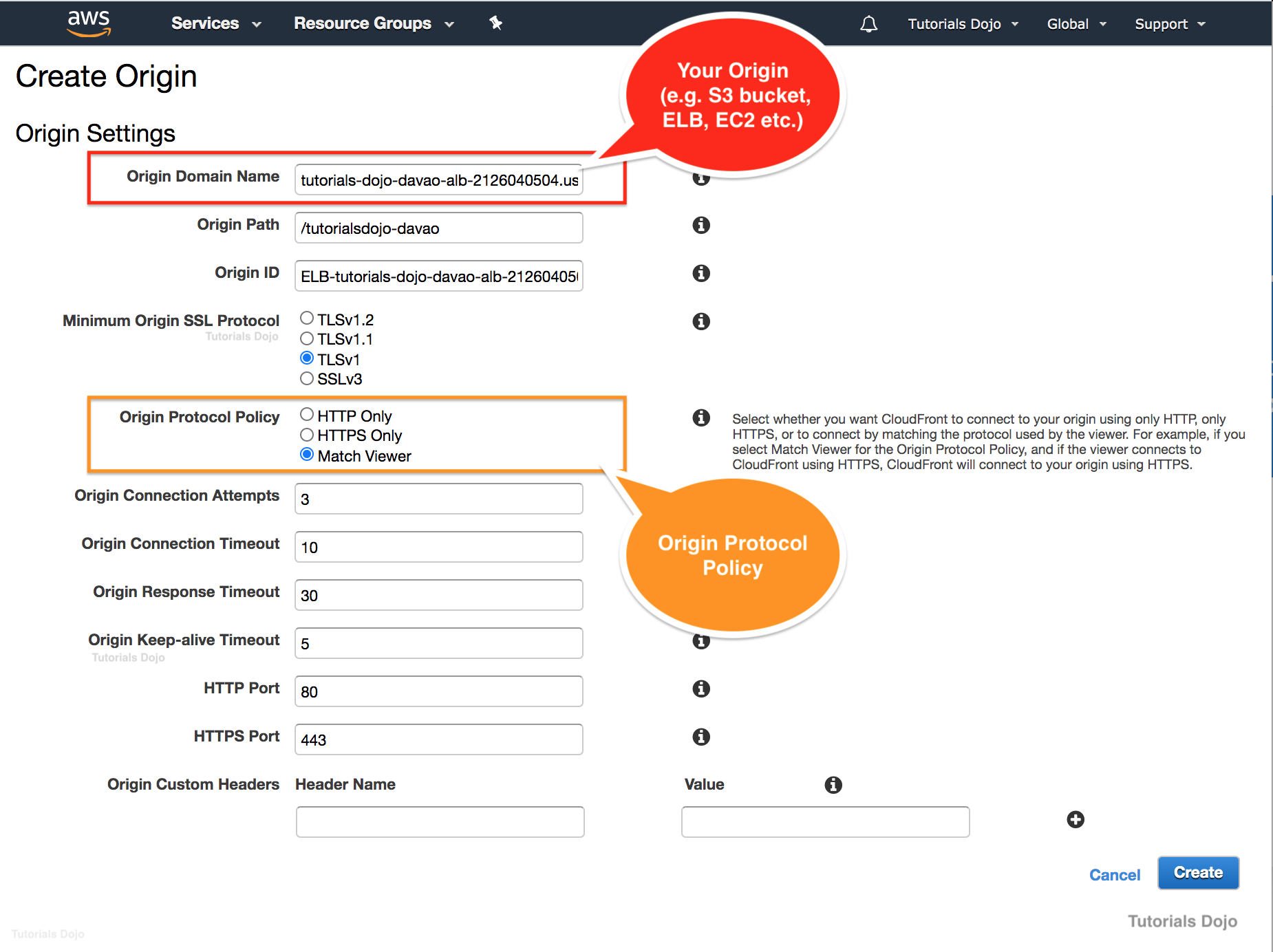
An online customer portal is hosted in an Amazon ECS cluster behind an Application Load Balancer. The portal is set as the origin of a CloudFront Web distribution to deliver the dynamic and static content to users in low-latency. A Cloud Engineer was assigned to configure CloudFront to communicate with your origin using HTTP or HTTPS, based on the protocol of the viewer request.
What should the Engineer implement to complete this task?
- Set the Origin Protocol policy of the CloudFront distribution to
Match Viewer. - Set the Origin Protocol policy of the CloudFront distribution to
HTTP and HTTPS. - Set the Viewer Protocol policy of the CloudFront distribution to
HTTP and HTTPS. - Set the Viewer Protocol policy of the CloudFront distribution to
Match Viewer.
Question 2
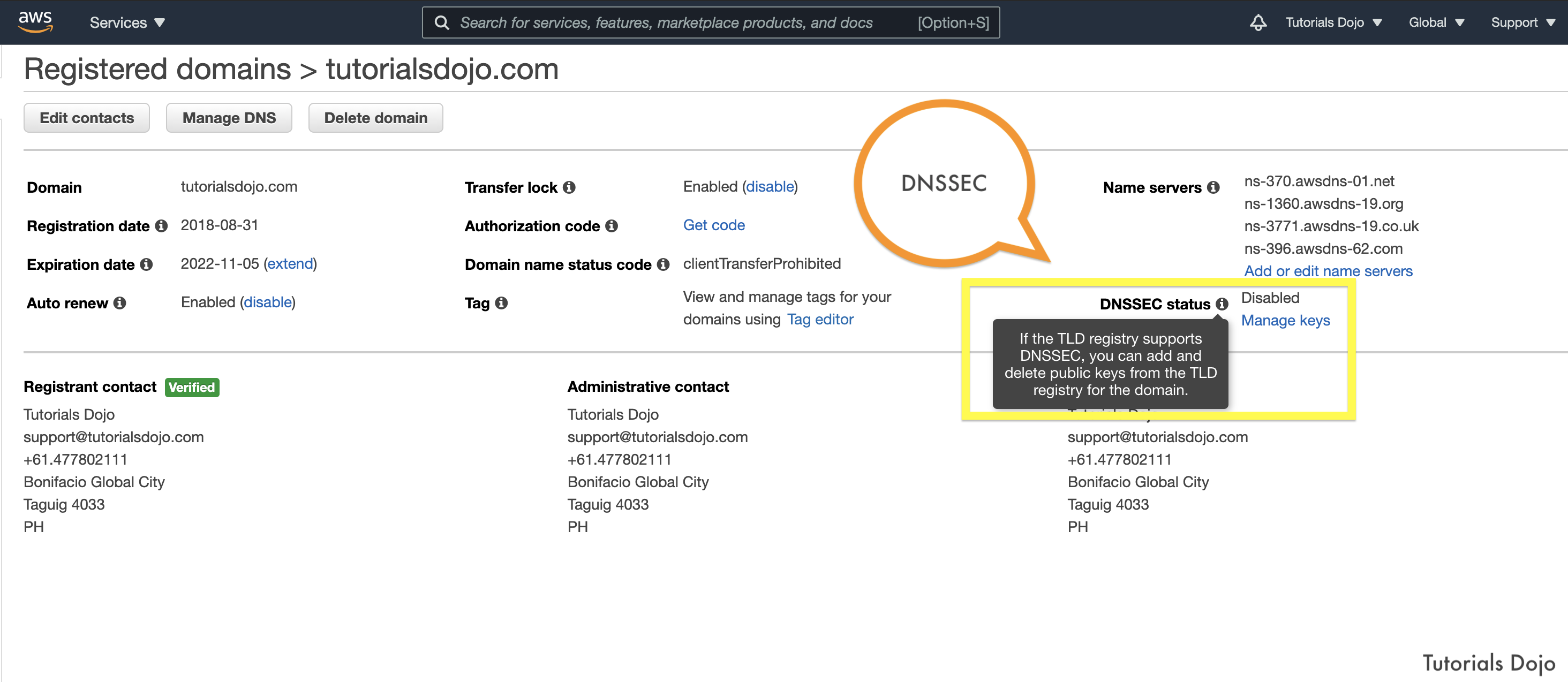
A company wants to launch its online shopping website to give customers an easy way to purchase the products they need. The proposed setup is to host the application on an AWS Fargate cluster, utilize a Load Balancer to distribute traffic between the Fargate tasks, and use Amazon CloudFront for caching and content delivery. The company wants to ensure that the website complies with industry best practices and should be able to protect customers from common “man-in-the-middle” attacks for e-commerce websites such as DNS spoofing, HTTPS spoofing, or SSL hijacking.
Which of the following configurations will provide the MOST secure access to the website?
- Register the domain name on Route 53 and enable DNSSEC validation for all public hosted zones to ensure that all DNS requests have not been tampered with during transit. Use AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) to generate a valid TLS/SSL certificate for the domain name. Configure the Application Load Balancer with an HTTPS listener to use the ACM TLS/SSL certificate. Use Server Name Identification and HTTP to HTTPS redirection on CloudFront.
- Register the domain name on Route 53. Use a third-party DNS provider that supports the import of the customer-managed keys for DNSSEC. Import a 2048-bit TLS/SSL certificate from a third-party certificate service to AWS Certificate Manager (ACM). Configure the Application Load Balancer with an HTTPS listener to use the imported TLS/SSL certificate. Use Server Name Identification and HTTP to HTTPS redirection on CloudFront.
- Use Route 53 for domain registration. Use a third-party DNS service that supports DNSSEC for DNS requests that use the customer-managed keys. Use AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) to generate a valid 2048-bit TLS/SSL certificate for the domain name and configure the Application Load Balancer HTTPS listener to use this TLS/SSL certificate. Use Server Name Identification and HTTP to HTTPS redirection on CloudFront.
- Register the domain name on Route 53. Since Route 53 only supports DNSSEC for registration, host the company DNS root servers on Amazon EC2 instances running the BIND service. Enable DNSSEC for DNS requests to ensure the replies have not been tampered with. Generate a valid certificate for the website domain name on AWS ACM and configure the Application Load Balancers HTTPS listener to use this TLS/SSL certificate. Use Server Name Identification and HTTP to HTTPS redirection on CloudFront.
For more AWS practice exam questions with detailed explanations, visit the Tutorials Dojo Portal:
Amazon CloudFront Cheat Sheet References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudFront/latest/DeveloperGuide
https://aws.amazon.com/cloudfront/features/
https://aws.amazon.com/cloudfront/pricing/
https://aws.amazon.com/cloudfront/faqs/