Last updated on June 5, 2023
Amazon S3 and Amazon VPC Relationship
Amazon S3 is a versatile object storage solution that boasts virtually unlimited storage capacity. You can expect that your files will be durably stored in S3 given that AWS provides an SLA for this service. When creating your S3 bucket, AWS provides you with a unique bucket URL that you can use to access your S3 bucket directly from the public internet, if you have public access enabled.
Amazon S3 is a service that is not used within a VPC. This means that traffic does not pass through VPC resources such as internet gateways or NAT gateways. This also means that, for security, instead of using security groups and network access control lists (NACL for short), you have bucket policies and S3 access control lists for managing access to your S3 bucket and objects. Amazon S3 traffic passes through the public internet. If you want your traffic to run only within the Amazon network then you will have to employ VPC endpoints.
What are VPC endpoints?
A VPC endpoint is what you use to privately connect your VPC to supported AWS services, such as Amazon S3. It adds a gateway entry in your VPC’s route table so that communication between your AWS resources, such as Amazon EC2 instances, and your S3 bucket pass through the gateway instead of the public internet. As a result, VPC endpoint is a regional service. You should create the endpoint in the same region as the VPC you want to link it to.
VPC endpoints are best used when you have compliance requirements or sensitive information stored in S3 that should not leave the Amazon network. A VPC endpoint is also a better option for private network connections in AWS, as compared to using a VPN solution or a NAT solution since it is easier to setup and offers you more network bandwidth at your disposal.
How to secure your S3 bucket using bucket policies and endpoint policies
VPC endpoints for S3 are secured through VPC endpoint access policies, which allows you to set which S3 buckets the endpoints should and should not have access to. By default, any user or service within the VPC, using credentials from any AWS account, has access to any Amazon S3 resource. Use these together with S3 bucket policies to further refine access control over your buckets and objects.
To get started with creating and securing your VPC endpoint via console,
-
- Go to VPC and select Endpoints
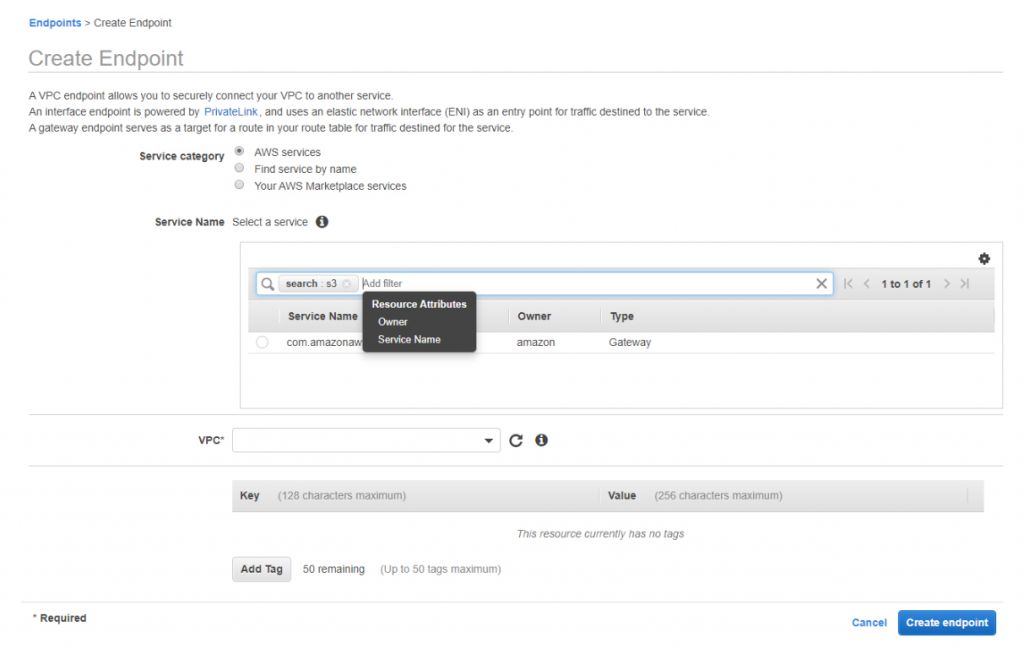
2. Then select Create Endpoint and search for the S3 service. Select the VPC where you would want to register the endpoint.
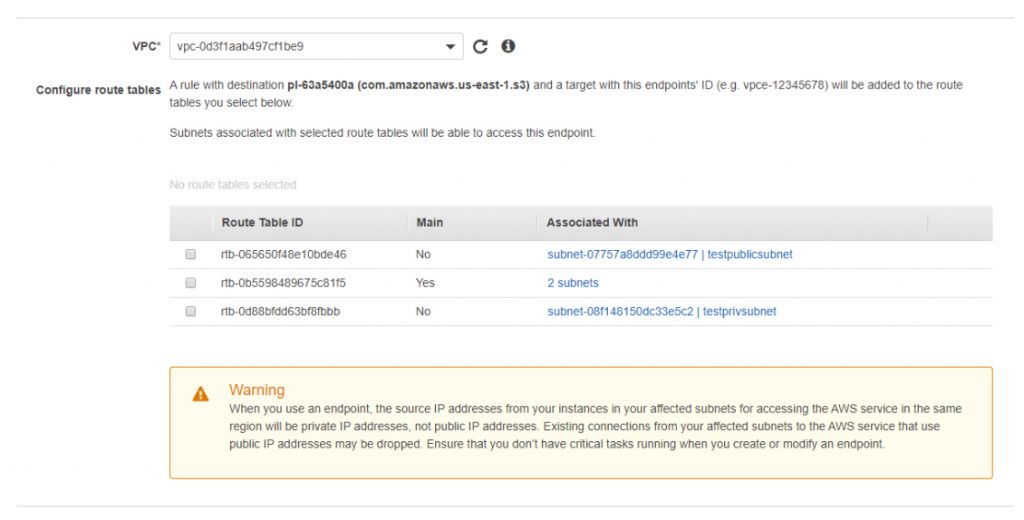
3. Choose which route tables will have the VPC endpoint entry
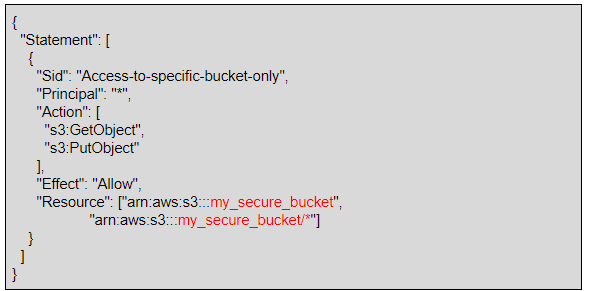
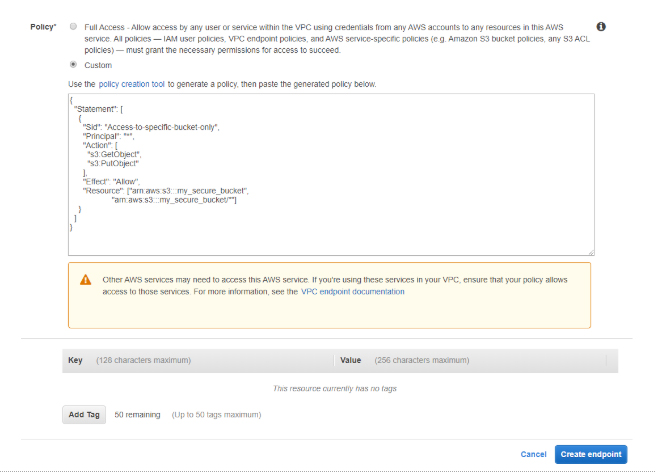
4. Modify your endpoint access control policy if you must. The example below shows a policy that allows only GetObject and PutObject actions to an S3 bucket named my_secure_bucket and the objects in it.
5. Add any tags you like. Then select Create endpoint
To further refine access control to your S3 bucket and objects, you can create bucket policies that restrict VPC endpoint or VPC access.
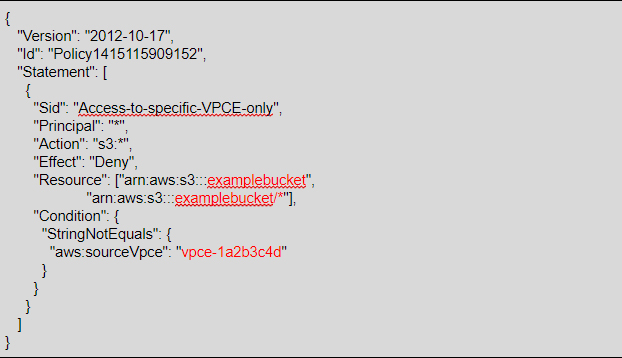
The following is an example of an Amazon S3 bucket policy that restricts access to examplebucket unless the origin is from the VPC endpoint vpce-1a2b3c4d. The aws:sourceVpce condition is used to specify the endpoint.
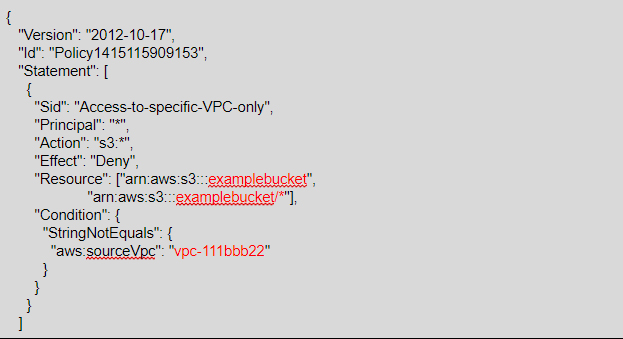
For the next example, we have an Amazon S3 bucket policy that restricts access to examplebucket unless the origin is from a resource within the VPC vpc-111bbb22. The aws:sourceVpc condition is used to specify the VPC ID.
Final thoughts
If you have resources in your AWS VPC that are connecting to Amazon S3, and you don’t want them to go through the public internet or use the S3 bucket DNS, then you should make use of Amazon S3 VPC Endpoint. Be sure to follow the principle of Least Privilege by setting up Endpoint Policies and S3 Bucket Policies so that only the appropriate entities get access to your buckets and objects.
Note: If you are studying for the AWS Certified Security Specialty exam, we highly recommend that you take our AWS Certified Security – Specialty Practice Exams and read our Security Specialty exam study guide.
Sources:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/example-bucket-policies-vpc-endpoint.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/vpc-endpoints-s3.html
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/new-vpc-endpoint-for-amazon-s3/