Cloud computing today demands efficiency and automation like never before. AWS Console-to-Code is an innovative tool designed to bridge manual operations with automated infrastructure management. By transforming console actions into reusable Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC), this feature streamlines workflows, enhances consistency, and accelerates deployment processes. This article will guide you through the process of implementing AWS Console-to-Code to launch Amazon EC2, VPC, and RDS.
What is AWS Console-to-Code?
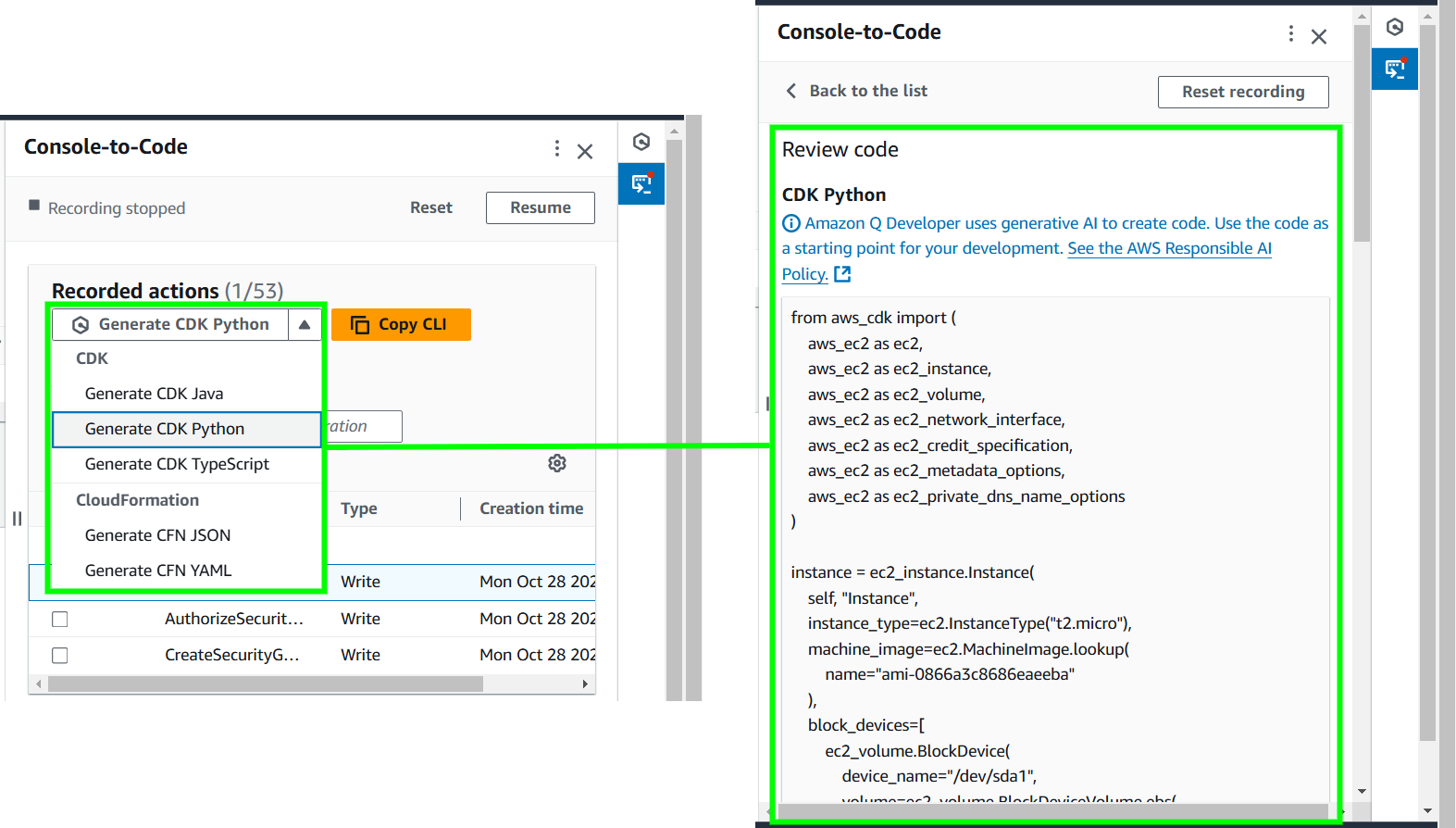
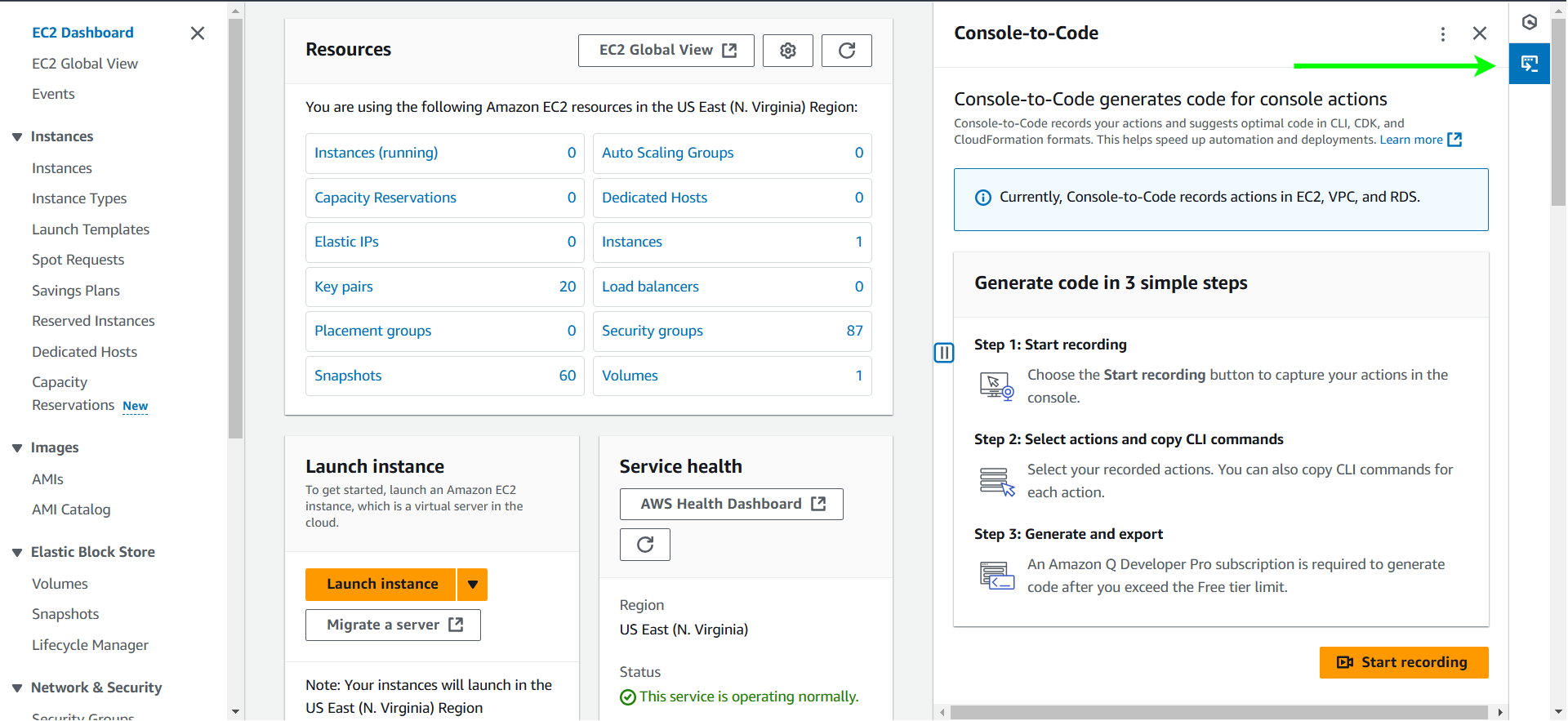
AWS Console-to-Code utilizes Amazon Q Developer to simplify the process of automatically converting your console actions into reusable code snippets. Whether you’re setting up an EC2 instance or configuring a VPC, AWS Console-to-Code can generate code in various formats, including JSON, YAML, Java, Python, or TypeScript. These snippets can be seamlessly integrated into AWS CloudFormation or other Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools. Utilizing Console-to-Code not only saves time but also reduces errors and improves reproducibility. Whether you’re managing a single instance or an entire cloud environment, it offers a seamless way to codify your actions, enabling scalable and efficient infrastructure management.
Key Benefits:
-
Ease of Use: Effortlessly generate code from manual configurations.
-
Flexibility: Supports multiple formats including CloudFormation, CDK, and CLI.
-
Efficiency: Accelerates the transition from prototyping to production-ready code.
This feature is perfect for developers aiming to simplify their infrastructure setup, ensuring consistent and repeatable configurations across various environments.
AWS Console-to-Code supports recording actions in the following services:
- Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
- Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
- Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service)
Automating EC2 Instance Creation with Console-to-Code
With Console-to-Code, you can automate the creation of EC2 instances, ensuring consistent configurations across deployments.
Implementation Steps:
-
Open the Amazon EC2 console and, in the right-hand panel, click on the Console-to-Code widget.
-
Click the Start recording button.
-
Launch an Instance:
-
Click on Launch Instance.
-
Choose an AMI.
-
Select an instance type, such as
t2.micro. -
Configure instance details, like VPC, subnets, and security groups.
-
Review and launch the instance.
-
-
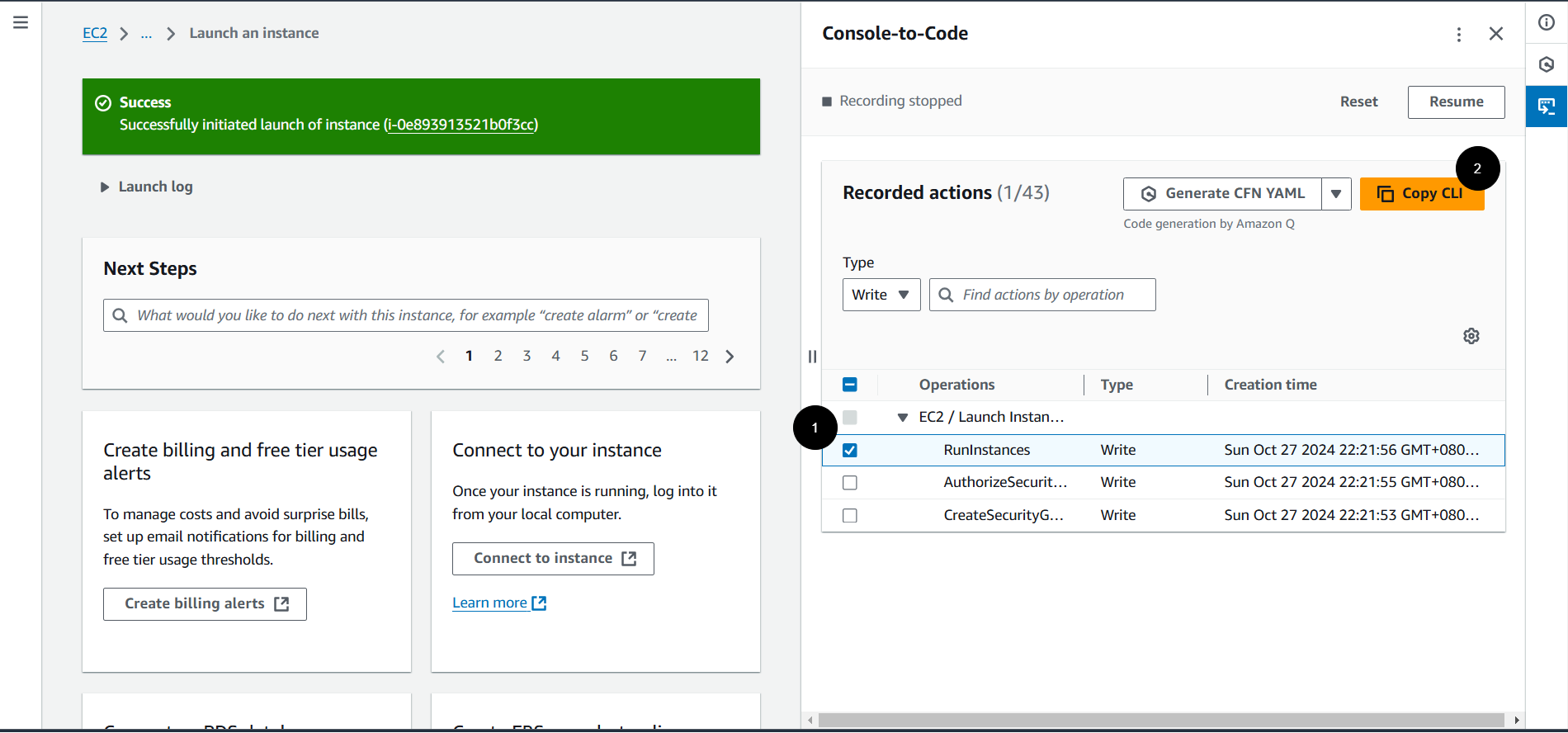
Stop Recording: After launching the instance, click Stop in the Console-to-Code panel.
-
Generate Code: Select the
RunInstancesoperation, then click the Copy CLI button.
-
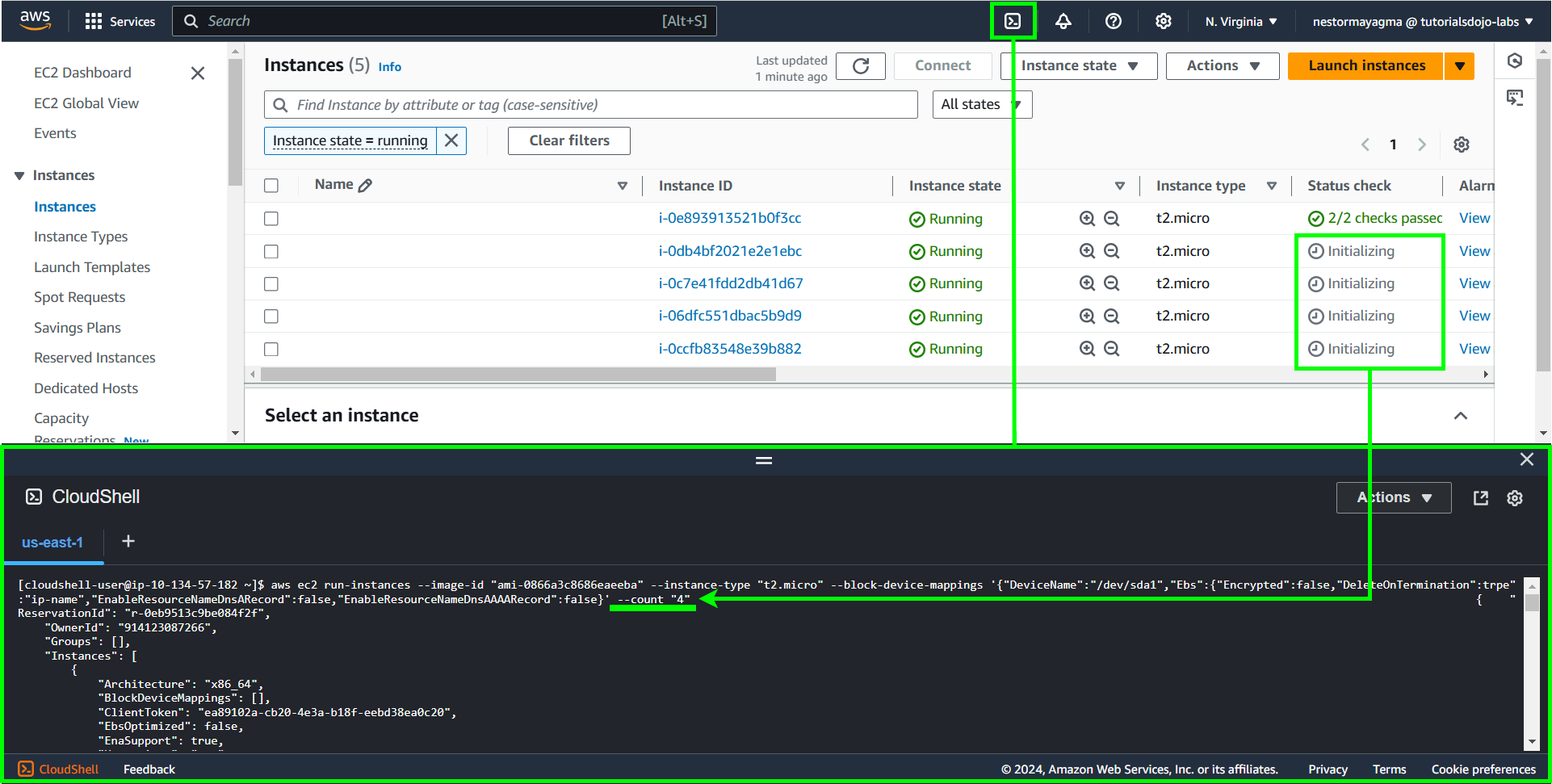
Customize and Deploy: Copy the generated CLI command and customize it as needed. Run this command in AWS CloudShell to launch your EC2 instance.
For this one, we can customize the generated CLI command to launch your desired number of instances by just changing the value of the--count. Additionally, other command line options can be further customized based on your requirements.
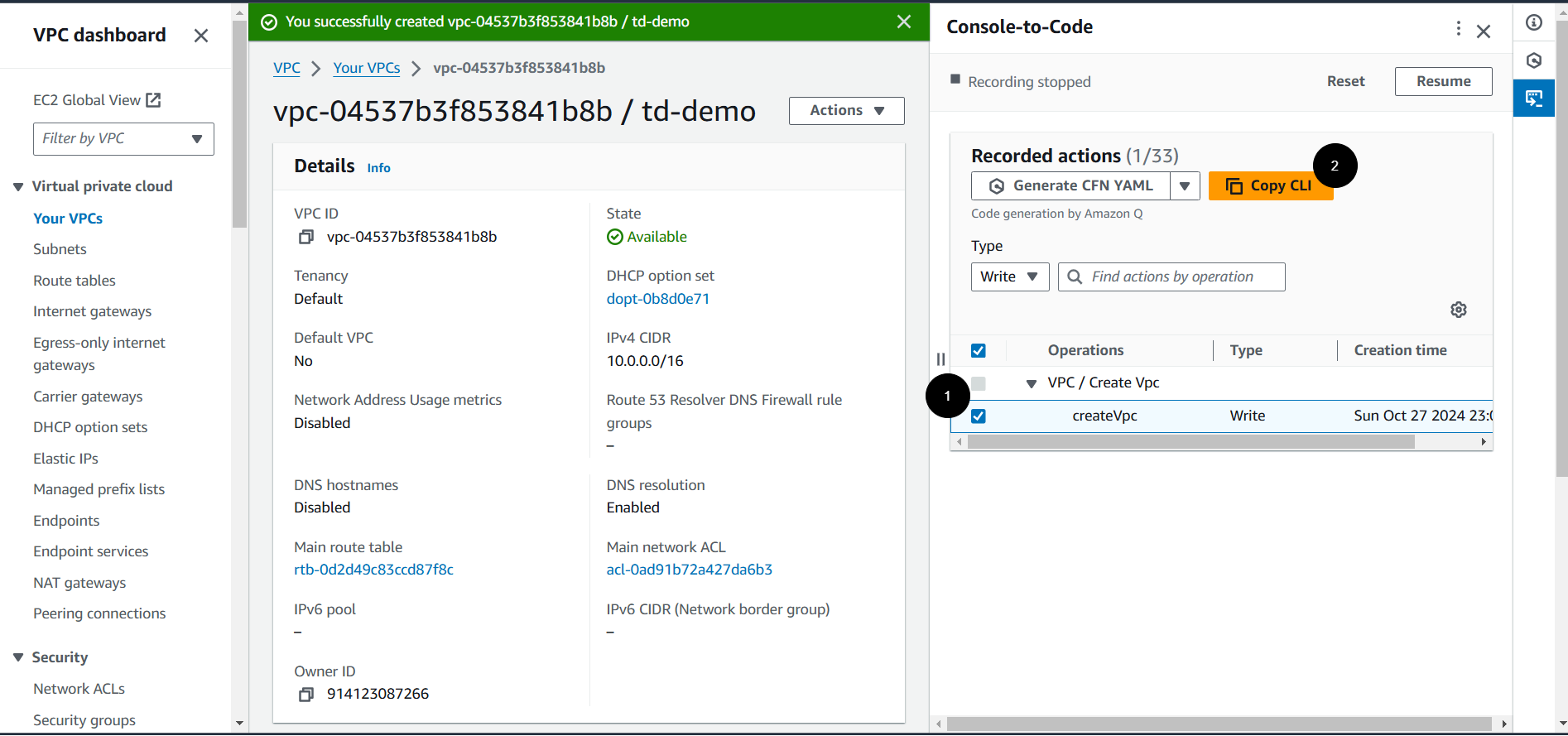
Automating VPC Creation with Console-to-Code
Using Console-to-Code, you can automate the setup of VPCs, ensuring network configurations are standardized.
Implementation Steps:
-
Open the Amazon VPC console and click Console-to-Code.
-
Click Start recording button.
-
Create a VPC:
-
Click on Create VPC button -> VPC only.
-
Enter a name for your VPC.
-
Define the IPv4 CIDR block, e.g.,
10.0.0.0/16. -
Specify IPv6 CIDR block if required.
-
Choose tenancy options and other configurations.
-
-
Stop Recording: After creating the VPC, click Stop in the Console-to-Code panel.
-
Generate Code: Select the
CreateVpcoperation, then click the Copy CLI button. -
Customize and Deploy: Copy the generated CLI command and customize it as needed. Run this command in AWS CloudShell to create your VPC.
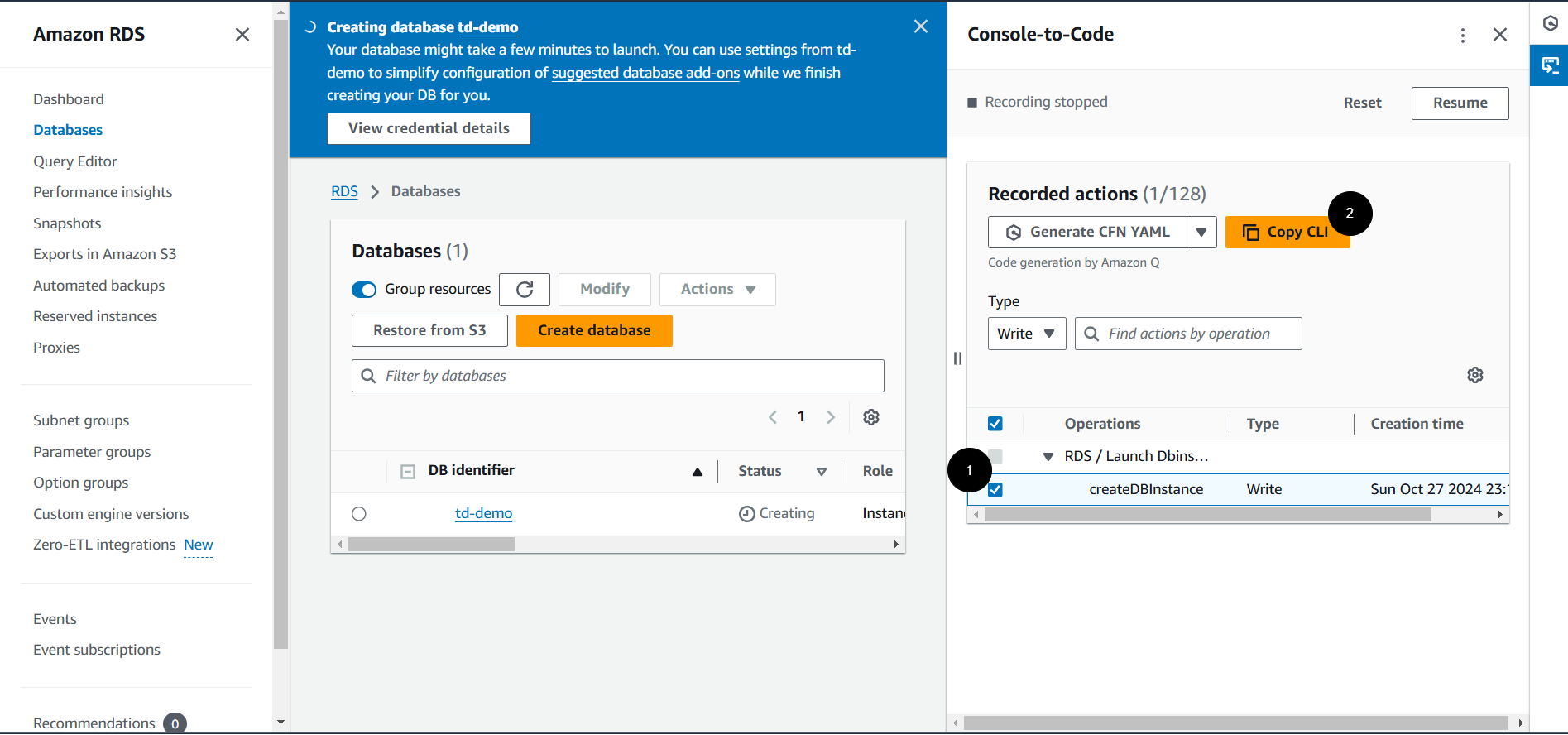
Automating RDS Instance Creation with Console-to-Code
With Console-to-Code, you can automate the creation of RDS instances, ensuring database configurations are consistent and efficient.
Implementation Steps:
-
Open the Amazon RDS console and click Console-to-Code.
-
Click Start recording button.
-
Create an RDS Instance:
-
Click on Create database.
-
Choose a database creation method, such as Standard create.
-
Select a database engine, e.g., MySQL.
-
Configure DB instance size, storage, and other settings.
-
Set up master username and password.
-
Configure additional settings like VPC, subnet group, and security groups.
-
-
Stop Recording: After creating the RDS instance, click Stop in the Console-to-Code panel.
-
Generate Code: Select the
CreateDBInstanceoperation, then click the Copy CLI button.
-
Customize and Deploy: Copy the generated CLI command and customize it as needed. Run this command in AWS CloudShell to setup your RDS database.
That’s it! AWS Console-to-Code simplifies the process of converting manual console actions into reusable code, making it easier to automate and scale your AWS infrastructure. By following the steps outlined above, you can quickly generate code for various AWS services and customize it for your specific use cases.