Last updated on November 24, 2025
Azure Kubernetes Service Cheat Sheet
- An open-source tool for orchestrating and managing many container images and applications.
- Lets you deploy a managed Kubernetes cluster in Azure.
Features
- Uses clusters and pods to scale and deploy applications.
- Kubernetes can deploy more images of containers as needed.
- It supports horizontal scaling, self-healing, load balancing, and secret management.
- Automatic monitoring of application load to determine when to scale the number of containers used.
- Allows you to replicate container architectures.
- Use Kubernetes with supported Azure regions and on-premises installations using Azure Stack.
- The images used by AKS come from Azure Container Registry.
- Use Azure Advisor to optimize your Kubernetes deployments with real-time, personalized recommendations.
- Latest stable version with enhanced security and performance on AKS support for Kubernetes 1.29.
- Streamline Kubernetes development with automated deployment setups using the Draft extension for AKS.
- Improved performance and security with AKS support for containerd as the default container runtime.
- Automated patch and minor version updates with AKS automatic version upgrades.
- Automatic node image updates for security patches with node OS auto-upgrade.
- Built-in cost optimization recommendations with cost analysis views.
Components
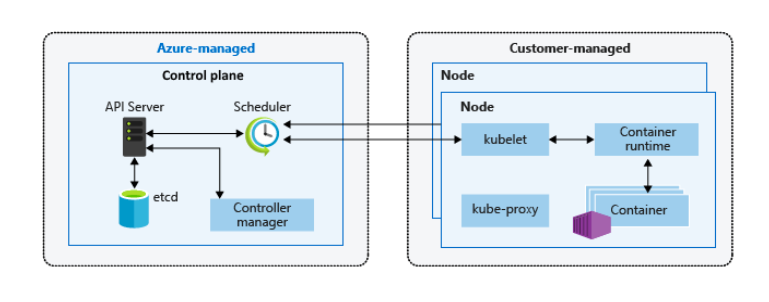
- A control plane is a managed Azure resource. It is where the components run, including API server and cluster database (etcd).
- kube-apiserver – allows communication for management tools (kubectl).
- etcd – a key-value store within Kubernetes.
- kube-scheduler – defines what nodes should run in the workload.
- kube-controller-manager – it oversees the smaller controllers that handle node operations and replication of pods.
- Kubernetes runs an application in your instance using pods.
- A node is made up of several pods, and node pools are a group of nodes with the same configuration.
- Use a node selector to control where a pod should be placed.
- You can run at least 2 nodes in the default node pool to ensure your cluster operates reliably.
- Multi-container pods are placed on the same node and allow containers to share the related resources.
- You can specify maximum resource limits that prevent a given pod from consuming too much compute resources from the underlying node.
- A deployment determines the number of replicas (pods) to be created, but you must define a manifest file in YAML format first.
- With StatefulSets, you can maintain the application’s state within a single pod life cycle.
- The resources are logically grouped into a namespace, and a user may only interact with resources within their assigned namespaces.
- Enhanced scheduling, security policies, and resource management with Kubernetes 1.28+ features.
- Native monitoring integration with Azure Monitor managed service for Prometheus.
Storage
- Persistent volumes are provided by Azure disk and file storage.
- Create a Kubernetes DataDisk resource using Azure Disk.
- Mount an SMB 3.0 share backed by an Azure Storage account to pods with Azure Files.
- Volumes that are defined and created as part of the pod lifecycle only exist until the pod is deleted.
- AKS has four initial storage classes:
- default – uses Azure StandardSSD storage to create a Managed Disk.
- managed-premium – uses Azure Premium storage to create Managed Disk.
- azurefile – uses Azure Standard storage to create an Azure File Share.
- azurefile-premium – uses Azure Premium storage to create an Azure File Share.
- If no StorageClass is specified for a persistent volume, the default StorageClass is used.
- Unified storage solution optimized for container workloads with Azure Container Storage.
- Faster node provisioning and reduced storage costs with ephemeral OS disks support.
Security
- With Kubernetes RBAC, you can create roles to define permissions and then assign those roles to users with role bindings.
- You can limit network traffic between pods in your cluster with Kubernetes network policies.
- Dynamic rules enforcement across multiple clusters with Azure Policy.
- Azure AD-integrated AKS clusters can grant users or groups access to Kubernetes resources within a namespace or across the cluster.
- Secure communication paths between namespaces and nodes with Azure Private Link.
- Integrate secrets from Azure Key Vault directly into pods using the Azure Key Vault Provider for Secrets Store CSI Driver.
- Secure pod-to-Azure-services authentication using Azure AD with Workload Identity.
- Advanced threat protection for Kubernetes workloads with Defender for Containers.
Azure Kubernetes Service Pricing
- You only pay for virtual machines, associated storage, and networking resources.
- There is no charge for cluster management.
Azure Kubernetes Service Versions
- Uses semantic versioning: [major].[minor].
- A user has 30 days from the version removal to upgrade into a supported patch and continue receiving support.
- Azure updates the cluster automatically if it has been out of support for more than 3 minor versions.
- Downgrading a version is not supported.
How to Create an Azure Kubernetes Service Cluster in the Azure Portal
Want to learn more about Azure? Watch the official Microsoft Azure YouTube channel’s video series called Azure Tips and Tricks.
Validate Your Knowledge
Question 1
Question Type: Single choice
You manage an Azure subscription with 120 virtual machines distributed across multiple resource groups.
You aim to identify unattached disks that can be safely deleted from specific resource groups to reduce costs.
You also want to ensure you only receive recommendations relevant to those selected resource groups.
What action should you take?
- Assign the Billing Administrator role to monitor unattached disks in selected resource groups for potential deletion.
- Modify the Advisor configuration in Azure Advisor to include only the targeted resource groups, then review its cost optimization recommendations.
- Use Azure Monitor to create a custom log query that identifies unattached disks in the specified resource groups.
- View the Advisor recommendations under Azure Cost Management and apply filters to focus on the resource groups in question.
For more Azure practice exam questions with detailed explanations, check out the Tutorials Dojo Portal:
Azure Kubernetes Service Cheat Sheet Resources:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/intro-kubernetes
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/kubernetes-service/