Last updated on May 5, 2023
In the previous section, we gave you an overview of AWS. In this section, we’ll give you an introduction to Microsoft Azure.
Azure is a cloud computing platform that was introduced by Microsoft in 2010. It gives you the ability to create, manage, and deploy applications across a vast global network. Microsoft Azure also offers a range of services to help your company address the existing and potential business challenges in your infrastructure and applications.
Microsoft Azure has the second-largest share in the cloud industry. It also has specialized regions for compliance or legal purposes.
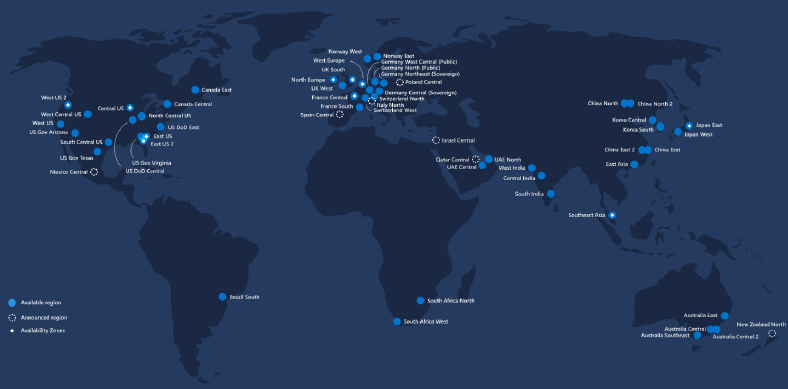
Azure Global Infrastructure
Azure Cloud Infrastructure is built around:
Regions – a group of data centers deployed in a latency-defined perimeter and connected through a dedicated regional low latency network.
Regions that are unique when it comes to compliance:
- Azure Government Cloud – only US federal, state, local, and tribal governments and their partners have access to this dedicated instance.
- China Region – data center is physically located within China and has no connection outside of China, including other Azure regions.
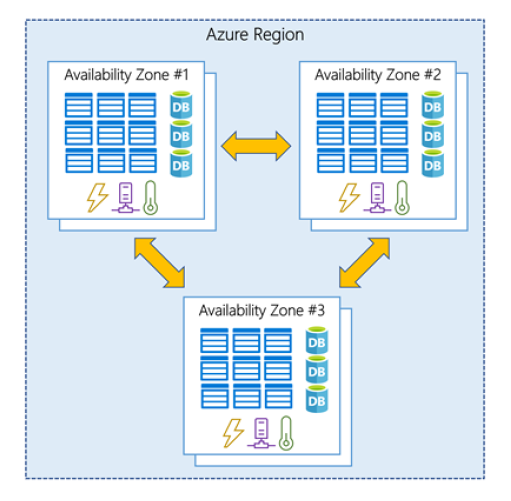
Availability Zones – a zone is composed of one or more data centers with independent power, cooling, and networking facilities.
Azure services that support Availability Zones fall into two categories:
- Zonal services – a resource is pinned to a specific zone.
- Zone-redundant services – replicates automatically across zones.
How does Azure Pricing Work?
Azure helps you estimate your monthly cost using the Pricing Calculator, and compare expenses and savings against on-premises and co-location environments with the Total Cost of Ownership Calculator.
This includes the following pricing models:
- Pay as you go – increase or decrease capacity and only pay for what you use.
- Reservations – commit one-year or three-year terms to reduce your infrastructure costs.
- Spot – significant discounts in purchasing unused compute capacity.
Essential Azure Services
Compute
- Azure VM – A virtual server that supports both Linux and Windows operating systems. You can allow or deny the traffic going to your VMs using a network security group.
- Azure Functions – A serverless compute that allows you to write functions using C#, Java, JavaScript, Python, and PowerShell.
- Azure Kubernetes Service – It allows you to orchestrate and manage multiple containers, but the control plane and worker nodes upgrades are done manually.
Storage
- Azure Blob – An object storage service of Azure. A single blob container size is the same as the maximum storage account capacity.
- Azure Disk – A block storage for virtual machines. You can protect your disks from failure with the data redundancy feature.
- Azure Files – It enables you to mount file shares in popular operating systems such as Linux, Windows, and macOS.
Database
- Azure SQL Database – A relational database service that supports Microsoft SQL server.
- Azure Cosmos DB – A database service for document store, graph DBMS, key-value, and wide column store.
Networking
- Azure VNet – A private network to run your VMs and applications. You can segment your virtual network between a /16 and /29 netmask.
- Azure CDN – It enables you to deliver web content closer to users. It has multiple point-of-presence locations in a region.
- Azure Traffic Manager – Distribute incoming traffic based on the routing method of your choice and Azure DNS helps you manage your DNS records.
Security
- Azure Active Directory – An identity and access management service that allows you to create and manage users and groups. You can use RBAC to grant users certain roles to access specific resources.
- Azure Key Vault – A service that allows you to store tokens, passwords, certificates, and other secrets. You can also create and manage the keys used to encrypt your data.
- Azure Application Gateway – A web traffic load balancer for the distribution of HTTP requests. It also has a web application firewall that protects your web applications from commonly known vulnerabilities.
In the next part of our Introduction to Cloud Computing tutorial, we will give you an overview of Google Cloud Platform.
This article is part of our free Journey to Cloud: A Beginner’s Guide eBook. Click here to get a free copy.
Ready to take your learning to the next level? Become a multi-cloud professional by being skilled in AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. Check out our list of FREE resources here: