Last updated on April 2, 2025
Have you wondered how Netflix streaming delivers your favorite series in HD quality without buffering or lagging? The answer lies in advanced CDN technology or Content Delivery Networks, a critical element of today’s global infrastructure. CDNs enable Netflix to optimize its global streaming performance, drastically reducing latency and providing seamless viewing experiences worldwide.
Understanding Global Infrastructure with a Simple Analogy
To understand how this works, let’s use a coffee shop analogy.
Imagine a coffee shop called “Athena Coffee” based in New York, becoming internationally popular. Customers from Thailand want their coffee but serving them directly from New York is impractical due to high costs and long delivery times.
Hundreds of thousands of customers in Thailand want to buy your coffee. How do you get it to them efficiently? You have two options:
Solution 1: Direct Transportation Delivery
One way to serve your Thai customers is to let them order your coffee and have it shipped from New York to their addresses in Thailand.
However, this approach has major downsides:
Coffee Product- 2.50 USD
Transportation Delivery Cost – 100 USD
Total – 102.50 USD
This is very expensive since customers would spend more on delivery than the actual coffee.
If you have hundreds of thousands of expected customers in another part of the world, this solution is not sustainable as customers will constantly be going to pay for the shipping cost of the product.
This solution is not accessible as well, we cannot assume that our customer can afford to pay more than 100 USD per transaction. Different financial backgrounds and regional economic differences make this solution completely irrational.
Other cons of this are that the time that the product will reach your customer will be in 7 or some even 14 days or more!
Potential Timeline:
- Day 1: Payment processing
- Day 2: Payment confirmation
- Day 3: Order sent to a local sorting center
- Day 4: Shipped overseas
- Day 5: Arrives at the local sorting center in Thailand
- Day 6-7: Delivered to the customer’s address
The amount of time that it can deliver the product is not practical for customers who usually buy coffee that is readily available for them in minutes to instant!
The provided option above is not Sustainable, Accessible, and Practical. So we need to come up with a solution that is Long-term, Cost-effective, and readily available near to your customer!
Solution 2: Establishing a Local Coffee Branch in Thailand
A better alternative is to invest in a coffee branch in Thailand. Instead of shipping coffee across the world for every order, you bring the coffee closer to your customers.
Readily available – The coffee products are already stocked at the local branch, eliminating the need for international shipping for customers in Thailand.
Cost-effective – Since the coffee is readily available in the area, customers no longer need to purchase it from New York. With an Athena Coffee shop nearby, they can enjoy the product without incurring expensive shipping costs.
Long-Term Solution – This approach is the most sustainable because it fosters customer retention by establishing a local presence. A physical branch builds brand loyalty, allowing customers to experience the product firsthand and return for repeat purchases.
Additionally, a local branch can support market expansion efforts, attract new customers through localized marketing strategies!
Back in the Days…

Years ago, the way Netflix delivered their movies was through traditional networking, which is a direct transfer of data from point A (Netflix Data Server) to Point B (Your Device).
Netflix is based in California, USA. If a user was streaming from Washington, D.C., the data transfer occurred through multiple network resources, traveling from the Netflix Data Server in California, through underground fiber-optic cables and internet backbone infrastructure, to the user’s local ISP (Internet Service Provider) in Washington, D.C.
From there, the data traveled via network distribution hubs to the user’s home modem and router, which then transmitted the data to their device over a Wi-Fi connection.
Since both locations are within the same country, this process was relatively straightforward, 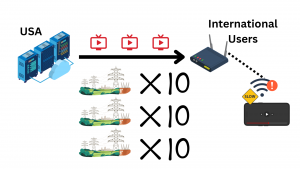
However, as Netflix expanded to international users, let’s say for example Thailand, the same data had to travel much farther, passing through multiple undersea cables, regional ISPs, and varying levels of network congestion.
Just like the delivery cost of Coffee Product earlier, expanding Netflix’s streaming service globally using traditional networking methods would have been both extremely expensive and unsustainable due to the amount of infrastructure and bandwidth required.
Netflix does not own all the cables and networks
Just like how the delivery of a Coffee Shop product would take you seven to fourteen shipping days before you can actually enjoy your coffee, it’s the same technical analogy here!
This results in noticeable delays, increased latency, potential buffering, and overall degraded streaming quality!
User Expansion Will Be Challenging, and Customers May Switch to Competitors…

Furthermore, economic disparities and regional pricing differences make this model completely irrational.
Just like in our coffee shop analogy earlier, if there is a competing coffee shop nearby, customers will likely choose the more accessible option instead of paying excessive costs for an imported product.
The same applies here: if users find a more affordable and locally optimized streaming service, they may switch to a competitor due to both financial and geographical inaccessibility.
Remember, users pay for their subscriptions not just because of entertainment service but the convenience and accessibility these streaming platforms give.
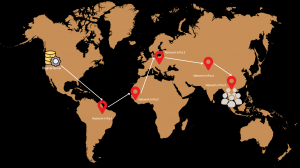
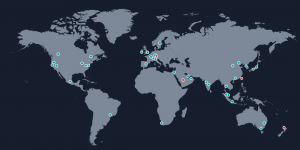
Data the Explorer: A Look at Pre-CDN Era Netflix Streaming
The map shown is a conceptual representation of how data might travel from the original server to end users on Netflix. While simplified, it illustrates the key idea behind content delivery networks (CDNs).
As you could see in the image above the data traveled from the USA to multiple network infrastructure before it reaches its target users in Thailand. To avoid the high costs and performance issues associated with long-distance data transfers, Netflix and other streaming services utilize Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)—a global network of cache servers that store copies of movies and TV shows closer to the user.
The need for CDN!
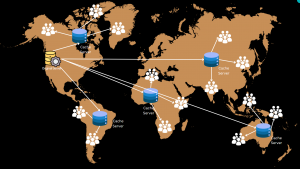
In the image I created, you can see:
- An original server (yellow) in North America, which hosts the primary content.
- Multiple cache servers (blue) positioned globally to store copies of the content.
- Users (represented by groups of icons) accessing the nearest cache server instead of the origin server.
- Arrows representing data flow, ensuring that content is delivered from the closest server rather than a distant origin, improving load speeds.

CDNs work similarly to everyday systems designed for efficiency and accessibility:
- Library System – Instead of traveling to the national library, local branches keep copies of popular books for easy access.
- Restaurant Chains – McDonald’s has outlets in multiple cities to serve food quickly instead of making customers travel to the headquarters.
- Supermarkets (e.g., Walmart) – Instead of visiting a central warehouse, grocery stores store commonly used products for immediate purchase.
CDNs follow the same principle: improving convenience, optimizing location-based access, and increasing efficiency.
- Faster Content Delivery – Users access content from the nearest server, reducing delays.
- Reduced Load on the Origin Server – Traffic is distributed across multiple cache servers, preventing overload.
- Lower Bandwidth Costs – Cached content reduces the need for repeated data transfers.
- Improved Reliability – If one server fails, another nearby server takes over.
- Better Security – CDNs provide protection against DDoS attacks by distributing traffic. (We’ll explain more how DDoS works and mitigation in the upcoming blogs!)
I’ll See you in Part 2!
In this article, that’s all I needed to explain here introducing you to the concept of CDN. Overall, CDNs enhance speed, scalability, and security, making them essential for modern websites and applications! For the 2nd part of the article, we’ll dive deeper into technicalities and proceed to AWS Global Infrastructure as a continuation of this blog!
Worry not! As we dive into a more technical approach to this introduction, I promise that I’ll try to simplify the approach so that we can understand the concepts thoroughly!
See you there!