Last updated on June 25, 2023
What is ChatGPT?
OpenAI’s ChatGPT is an improved version of the GPT3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer, released in 2020) language model specifically designed to generate human-like text for chatbot applications. ChatGPT is trained on a large dataset of conversation transcripts and is able to generate appropriate responses to a wide range of inputs, including questions and prompts. ChatGPT uses a transformer architecture, which is a type of neural network designed for natural language processing tasks.
ChatGPT’s language model is fined-tuned with supervised learning and reinforcement learning which means that human feedback is included in the training process. The training process includes human actions that rank multiple versions of the AI responses based on their quality. The end result is a language model that is able to generate text that is highly coherent and resembles human conversation.
ChatGPT can be used to build chatbots that can engage in natural, human-like conversations with users. It can also be used for tasks such as generating responses to customer inquiries or generating conversational content for social media or chat applications.
For example, ChatGPT can easily generate explanations to user queries as shown below:
It even remembers what the user said earlier in the conversation so it can generate relevant replies using the previous conversation’s context.
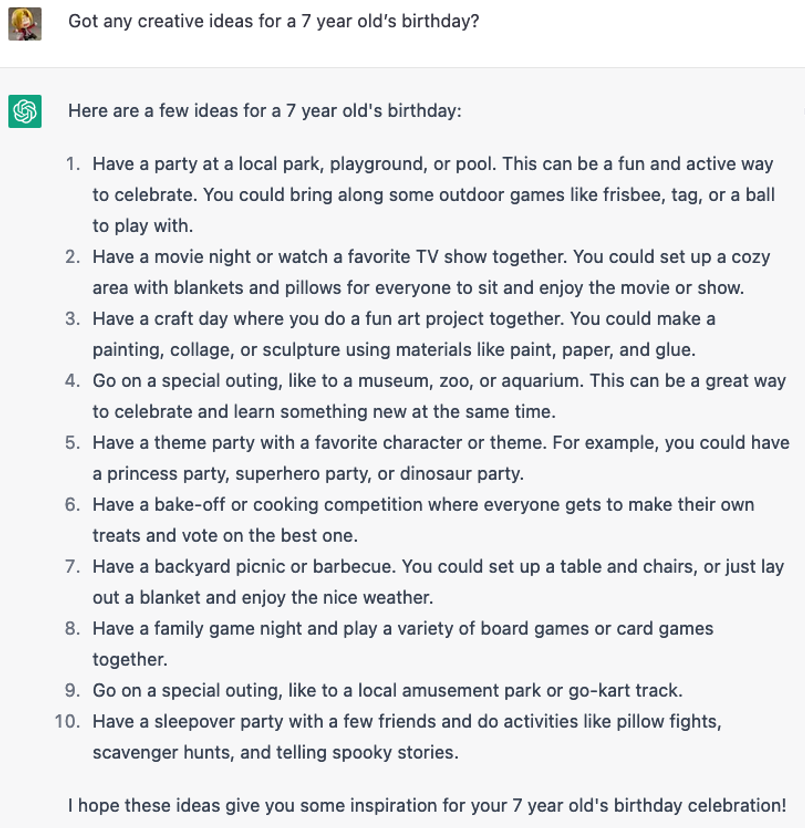
ChatGPT can generate essays, full articles, or even provide opinions on pretty much any topic as shown in the below example:
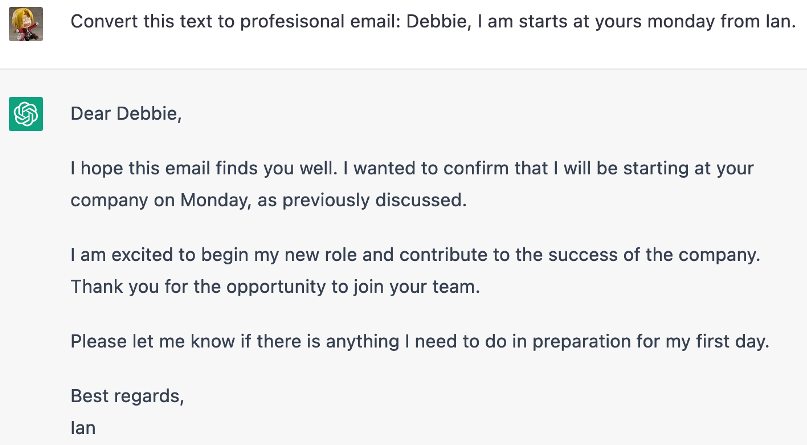
ChatGPT also excels in providing answers to user commands, it can be as simple as converting a text string to a formal email or just asking for ideas for a birthday party. ChatGPT can generate human-like responses as shown here:
As powerful as ChatGPT has become, it is still not perfect. There is always room to improve its language model. While safeguards are in place, the system may occasionally generate incorrect or misleading information and produce offensive or biased content.
For more information on ChatGPT: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt/
ChatGPT and Amazon Lex
ChatGPT is designed as a conversational chatbot. Similarly, AWS offers Amazon Lex for developers that want to build conversational interfaces for applications using voice and text. With Amazon Lex, developers can quickly build a bot by specifying a basic conversation flow in the Amazon Lex console. You can then configure the bot with one or more intents. These intents are actions that can be triggered depending on the corresponding utterances recognized from the user query. Developers can create Lambda functions and add them as code hooks in the intent configuration to perform user data validation and fulfillment tasks.
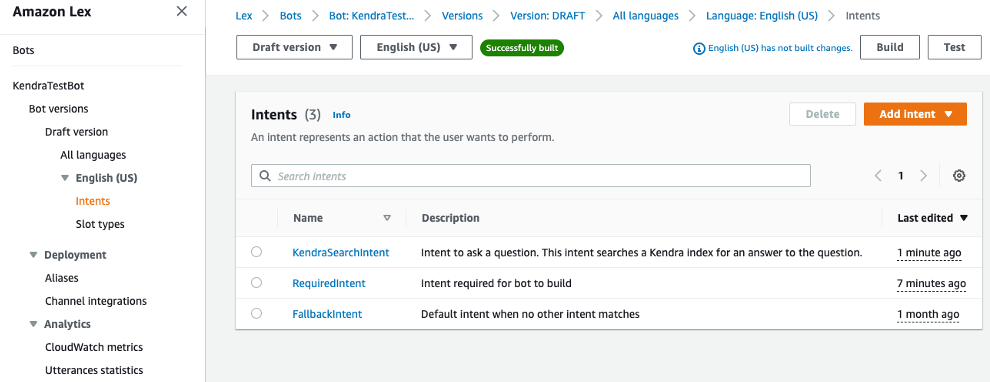
See the below screenshot of the Amazon Lex console for configuring intents and utterances.
Amazon Lex provides natural language understanding (NLU) and automatic speech recognition (ASR) you developers can build engaging bot-based applications. Amazon Lex is the same technology that powers Amazon Alexa.
For more information on Amazon Lex: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lex/latest/dg/how-it-works.html
ChatGPT and Amazon CodeWhisperer
OpenAI’s ChatGPT isn’t limited to mimicking human-like conversational language. It can also generate code snippets if you ask it to. It can provide explanations along with the code generated, which can be helpful as a reference for developers.
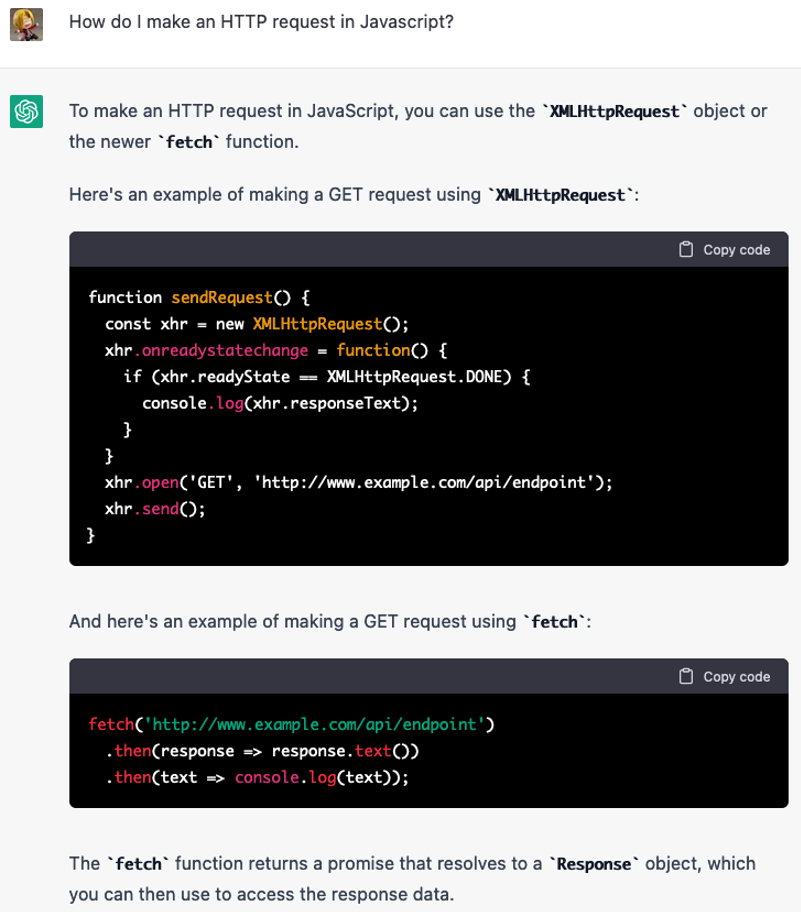
Here’s an example of how it generates Javascript code:
AWS provides a similar service that can help developers write code using the power of Machine Learning. Amazon CodeWhisperer can be considered a machine learning (ML) – powered coding companion that helps improve developer productivity by generating code recommendations based on prior code and comments.
With CodeWhisperer, developers can write comments for specific tasks in plain English, such as “upload a file to S3.” CodeWhisperer will then automatically determine which cloud services and public libraries are best suited for the specified task, creates the specific code on the fly, and recommends the generated code snippets directly in the IDE.
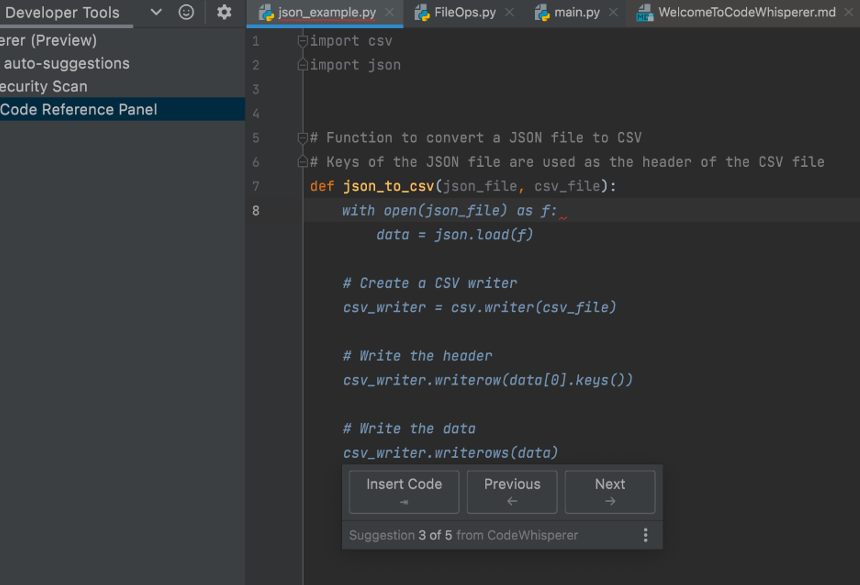
It is more than your traditional autocomplete because it can create entire functions and logical code blocks at a time, as shown in the below example:
Amazon CodeWhisperer is available as part of the AWS Toolkit extension for major IDEs, including JetBrains, Visual Studio Code, AWS Cloud9, and it is natively supported by the AWS Lambda console. It can generate code recommendations for Python, Java, and JavaScript.
For more information on Amazon CodeWhisperer: https://aws.amazon.com/codewhisperer/features/