AWS Lambda Web Adapter: Turning Functions Into Full-Fledged Web Apps
When people hear about AWS Lambda, they usually imagine tiny snippets of code that run briefly in response to an event. It might be a function that resizes an image after it’s uploaded, or one that processes a payment notification before disappearing again. Lambda is built for these short, event-driven tasks, which makes it incredibly powerful but also somewhat limited in perception. After all, who would think of Lambda as a place to host an entire website?
This is where the AWS Lambda Web Adapter changes the game. Instead of treating Lambda as just a background function runner, the adapter allows developers to treat it like a web server. In other words, you can run a website, an API, or even a full application framework inside Lambda without rewriting your code to fit the usual “Lambda event” format.
Understanding the Lambda Web Adapter
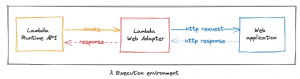
To put it simply, the Lambda Web Adapter is a translator. Normally, Lambda expects its input in a specific structure, an event that comes from services like API Gateway. But web applications don’t speak that language; they work with plain HTTP requests and responses. This sits in the middle, translating those HTTP calls into something Lambda can understand, and then translating the output back into the familiar format of a web response.
What this means is that frameworks like Express.js, Flask, or FastAPI can run on Lambda almost exactly as they would on a traditional server. You don’t need to rebuild your app from scratch or abandon your favorite tools. The adapter makes it possible to drop your existing app into Lambda and watch it work.
Why Host a Website on Lambda?
At first, the idea might sound unusual. Websites are supposed to live on servers or containers that run all day, right? Yet the more you think about it, the more appealing the concept becomes. Hosting on Lambda means that your site only “wakes up” when someone visits it. If you go a whole day without any visitors, you don’t pay for idle time. When traffic suddenly spikes, maybe your article goes viral, Lambda scales instantly to meet the demand without you lifting a finger.
Beyond cost and scalability, there’s also the question of maintenance. Running servers means monitoring uptime, patching vulnerabilities, and sometimes dealing with hardware failures. With Lambda, all of that disappears. AWS handles the infrastructure, while you focus entirely on your application. The Web Adapter completes the picture by letting you run the frameworks you already know, so you’re not locked into unfamiliar tooling just to go serverless.
How It Works in Practice
The process is simpler than it might sound. A user types your website’s URL into their browser, which triggers a request to AWS. That request goes through either an API Gateway or an Application Load Balancer. Instead of hitting a traditional web server, the request wakes up your Lambda function. The Lambda Web Adapter then intercepts it, converts it into the proper format, and hands it to your application. Your app processes it like it would anywhere else, produces a response, and the adapter sends that response back to the browser.
From the visitor’s point of view, nothing looks different, they see a normal website. But under the hood, your entire application is running in a serverless environment that springs into action only when needed.
Where This Approach Makes Sense
Of course, not every project is meant to live on Lambda. High-traffic enterprise systems that demand ultra-low latency might be better suited to container clusters or dedicated servers. But for many use cases, the Lambda Web Adapter is a perfect fit. A personal blog that only gets a handful of visits each day can stay online for almost no cost. A startup experimenting with a new product can launch quickly without building complex infrastructure. Developers working on microservices or quick prototypes can deploy fast, test ideas, and scale only if the project takes off.
In these situations, serverless hosting is not just a neat trick but a genuinely practical solution.
Running Web Apps on AWS Lambda with the Web Adapter
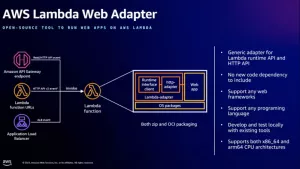
The AWS Lambda Web Adapter (LWA) makes it possible to run traditional applications (Express, Fastify, Flask, Spring Boot, etc.) directly inside — turning simple functions into full-fledged web apps.
Here’s a clear breakdown of how it works:
1. Your Web App
Start with a basic web application in your preferred framework.
Example (pseudocode, works for any framework):
This is just a normal server — nothing Lambda-specific yet.
2. Deploying on AWS Lambda with LWA
To run this app on Lambda:
-
Bundle your app into a
.zip(or container image). -
Attach the LWA layer to your Lambda function.
-
The LWA layer converts API Gateway / ALB requests into HTTP requests your app understands.
-
-
Startup script (
run.sh)-
Instead of calling the handler directly, you start your app server:
- #!/bin/sh
exec node app.js
-
-
Set environment variable
AWS_LAMBDA_EXEC_WRAPPER=/opt/bootstrap
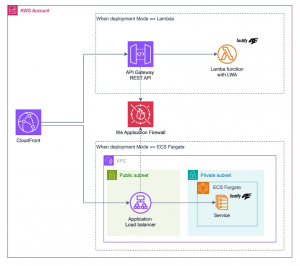
3. Alternative: Deploying on ECS Fargate
If Lambda isn’t the right fit, you can deploy the exact same app to ECS Fargate:
-
Package it as a container image.
-
Use AWS CDK’s
LoadBalancedFargateServiceconstruct. -
Add HTTPS with an ACM certificate.
This way, your app is deployed behind a load balancer, fully managed by ECS.
4. Flexible Deployment with CDK
You can design a single CDK construct that supports both strategies:
-
Lambda + LWA → deploys as a Lambda function with an API Gateway or ALB.
-
ECS Fargate → deploys as a containerized service with a Load Balancer.
Switching between them is just a configuration choice, no code changes needed.
5. Adding Security with AWS WAF
Attach a WAF WebACL:
-
Example: block requests without a custom header (
x-origin-header). -
Helps filter unwanted traffic before it reaches your app.
6. Testing the Deployment
Once deployed, hit your app’s endpoint:
On Lambda:
Conclusion
The AWS Lambda Web Adapter reimagines what Lambda can be. Instead of being limited to small, event-driven snippets of code, it can now host full-fledged applications with almost no infrastructure overhead. It’s a shift that combines the reliability of serverless with the flexibility of traditional web frameworks. Check out this guide on Getting Started with Serverless.
For developers, this means freedom: freedom from managing servers, freedom from worrying about scaling, and freedom to experiment without breaking the bank. Whether you’re running a small personal site, prototyping a new idea, or simply exploring what’s possible with serverless, it offers a powerful way forward.
References
- AWS Lambda Web Adapter on GitHub
- Official AWS Lambda Documentation
- https://levelup.gitconnected.com/adding-flexibility-to-your-deployments-with-lambda-web-adapter-67aecb0ecbff
- https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/aws-lambda
- https://www.cloudzero.com/blog/aws-lambda/