Last updated on March 12, 2025
The AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 exam, or SAA for short, is one of the most sought-after certifications in the Cloud industry today. This certification verifies your knowledge of the AWS Cloud and your know-how in building a well-architected infrastructure in AWS. This AWS Certification exam helps companies identify and develop their in-house talent in implementing cloud initiatives. Achieving the latest version of the AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 certification validates one’s ability to design and implement various solutions on AWS, such as distributed architecture, serverless, containerized applications, and the like.
The AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Certification Exam Overview
The AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 certification exam is intended for people who perform in a solutions architect role, but any IT Professional can take this. College students who want to get ahead of their peers can also take this test. The SAA-C03 exam validates your ability to use various Amazon Web Services (AWS) technologies to design solutions based on the AWS Well-Architected Framework.
If you are interested in taking the AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 exam soon, you must prepare first by studying the core cloud concepts and design principles in AWS. Pay close attention to how you can properly secure your cloud architecture as this exam constitutes a lot of security-related scenarios. Take note that the SAA-C03 exam also validates a candidate’s ability to complete the following tasks:
- Design solutions that incorporate AWS services to meet current business requirements and future projected needs
- Design architectures that are secure, resilient, high-performing, and cost-optimized
- Review existing solutions and determine improvements
The official AWS Exam Guide, AWS Documentation, and AWS Whitepapers will be your primary study materials for this exam. Experience in building systems will also be helpful since the exam constitutes of multiple scenario-type questions. You can learn more details on your exam through the official AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate SAA-C03 Exam Guide here. Do a quick read on it to be aware of how to prepare and what to expect on the exam itself.
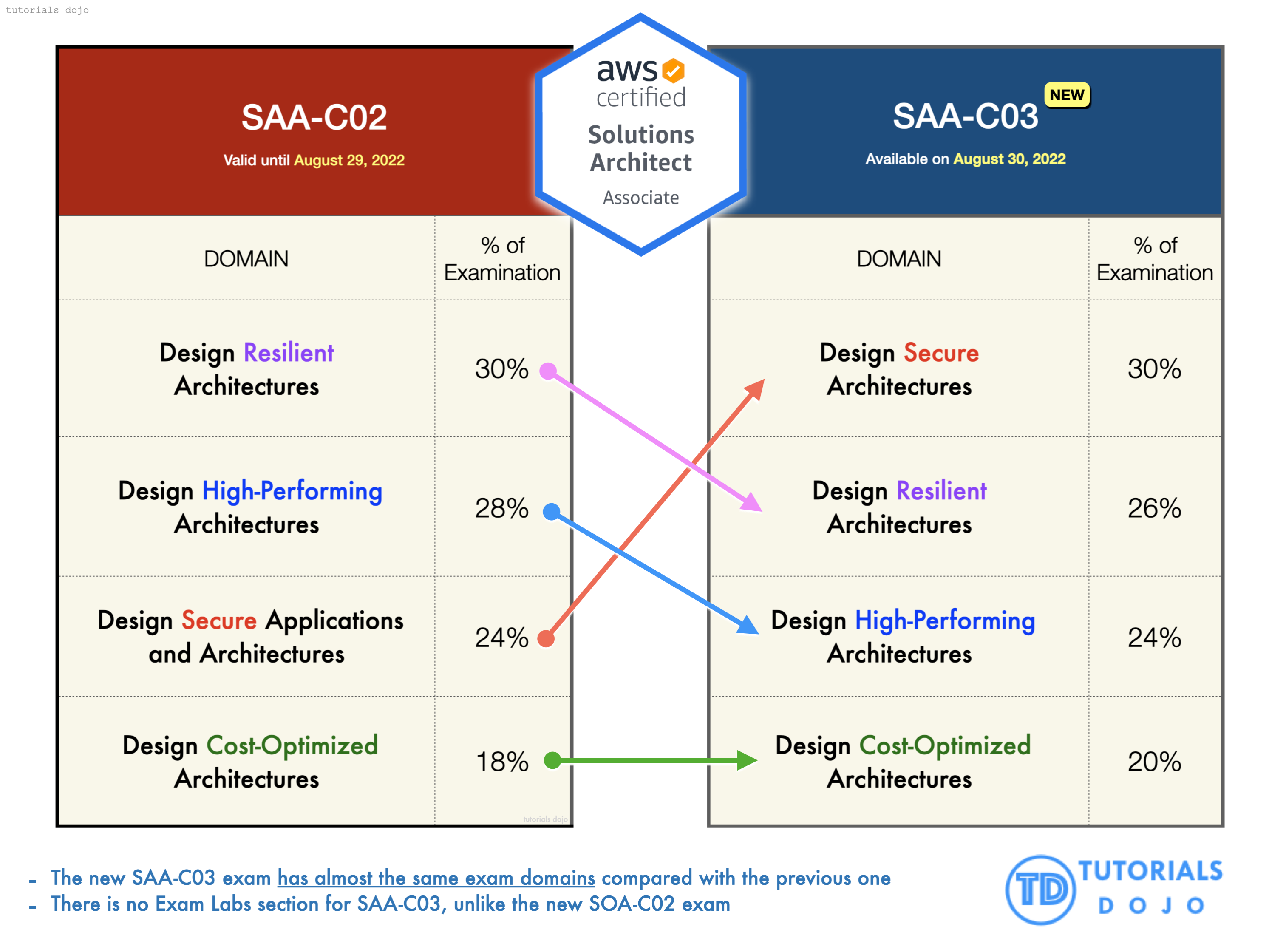
Difference between the SAA-C02 and SAA-C03 AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Exam Versions
Before you start preparing for the exam, you have to know the exact knowledge areas and topics that you should focus on. It is also beneficial for you to learn the differences between the previous SAA-C02 version and the new SAA-C03 AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate certification exam.
Both exam domains of the SAA-C02 and SAA-C03 are virtually the same. As you can see in the diagram below, the new SAA-C03 exam has retained the Design Resilient Architectures, Design High-Performing Architectures, and Design Cost-Optimized Architectures exam domains from the previous one. However, the existing Design Secure Applications and Architectures exam domain was renamed to Design Secure Architectures.
Another important thing to note here is the change in the percentage of its exam domain coverage. The previous version of the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate exam was focused on the topic of resiliency. This time, the new AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-c03 exam version has put a spotlight on security. Its biggest exam domain is Design Secure Architecture (30%) so you have to focus on the various security services in AWS as well as the different security features available on each related AWS service.
The AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 Study Materials
As a starting point for your AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate exam studies, we recommend taking the FREE AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Essential digital course. If you are quite new to AWS, taking and completing this digital course should be your first step for your SAA-C03 exam prep.
There are a lot of posts on the Internet claiming the “best” course for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 Exam. However, some of these resources are already obsolete and don’t cover the latest topics that were recently introduced in the SAA-C03 test. How can I ensure that you are using the right study materials for your upcoming AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate test?
The best thing to do is to check the official AWS Certification website for the most up-to-date information. You can also head on to the official AWS Certification page for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 exam. This page is where you can find the actual link to schedule your SAA-C03 exam as well as get the official SAA-C03 Exam Guide and Sample Questions as shown below:
Let’s now enumerate the top study materials for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 certification test. This list contains the official SAA-C03 Exam Guide, Sample Questions, and other free/paid resources, The official AWS materials are more reliable than the other ones you’ll find over the Internet since the information you’ll get there is straight from the AWS Certification and Training team itself. Thus, you have to give more credit to what the official SAA-C03 Exam Guide says in deciding the AWS topics that you’ll focus on.
1. Official Exam Guide for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 Exam
2. AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 Video Course
3. AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 Practice Exams
4. Official Sample Questions for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03
Additional SAA-C03 Whitepapers
For whitepapers, focus on the following:
- AWS Well-Architected Framework
- An Overview of the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework
- Cost Optimization Pillar – AWS Well-Architected Framework
- Disaster Recovery of On-Premises Applications to AWS
- Security Best Practices for Manufacturing OT
Core AWS Services to Focus On for the SAA-C03 Exam
- EC2 – As the most fundamental compute service offered by AWS, you should know about EC2 inside out.
- Lambda – Lambda is the common service used for serverless applications. Study how it is integrated with other AWS services to build a full-stack serverless app.
- Elastic Load Balancer – Load balancing is very important for a highly available system. Study the different types of ELBs, and the features each of them supports.
- Auto Scaling – Study what services in AWS can be auto-scaled, what triggers scaling, and how auto scaling increases/decreases the number of instances.
- Elastic Block Store – As the primary storage solution of EC2, study on the types of EBS volumes available. Also study how to secure, backup and restore EBS volumes.
- S3 / Glacier – AWS offers many types of S3 storage depending on your needs. Study what these types are and what differs between them. Also review on the capabilities of S3 such as hosting a static website, securing access to objects using policies, lifecycle policies, etc. Learn as much about S3 as you can.
- Storage Gateway – There are occasional questions about Storage Gateway in the exam. You should understand when and which type of Storage Gateway should be used compared to using services like S3 or EBS. You should also know the use cases and differences between DataSync and Storage Gateway.
- EFS – EFS is a service highly associated with EC2, much like EBS. Understand when to use EFS, compared to using S3, EBS or instance store. Exam questions involving EFS usually ask the trade off between cost and efficiency of the service compared to other storage services.
- RDS / Aurora – Know how each RDS database differs from one another, and how they are different from Aurora. Determine what makes Aurora unique, and when it should be preferred from other databases (in terms of function, speed, cost, etc). Learn about parameter groups, option groups, and subnet groups.
- DynamoDB – The exam includes lots of DynamoDB questions, so read as much about this service as you can. Consider how DynamoDB compares to RDS, Elasticache and Redshift. This service is also commonly used for serverless applications along with Lambda.
- Elasticache – Familiarize yourself with Elasticache redis and its functions. Determine the areas/services where you can place a caching mechanism to improve data throughput, such as managing session state of an ELB, optimizing RDS instances, etc.
- VPC/NACL/Security Groups – Study every service that is used to create a VPC (subnets, route tables, internet gateways, nat gateways, VPN gateways, etc). Also, review on the differences of network access control lists and security groups, and during which situations they are applied.
- Route 53 – Study the different types of records in Route 53. Study also the different routing policies. Know what hosted zones and domains are.
- IAM – Services such as IAM Users, Groups, Policies and Roles are the most important to learn. Study how IAM integrates with other services and how it secures your application through different policies. Also read on the best practices when using IAM.
- CloudWatch – Study how monitoring is done in AWS and what types of metrics are sent to CloudWatch. Also read upon Cloudwatch Logs, CloudWatch Alarms, and the custom metrics made available with CloudWatch Agent.
- CloudTrail – Familiarize yourself with how CloudTrail works, and what kinds of logs it stores as compared to CloudWatch Logs.
- Kinesis – Read about Kinesis sharding and Kinesis Data Streams. Have a high level understanding of how each type of Kinesis Stream works.
- CloudFront – Study how CloudFront helps speed up websites. Know what content sources CloudFront can serve from. Also, check the kinds of certificates CloudFront accepts.
- SQS – Gather info on why SQS is helpful in decoupling systems. Study how messages in the queues are being managed (standard queues, FIFO queues, dead letter queues). Know the differences between SQS, SNS, SES, and Amazon MQ.
- SNS – Study the function of SNS and what services can be integrated with it. Also be familiar with the supported recipients of SNS notifications.
- SWF / CloudFormation / OpsWorks – Study how these services function. Differentiate the capabilities and use cases of each of them. Have a high-level understanding of the kinds of scenarios they are usually used in.
Other SAA-C03 AWS Services that you should prepare for:
For the exam version ( SAA-C03 ), you should also know the following services:
- AWS Global Accelerator
- Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA)
- Elastic Network Adapter (ENA)
- AWS ParallelCluster
- Amazon FSx
- AWS DataSync
- AWS Directory Service
- High Performance Computing
- Aurora Serverless
- Amazon Redshift
- AWS Glue
… plus a few more services and new SAA-C03 topics that we have recently added to our AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Practice Exams
For more information, check out the SAA-C03 official exam guide for the new SAA-C03 version here.
Based on our exam experience, you should also know when to use the following:
- AWS DataSync vs Storage Gateway
- FSx (Cold and Hot Storage)
- Cross-Region Read Replicas vs. Multi-Az RDS – which database provides high-availability
- Amazon Object key vs Object Metadata
- Direct Connect vs. Site-to-Site VPN
- AWS Config vs AWS CloudTrail
- Security Group vs NACL
- NAT Gateway vs NAT Instance
- Geolocation routing policy vs. Geoproximity routing policy on Route 53
The AWS Documentation and FAQs will be your primary source of information. You can also visit Tutorials Dojo’s AWS Cheat Sheets to gain access to a repository of thorough content on the different AWS services mentioned above. Lastly, try out these services yourself by signing up on AWS and performing some lab exercises. Experiencing them on your own will help you greatly in remembering what each service is capable of.
Also check out this article: Top 5 FREE AWS Review Materials.
Common Exam Scenarios for the SAA-C03 exam
|
Scenario |
Solution |
|
Domain 1: Design Resilient Architectures |
|
|
Set up asynchronous data replication to another RDS DB instance hosted in another AWS Region |
Create a Read Replica |
|
A parallel file system for “hot” (frequently accessed) data |
Amazon FSx For Lustre |
|
Implement synchronous data replication across Availability Zones with automatic failover in Amazon RDS. |
Enable Multi-AZ deployment in Amazon RDS. |
|
Needs a storage service to host “cold” (infrequently accessed) data |
Amazon S3 Glacier |
|
Set up a relational database and a disaster recovery plan with an RPO of 1 second and RTO of less than 1 minute. |
Use Amazon Aurora Global Database. |
|
Monitor database metrics and send email notifications if a specific threshold has been breached. |
Create an SNS topic and add the topic in the CloudWatch alarm. |
|
Set up a DNS failover to a static website. |
Use Route 53 with the failover option to a static S3 website bucket or CloudFront distribution. |
|
Implement an automated backup for all the EBS Volumes. |
Use Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager to automate the creation of EBS snapshots. |
|
Monitor the available swap space of your EC2 instances |
Install the CloudWatch agent and monitor the SwapUtilizationmetric. |
|
Implement a 90-day backup retention policy on Amazon Aurora. |
Use AWS Backup |
|
Domain 2: Design High-Performing Architectures |
|
|
Implement a fanout messaging. |
Create an SNS topic with a message filtering policy and configure multiple SQS queues to subscribe to the topic. |
|
A database that has a read replication latency of less than 1 second. |
Use Amazon Aurora with cross-region replicas. |
|
A specific type of Elastic Load Balancer that uses UDP as the protocol for communication between clients and thousands of game servers around the world. |
Use Network Load Balancer for TCP/UDP protocols. |
|
Monitor the memory and disk space utilization of an EC2 instance. |
Install Amazon CloudWatch agent on the instance. |
|
Retrieve a subset of data from a large CSV file stored in the S3 bucket. |
Perform an S3 Select operation based on the bucket’s name and object’s key. |
|
Upload 1 TB file to an S3 bucket. |
Use Amazon S3 multipart upload API to upload large objects in parts. |
|
Improve the performance of the application by reducing the response times from milliseconds to microseconds. |
Use Amazon DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX) |
|
Retrieve the instance ID, public keys, and public IP address of an EC2 instance. |
Access the URL: http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/ using the EC2 instance. |
|
Route the internet traffic to the resources based on the location of the user. |
Use Route 53 Geolocation Routing policy. |
|
A fully managed ETL (extract, transform, and load) service provided by Amazon Web Services. |
|
|
A fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service. |
|
| Domain 3: Design Secure Applications and Architectures | |
|
Encrypt EBS volumes restored from the unencrypted EBS snapshots |
Copy the snapshot and enable encryption with a new symmetric CMK while creating an EBS volume using the snapshot. |
|
Limit the maximum number of requests from a single IP address. |
Create a rate-based rule in AWS WAF and set the rate limit. |
|
Grant the bucket owner full access to all uploaded objects in the S3 bucket. |
Create a bucket policy that requires users to set the object’s ACL to bucket-owner-full-control. |
|
Protect objects in the S3 bucket from accidental deletion or overwrite. |
Enable versioning and MFA delete. |
|
Access resources on both on-premises and AWS using on-premises credentials that are stored in Active Directory. |
Set up SAML 2.0-Based Federation by using a Microsoft Active Directory Federation Service. |
|
Secure the sensitive data stored in EBS volumes |
Enable EBS Encryption |
|
Ensure that the data-in-transit and data-at-rest of the Amazon S3 bucket is always encrypted |
Enable Amazon S3 Server-Side or use Client-Side Encryption |
|
Secure the web application by allowing multiple domains to serve SSL traffic over the same IP address. |
Use AWS Certificate Manager to generate an SSL certificate. Associate the certificate to the CloudFront distribution and enable Server Name Indication (SNI). |
|
Control the access for several S3 buckets by using a gateway endpoint to allow access to trusted buckets. |
Create an endpoint policy for trusted S3 buckets. |
|
Enforce strict compliance by tracking all the configuration changes made to any AWS services. |
Set up a rule in AWS Config to identify compliant and non-compliant services. |
|
Provide short-lived access tokens that act as temporary security credentials to allow access to AWS resources. |
Use AWS Security Token Service |
|
Encrypt and rotate all the database credentials, API keys, and other secrets on a regular basis. |
Use AWS Secrets Manager and enable automatic rotation of credentials. |
| Domain 4: Design Cost-Optimized Architectures | |
|
A cost-effective solution for over-provisioning of resources. |
Configure a target tracking scaling in ASG. |
|
The application data is stored in a tape backup solution. The backup data must be preserved for up to 10 years. |
Use AWS Storage Gateway to backup the data directly to Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive. |
|
Accelerate the transfer of historical records from on-premises to AWS over the Internet in a cost-effective manner. |
Use AWS DataSync and select Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive as the destination. |
|
Globally deliver the static contents and media files to customers around the world with low latency. |
Store the files in Amazon S3 and create a CloudFront distribution. Select the S3 bucket as the origin. |
|
An application must be hosted to two EC2 instances and should continuously run for three years. The CPU utilization of the EC2 instances is expected to be stable and predictable. |
Deploy the application to a Reserved instance. |
|
Implement a cost-effective solution for S3 objects that are accessed less frequently. |
Create an Amazon S3 lifecyle policy to move the objects to Amazon S3 Standard-IA. |
|
Minimize the data transfer costs between two EC2 instances. |
Deploy the EC2 instances in the same Region. |
|
Import the SSL/TLS certificate of the application. |
Import the certificate into AWS Certificate Manager or upload it to AWS IAM. |
AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Video Course – SAA-C03
This is a concise Solutions Architect Associate video training course for the SAA-C03 exam. The goal of this video course is to equip you with the exam-specific knowledge that you need to understand in order to pass the SAA-C03 exam, presented in a highly visual form. Click here to enroll. Here is a sneak peek of our video course introduction:
Validate Your SAA-C03 Knowledge
When you are feeling confident with your review, it is best to validate your knowledge through sample exams. You can take this practice exam from AWS for free as additional material but do not expect your real exam to be on the same level of difficulty as this practice exam on the AWS website. Tutorials Dojo offers a very useful and well-reviewed set of practice tests for AWS Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 takers here. The practice test has over 400 unique questions and each question comes with detailed explanations, reference links, and cheat sheets. You can also pair our practice exams with our video course and exam study guide eBook to further help in your exam preparations.
If you have scored well on the Tutorials Dojo AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 practice tests and you think you are ready, then go earn your certification! If you think you are lacking in certain areas, better review them again and take note of any hints in the questions that will help you select the correct answers.
Sample SAA-C03 Practice Test Questions
Question 1
A tech company has a CRM application hosted on an Auto Scaling group of On-Demand EC2 instances with different instance types and sizes. The application is extensively used during office hours from 9 in the morning to 5 in the afternoon. Their users are complaining that the performance of the application is slow during the start of the day but then works normally after a couple of hours.
Which of the following is the MOST operationally efficient solution to implement to ensure the application works properly at the beginning of the day?
- Configure a Dynamic scaling policy for the Auto Scaling group to launch new instances based on the CPU utilization.
- Configure a Dynamic scaling policy for the Auto Scaling group to launch new instances based on the Memory utilization.
- Configure a Scheduled scaling policy for the Auto Scaling group to launch new instances before the start of the day.
- Configure a Predictive scaling policy for the Auto Scaling group to automatically adjust the number of Amazon EC2 instances
Question 2
A financial application consists of an Auto Scaling group of Amazon EC2 instances, an Application Load Balancer, and a MySQL RDS instance set up in a Multi-AZ Deployment configuration. To protect customers’ confidential data, it must be ensured that the Amazon RDS database is only accessible using an authentication token specific to the profile credentials of EC2 instances.
Which of the following actions should be taken to meet this requirement?
- Enable the IAM DB Authentication.
- Configure SSL in your application to encrypt the database connection to RDS.
- Create an IAM Role and assign it to your EC2 instances which will grant exclusive access to your RDS instance.
- Use a combination of IAM and STS to enforce restricted access to your RDS instance using a temporary authentication token.
Click here for more AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate practice exam questions.
Check out our other AWS practice test courses here:
To increase your chances of passing the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate exam, we recommend using a combination of our video course, our practice tests, and our study guide eBook. You can view our triple bundles here.
Additional SAA-C03 Training Materials: High-Quality Video Courses for the AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Exam
There are a few top-rated AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 video courses that you can check out as well, which can help in your exam preparations. The list below is constantly updated based on feedback from our students on which course/s helped them the most during their exams.
- Courses from AWS SkillBuilder site which includes:
- Standard Exam Prep Plan – only free resources; and
- Enhanced Exam Prep Plan – includes additional content for AWS SkillBuilder subscribers, such as AWS Builder Labs, game-based learning, Official Pretests, and more exam-style questions.
- Andrew Brown’s Free SAA-C03 Course on FreeCodeCamp YouTube
- Another awesome resource that we recommend for your AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate SAA-C03 exam preparation is Andrew Brown’s SAA-C03 course on FreeCodeCamp YouTube. Andrew Brown is the CEO of ExamPro and also an AWS Community Hero as well. Check out his informative 50-hour FREE SAA-C03 course here:
Some Notes Regarding Your SAA-C03 Exam
The AWS Solutions Architect Associate (SAA-C03) exam loves to end questions that ask for highly available or cost-effective solutions. Be sure to understand the choices provided to you, and verify that they have the correct details. Some choices are very misleading such that it seems it is the most appropriate answer to the question but contains incorrect detail about some services.
When unsure of which options are correct in a multi-select question, try to eliminate some of the choices that you believe are false. This will help narrow down the feasible answers to that question. The same goes for multiple-choice type questions. Be extra careful as well when selecting the number of answers you submit.
As mentioned in this review, you should be able to differentiate services that belong to one category from another. Common comparisons include:
- EC2 vs ECS vs Lambda
- S3 vs EBS vs EFS
- CloudFormation vs OpsWorks vs Elastic Beanstalk
- SQS vs SNS vs SES vs MQ
- Security Group vs nACLs
- The different S3 storage types vs Glacier
- RDS vs DynamoDB vs Elasticache
- RDS engines vs Aurora
The Tutorials Dojo Comparison of AWS Services contains excellent cheat sheets comparing these seemingly similar services which are crucial to solving the tricky scenario-based questions in the actual exam. By knowing each service’s capabilities and use cases, you can consider these types of questions already half-solved.
Lastly, be on the lookout for “key terms” that will help you realize the answer faster. Words such as millisecond latency, serverless, managed, highly available, most cost-effective, fault-tolerant, mobile, streaming, object storage, archival, polling, push notifications, etc are commonly seen in the exam. Time management is very important when taking AWS certification exams, so be sure to monitor the time you consume for each question.