Last updated on December 5, 2025
Azure Files Cheat Sheet
- Offers fully managed cloud-based file storage that can be accessed through the industry-standard server message block (SMB) protocol.
Features
- Mount your Azure File share from Windows, Linux, or macOS.
- Azure File Sync enables you to access your data from SMB, REST, or even on-premises.
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit using SMB 3.0 and HTTPS.
- Lift and shift applications to the cloud, where the application data is moved to Azure Files, and the application continues to run on-premises.
- Store configuration files in a centralized location where they can be accessed from many application instances.
- Azure Files provides the capability of taking share snapshots of file shares.
- Azure Files now supports the NFS 4.1 protocol for premium file shares, providing a standard network file system for Linux and macOS clients.
- SMB Multichannel support increases throughput and provides network redundancy for SMB 3.x connections.
- Integrated Azure Backup for premium file shares offers managed backup, retention policies, and point-in-time restore.
- Soft delete for file shares allows you to recover accidentally deleted files, directories, and shares within a configurable retention period.
Storage Tiers
- Premium file shares (SSD)
- High performance & low latency, within single-digit milliseconds for most IO operations.
- For IO-intensive workloads.
- Standard file shares (HDD)
- Reliable performance for IO workloads which are less latency-sensitive.
- If you created either a premium or a standard file share, you cannot automatically convert it to the other tier.
- 5 TiB by default, can be increased up to 100 TiB for all redundancy options (LRS, ZRS, GRS, GZRS)
|
Detail |
Premium |
Standard |
|
Billing model |
Provisioned Billing Model, pay for how much storage you provision rather than how much storage you actually ask for. |
Pay-As-You-Go Model, the bill will increase if you use (read/write/mount) the Azure file share more. |
|
Redundancy options |
It is available for locally redundant (LRS) and zone redundant (ZRS) storage. |
It is available for locally redundant, zone redundant, geo-redundant (GRS), and geo-zone redundant (GZRS) storage. |
|
Maximum size of file share |
Provisioned for up to 100 TiB. |
100 TiB for all redundancy options (Locally Redundant, Zone-Redundant, Geo-Redundant, and Geo-Zone-Redundant storage). 5 TiB remains the default size but can be increased. |
|
Regional availability |
File shares are not available in each region, but zone redundant support is available in a smaller subset of regions. |
Available in every Azure region. |
Supported Devices
- To use an Azure file share outside of the Azure region the OS must support SMB 3.0
- To mount an Azure file sharing on Windows, you must have access to port 445.
|
Windows version |
SMB version |
Mountable in Azure VM |
Mountable on-premises |
|
Windows Server 2019 |
SMB 3.0 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows 101 |
SMB 3.0 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows Server semi-annual channel2 |
SMB 3.0 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows Server 2016 |
SMB 3.0 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows 8.1 |
SMB 3.0 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows Server 2012 R2 |
SMB 3.0 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows Server 2012 |
SMB 3.0 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Windows 73 |
SMB 2.1 |
Yes |
No |
|
Windows Server 2008 R23 |
SMB 2.1 |
Yes |
No |
| Windows Server 2022 |
SMB 3.1.1 |
Yes |
Yes |
- Linux clients can also access the file storage through the SMB protocol.
|
Linux distribution |
SMB 2.1 (Mounts on VMs within same Azure region) |
SMB 3.0 (Mounts from on-premises and cross-region) |
|
Ubuntu |
14.04+ |
16.04+ |
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) |
7+ |
7.5+ |
|
CentOS |
7+ |
7.5+ |
|
Debian |
8+ |
10+ |
|
openSUSE |
13.2+ |
42.3+ |
|
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server |
12+ |
12 SP3+ |
Encryption
- By default, encrypted with Microsoft-managed keys and responsible for rotating them on a regular basis.
- Using Microsoft-managed keys, you can also choose to manage your own keys, which gives you control over the rotation process.
- With customer-managed keys, Azure file storage is authorized to access your keys to fulfill read and write requests from your clients.
- Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) authentication for SMB access allows identity-based access to file shares using Azure AD credentials, enabling secure access without a traditional domain.
Networking
- SMB uses port 445.
- Accessible from anywhere, via the public endpoint of the storage account.
- Azure file shares over an ExpressRoute or VPN connection:
- Tunneling into a virtual network, even if port 445 is blocked.
- Private endpoints give you a dedicated IP address from within the address space of the virtual network.
- Allows you to configure DNS forwarding.
- The UNC path format of an Azure File Share is: \\<storageAccountName>.file.core.windows.net\
Azure File Sync
- Transform an on-premises (or cloud) Windows Server into a quick cache of your Azure file share.
- Use Azure File Sync agent to synchronize files from a server to an Azure file share.
- To create sync groups, you need to deploy a Storage Sync Service.
- A sync group defines the sync relationship between a cloud endpoint and a server endpoint.
- Cloud endpoint – represents an Azure file share and multiple server endpoints.
- Server endpoint – a path registered on the Windows Server.
- When you make changes to your cloud endpoint or server endpoint, your files are automatically synced to your sync group’s remaining endpoints.
- When you make a change directly to the cloud endpoint, Azure files must first detect it via a change detection job, which only happens once every 24 hours.
- A change detection job enumerates all the files in the file share and compares it to the sync version of that file. When the change detection job determines that there are changes, Azure File sync will initiate a sync session.
- The sync group you created should only have one cloud endpoint.
- A sync group may have server endpoints with different Active Directory memberships, even if they are not domain-joined.
- The storage accounts used for Azure Files deployments are:
- General purpose version 2 (GPv2) storage accounts
- FileStorage storage accounts
- You can use cloud tiering to cache frequently accessed files locally on the server.
- Only NTFS volumes are supported; ReFS, FAT, FAT32, and other file systems are not supported.
- The service supports interop with DFS Namespaces (DFS-N) and DFS Replication (DFS-R).
- DFS-N allows you to group shared folders located on multiple servers into one or more logically structured namespaces.
- DFS-R enables you to replicate folders across multiple servers and sites.
- Azure File Sync has three layers of encryption:
- Encryption at rest (Windows Server)
- Encryption in transit
- Encryption at rest (Azure file share)
- Cloud tiering is now supported on Windows Server 2022 in addition to earlier versions.
Azure Blob vs Disk vs File Storage:
https://tutorialsdojo.com/azure-blob-vs-disk-vs-file-storage/
Validate Your Knowledge
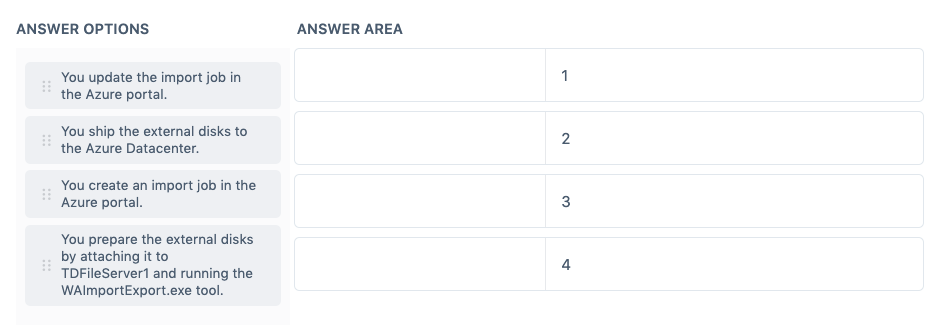
Question 1
Question Type: Matrix Sorting Choice
You have an on-premises data center that contains a file server named TDFileServer1 which has 20 TB of data.
You created an Azure subscription and an Azure file share named TDFile1.
There is a requirement to transfer 20 TB of data to TDFile1 using the Azure Import/Export service.
In which order should you perform the actions?
Instructions: To answer, drag the appropriate item from the column on the left to its description on the right. Each correct match is worth one point.
For more Azure practice exam questions with detailed explanations, check out the Tutorials Dojo Portal:
Azure Files Cheat Sheet Resources:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/storage/files/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/files/storage-files-introduction
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/files/storage-how-to-use-files-windows
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/files/storage-how-to-use-files-linux