Last updated on September 3, 2025
Thinking of joining the booming cloud computing field but not a coder? You’re not alone. Many professionals today are realizing that a successful career in cloud computing isn’t limited to those with programming skills. This article breaks down how non-coders can carve out rewarding careers in this high-demand industry—what roles are available, which skills to focus on, where to take courses, and how to take your first steps. If you’ve been hesitating to enter cloud because you don’t code, this guide is for you.
What is Cloud Computing and Why It Matters
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including storage, servers, software, and analytics—over the internet. Instead of maintaining expensive hardware, organizations rent resources from providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Here’s why the industry is growing fast:
-
Scalability – Companies can increase or decrease resources on demand
-
Cost-effectiveness – No need for physical infrastructure
-
Innovation – Easier to test and deploy new ideas quickly
-
Global reach – Services can be accessed from anywhere
These advantages drive massive demand for cloud talent—not just programmers, but professionals across operations, project management, business strategy, and more.
Why Cloud Computing Isn’t Just for Coders
Although software development is often associated with cloud computing, the truth is that the cloud ecosystem extends far beyond coding. In fact, many high-impact roles require little to no programming at all. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP, they also need professionals who can align cloud solutions with business goals, support operations, maintain security, and ensure project delivery.
Whether someone is transitioning from another IT field, coming from a business background, or simply not inclined toward coding, there are many roles in the cloud space that play a critical part in modern organizations.
Here are several non-coding cloud roles worth exploring:
1. Agile Project Manager / Scrum Master
While this role doesn’t involve writing code, it is essential for driving the execution of cloud initiatives. Agile Project Managers and Scrum Masters lead cross-functional teams and keep cloud migration or modernization projects on track.
-
Facilitates sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives
-
Ensures alignment between cloud engineers and business stakeholders
-
Manages cloud project timelines, resource allocation, and risk mitigation
-
Focuses on delivering business value incrementally and efficiently
This role is ideal for professionals with experience in project delivery, process improvement, or Agile frameworks such as Scrum or SAFe.
2. IT Business Analyst
While not technical in the traditional sense, IT Business Analysts play a strategic role by bridging the gap between cloud engineering teams and business units. They help ensure that cloud investments solve real problems and align with broader objectives.
-
Gathers, analyzes, and translates business requirements into technical documentation
-
Works closely with Solutions Architects, Product Managers, and Developers
-
Identifies inefficiencies and proposes cloud-based solutions
-
Supports decision-making through cost-benefit analysis and stakeholder engagement
Those with strong analytical skills and a solid grasp of business processes will thrive in this role—even without writing a single line of code.
3. Cloud Security Specialist
As cloud adoption grows, so does the need for robust security practices. Cloud Security Specialists focus on protecting data, systems, and workloads within cloud environments—often without programming, but with strong knowledge of tools and frameworks.
-
Implements encryption, identity and access management (IAM), and firewall policies
-
Monitors systems for vulnerabilities and compliance violations
-
Ensures adherence to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001
-
Collaborates with DevOps and compliance teams to enforce security controls
While basic scripting may help with automation, most of the work revolves around policies, risk assessments, audits, and security tools.
4. DevOps Support / Infrastructure Operations
Not all DevOps professionals need to write infrastructure-as-code or develop deployment pipelines. Many DevOps support roles focus on managing cloud-based infrastructure, monitoring system performance, and using low-code tools for automation.
-
Assists with deployments, uptime monitoring, and configuration management
-
Utilizes CI/CD platforms like AWS CodePipeline, GitHub Actions, or Jenkins
-
Understands core DevOps principles like continuous delivery, even without coding
-
Responds to incidents, performs root-cause analysis, and ensures SLAs are met
This role is well-suited to individuals who are hands-on, systems-oriented, and detail-focused.
5. Cloud Consultant
Cloud Consultants play an advisory role, helping businesses choose, design, or optimize their cloud solutions. While some may have a technical background, coding is not a requirement for delivering high-value cloud strategy.
-
Analyzes client needs and recommends suitable AWS/GCP/Azure services
-
Leads cloud adoption workshops and migration planning
-
Offers architectural guidance at a high level, without direct implementation
-
Helps optimize costs, security, and operational efficiency
This is an excellent path for professionals with client-facing experience, solution design expertise, or a background in IT consulting.
6. AWS Solutions Architect (Non-Developer Track)
Although some Solutions Architects do write code, many focus more on designing architectures and guiding technical decisions than building them. In this role, the ability to explain complex solutions to diverse stakeholders is often more important than programming.
-
Works with clients to understand workloads, constraints, and goals
-
Designs high-availability, secure, and scalable cloud solutions
-
Prepares architectural diagrams, technical presentations, and deployment recommendations
-
Coordinates with engineering teams to ensure correct implementation
A strong grasp of AWS services and architectural principles is key—but coding is not mandatory to succeed.
7. Cloud Support Engineer
For those who enjoy problem-solving and customer interaction, the Cloud Support Engineer role involves helping customers troubleshoot and optimize their use of cloud services—typically through the AWS Management Console or by guiding configurations.
-
Responds to technical support tickets and outage incidents
-
Provides guidance on service usage, billing issues, and resource limits
-
Uses diagnostic tools to identify root causes without needing to write code
-
Communicates clearly with non-technical users and engineering teams
Strong communication skills and a service-oriented mindset are more essential than programming in this role.
Practical Skills Non-Coders Should Learn
Even without coding, there are technical concepts every cloud professional should understand. These skills make it easier to work across departments and stand out to employers.
Learn Cloud Fundamentals
-
Understand cloud service models: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
-
Know deployment models: Public, Private, Hybrid
-
Gain platform awareness (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
Study Cloud Security
-
Learn basics of encryption, firewalls, access control
-
Get familiar with frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST, and SOC 2
-
Explore certifications like Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)
Get Comfortable with Data Analysis
-
Use tools like Excel, Power BI, or Tableau
-
Understand cloud data platforms like BigQuery or Redshift
-
Analyze data for trends, costs, and performance metrics
Master Cost Optimization
-
Track usage through cost calculators and billing dashboards
-
Spot opportunities to reduce spend
-
Learn tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Azure Cost Management
Understand Networking Basics
-
Know the essentials: DNS, IP addressing, routing
-
Understand how cloud networks differ from traditional networks
-
Consider certifications like AWS Certified Advanced Networking
Best Online Platforms for Learning Cloud Computing
To build these skills as a non-coder, start by choosing the right learning platforms. Below are trusted websites where you can study at your own pace or through guided programs:
1. AWS Skill Builder
Official Platform by Amazon Web Services
AWS Skill Builder is the official learning hub developed by Amazon Web Services, designed to help individuals and teams build cloud expertise at their own pace. It offers more than 600 free digital courses, along with curated learning paths that cover foundational to advanced topics. In addition, users can access hands-on labs to reinforce practical skills.
For those seeking a deeper learning experience, subscribing to an individual or team plan unlocks premium features such as full certification exam preparation, interactive labs, game-based learning experiences like AWS Cloud Quest, and instructor-led video content through the AWS Digital Classroom.
Whether the goal is to earn AWS certifications, expand AI/ML capabilities, or enhance team-wide cloud fluency, AWS Skill Builder delivers a structured and regularly updated learning journey that stays aligned with the latest AWS service offerings.
Best for: Learners who want official, up-to-date AWS training
Key Features: Free and premium plans, hands-on labs, game-based learning, team management tools
Ideal for: Individuals, IT professionals, developers, cloud engineers, and enterprise teams
2. Tutorials Dojo
Highly Recommended by the Cloud Certification Community
Tutorials Dojo is a widely recommended cloud learning platform created by AWS Certified expert Jon Bonso. Unlike other platforms, Tutorials Dojo is particularly known for its certification-focused approach, offering in-depth practice exams and learning materials that are closely aligned with actual AWS, Azure, and GCP certification objectives.
What sets Tutorials Dojo apart is its strong community backing and its affordability. While many learners rely on paid subscriptions elsewhere, this platform provides a wide selection of free resources including cheat sheets and blog tutorials—alongside highly affordable premium content. Moreover, the practice exams feature both timed and section-based modes, helping users target specific areas of weakness and simulate real exam conditions.
Furthermore, Tutorials Dojo includes access to PlayCloud, a practical lab environment that replicates real-world cloud scenarios. This allows learners to gain hands-on experience without needing a personal AWS account—an invaluable feature for those seeking to bridge the gap between theory and practice.
In short, if the goal is to prepare for certifications in a cost-effective, targeted, and highly practical way, Tutorials Dojo remains one of the most trusted platforms available.
Best for: Learners focused on certification preparation with exam-style practice
Key Features: Practice exams, cheat sheets, PlayCloud hands-on labs, free and budget-friendly study content
Ideal for: Certification candidates, developers, self-paced learners, and cloud professionals seeking affordable training
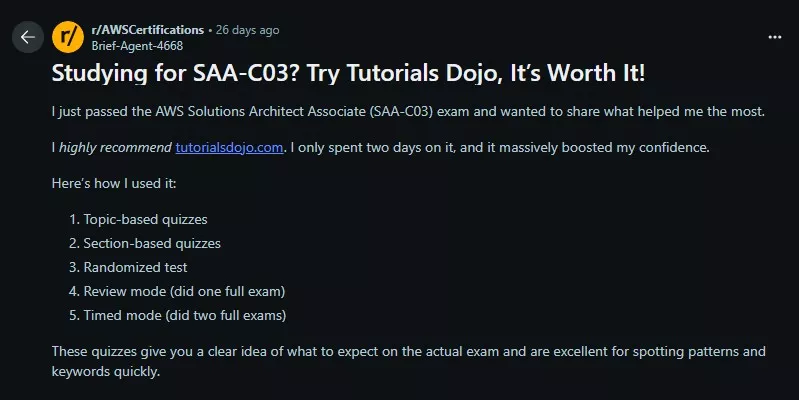
Comment from Reddit:
3. Udemy
Marketplace of On-Demand Courses
Udemy is one of the world’s largest online course marketplaces, featuring thousands of cloud computing courses across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and DevOps topics. Courses are created by individual instructors, offering a wide range of perspectives, practice tests, and learning styles.
While the quality varies by instructor, top-rated courses—such as those by Stephane Maarek or Andrew Brown—are often favored by AWS learners. Frequent discounts make premium courses highly affordable.
Best for: Flexible, topic-specific cloud training at budget-friendly prices
Key Features: Lifetime access to purchased courses, instructor Q&A, downloadable resources
Ideal for: Beginners to intermediate learners, and certification-focused individuals
4. freeCodeCamp
Free, Open-Source Computer Science Education
freeCodeCamp is a nonprofit organization offering a completely free, self-paced curriculum that teaches computer science fundamentals, programming, cloud basics, and DevOps skills.
In addition to the interactive coding platform, the freeCodeCamp YouTube Channel features in-depth tutorials on AWS, Terraform, Docker, Kubernetes, and more—ideal for visual learners and those looking to build foundational knowledge without financial barriers.
Best for: Free, beginner-friendly cloud and tech education
Key Features: Open-source curriculum, project-based learning, high-quality video tutorials
Ideal for: Students, career switchers, and anyone exploring cloud from scratch
5. ZeroToCloud by Lucy Wang
Cloud Education Designed for the Gen Z Learner
ZeroToCloud is a modern cloud learning platform created by Lucy Wang, a former AWS Solutions Architect based in Sydney, Australia. The platform was designed with Gen Z learners in mind, combining relatable teaching styles with practical cloud fundamentals and career guidance.
ZeroToCloud stands out for its beginner-first, community-supported learning model—ideal for students and young professionals looking to gain cloud fluency and stand out in tech roles.
Best for: Gen Z learners exploring cloud computing as a career
Key Features: Real-world explanations, career coaching, beginner-focused resources
Ideal for: Students, junior cloud engineers, and career starters in tech
These platforms help non-coders stay competitive by offering certifications, project-based learning, and cloud playgrounds for experimentation.
FAQs: Common Concerns for Non-Coders
Do all cloud jobs require coding?
No. Many roles—like security analysts, support engineers, and project managers—require cloud knowledge, but not programming.
Is it harder to enter cloud computing without technical skills?
Not necessarily. While some roles may require more technical depth, many others rely on understanding systems, communicating with stakeholders, and guiding projects.
Can I succeed in cloud without learning to code at all?
Yes, but basic scripting (like JSON or YAML) can still be helpful. Even light tech literacy opens more opportunities.
Should I still consider certifications?
Absolutely. Certifications like AWS Cloud Practitioner, Azure Fundamentals, or Google Cloud Digital Leader are beginner-friendly and prove your knowledge—even if you don’t code.
There’s Space for You in the Cloud
Cloud computing is one of the fastest-growing fields in tech, and it welcomes more than just coders. Non-programmers bring essential value—from strategy to security to operations. By building relevant skills and certifications, you can contribute meaningfully to this space and enjoy a future-proof career.
There has never been a better time to start. Whether you’re a career changer, recent graduate, or industry professional looking to pivot—cloud computing offers a place for you.