Generative AI Security Scoping Matrix Cheat Sheet
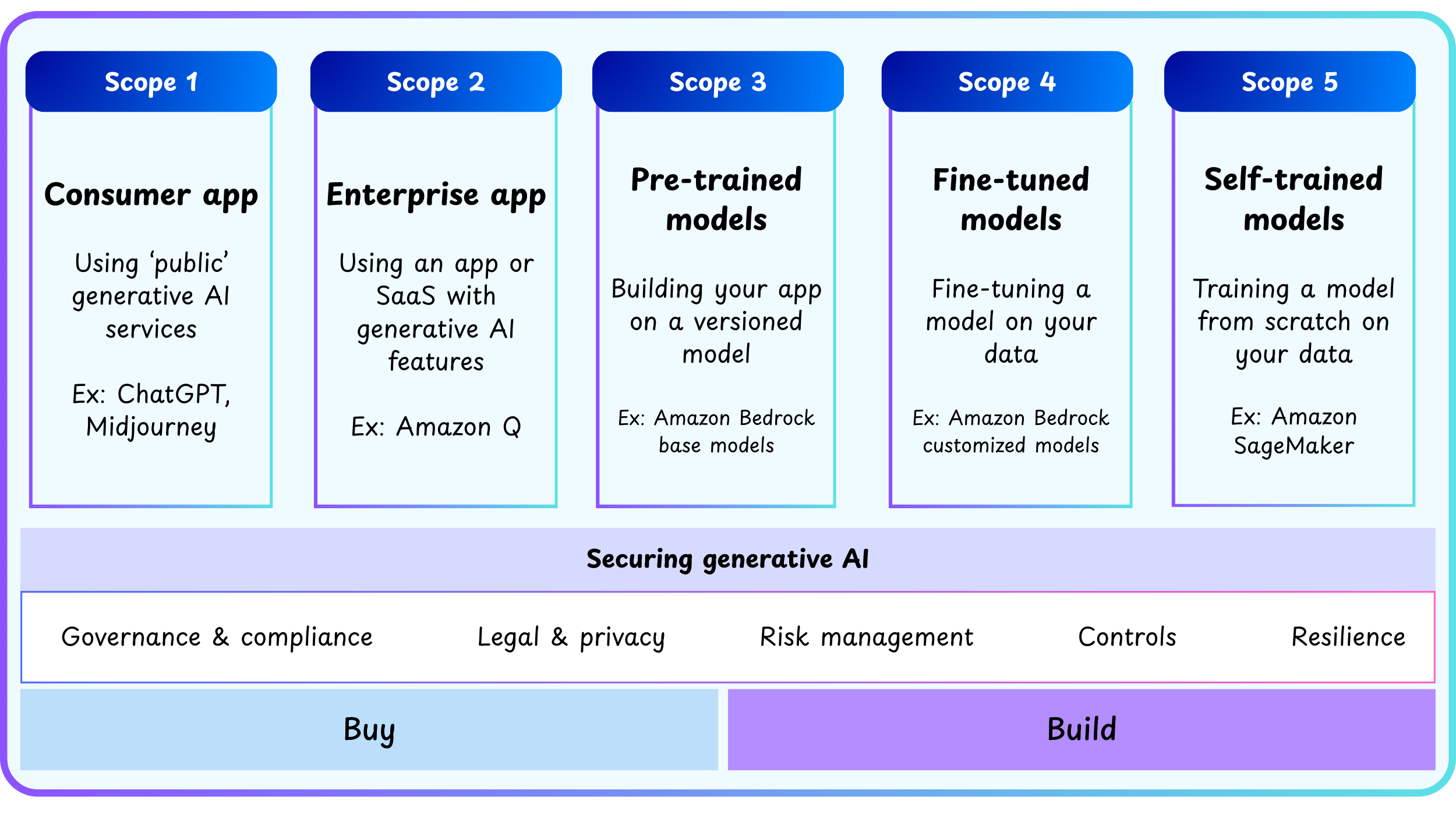
- The Generative AI Security Scoping Matrix is a framework to classify generative AI (GenAI) use cases by the level of ownership and control over the models and data.
- It helps organizations assess and prioritize security requirements based on their generative AI deployment approach.
- The matrix defines 5 scopes from least to most ownership and control:
- Governance & Compliance
- Legal & Privacy
- Risk Management
- Controls
- Resilience
Scopes of Generative AI Use Cases
Buying Generative AI (Low Ownership)
-
Scope 1: Consumer app
-
Uses free or paid public third-party services like ChatGPT and Midjourney.
-
No ownership or visibility into the underlying training data, models, or infrastructure. Can’t modify or fine-tune the model.
-
Direct use of APIs or UI of public services governed entirely by the service provider’s terms.
-
Security Considerations:
-
Educate employees and users on avoiding input of sensitive or proprietary information.
-
Restrict use for specific business processes if data confidentiality cannot be guaranteed.
-
Monitor usage for compliance with corporate policies.
-
-
Example: Employees use ChatGPT for marketing ideas.
-
-
Scope 2: Enterprise app
-
Uses third-party enterprise SaaS with embedded GenAI features.
-
Business relationships with vendors offer higher protection and configuration options than in Scope 1.
-
Users leverage enterprise-grade AI services embedded in software applications with some degree of corporate control.
-
Security Considerations:
-
Review and negotiate vendor agreements emphasizing data privacy, usage restrictions, and security controls.
-
Ensure contractual commitments do not allow the use of your data for additional training or model improvements without consent.
-
Implement access controls and audit logging where supported.
-
-
Example: Using an enterprise scheduling app with AI-generated agendas.
-
Building Generative AI (More Ownership)
-
Scope 3: Pre-trained models
-
Builds applications on third-party foundation models via API.
-
Integrates models into business apps without modification.
- Own the application and input/output data, not the base model or training data.
-
Security Considerations:
-
Apply strong identity and access controls on API usage.
-
Sanitize and filter prompt inputs to reduce injection risk.
-
Use techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to protect sensitive data by not embedding it directly in prompts.
-
Monitor usage patterns and anomalies.
-
-
Example: Support chatbot using Anthropic Claude through Amazon Bedrock.
-
-
Scope 4: Fine-tuned models
-
Fine-tunes third-party pre-trained models with proprietary data.
- Owns fine-tuned models, training datasets, and custom configurations.
-
Creates enhanced models specialized for business needs.
-
Security Considerations:
-
Protect training data with classification, encryption, and role-based access controls.
-
Maintain audit trails of model versions and datasets used.
-
Perform rigorous testing for data leakage, output bias, and hallucinations.
-
Restrict inference to authorized users and environments.
-
-
Example: Marketing content generator fine-tuned on company data.
-
-
Scope 5: Self-trained models
-
Full lifecycle ownership, building and training generative AI models from scratch using owned or licensed data.
-
Full ownership of data, training, and model.
- Models tailored entirely to organizational or industry-specific use cases.
-
Security Considerations:
-
Implement enterprise-grade governance covering data sourcing, model training infrastructure, and deployment.
-
Employ zero-trust architectures for cloud compute and data storage.
-
Continuously assess and address model risks such as adversarial attacks, data poisoning, and extraction threats.
-
Establish AI ethics reviews and compliance audits.
-
Plan for disaster recovery and resilience through checkpoints and multi-region availability.
-
-
Example: Industry-specific video generation AI trained from ground-up.
-
Core Security Disciplines Across Scopes
-
Governance & Compliance
-
Establish a cross-functional AI governance committee including legal, compliance, security, HR, and product teams.
-
Define clear AI usage policies covering acceptable use, data handling, regulatory compliance, and ethical guidelines.
-
Implement transparency and explainability protocols for model decisions, including automated metadata capture, audit trails, and model behavior and data provenance documentation.
-
Maintain thorough AI-generated content records including source data, generation timestamps, and modification history to meet compliance audit requirements.
-
Employ continuous monitoring and auditing to detect policy violations, ethical risks, and compliance gaps.
-
Align with standards such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) AI Risk Management Framework and industry-specific regulations.
-
Promote ongoing training and awareness programs for all stakeholders on responsible AI use and evolving compliance mandates.
2. Legal & Privacy
-
Conduct detailed privacy impact assessments (PIAs) before deploying generative AI solutions.
-
Implement data minimization strategies and rigorous data masking, tokenization, and de-identification of personal or sensitive data before model training or inference.
-
Establish robust contracts and data processing agreements with third-party AI providers to clarify responsibilities for data protection and IP rights.
-
Address the right to be forgotten by defining processes for data removal or retraining models to exclude specific data.
-
Monitor and enforce compliance with global privacy laws (GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA) considering cross-border data flows in AI use.
-
Include intellectual property considerations relating to data inputs and AI-generated outputs.
3. Risk Management
-
Perform comprehensive threat modeling and risk assessments focused on GenAI-specific risks such as prompt injections, model hallucination, data poisoning, adversarial attacks, data leakage, and bias amplification.
-
Develop and apply risk-based controls and guardrails aligned with risk tolerance and use case sensitivity.
-
Include human oversight mechanisms at critical decision points or high-impact AI outputs to mitigate errors or unintended consequences.
-
Use anomaly detection and monitoring to identify unusual or malicious AI usage patterns in real time.
-
Regularly test AI models for biases, fairness, accuracy, and robustness using AI fairness and security assessment tools.
-
Incorporate incident response playbooks specific to AI, addressing breaches, misuse, or unsafe outputs.
4. Controls
-
Implement least privilege access control with strong IAM policies for AI model and data resources.
-
Use end-to-end encryption for data at rest and in transit, leveraging customer-managed keys where possible.
-
Integrate input validation and sanitization to prevent injection attacks or harmful prompt manipulation.
-
Apply output filtering and moderation to mitigate harmful, biased, or disallowed content generation.
-
Employ API management tools to enforce rate limiting, usage quotas, and authentication for model endpoints.
-
Use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and watermarking techniques to protect sensitive data and identify AI-generated content.
-
Configure comprehensive audit logging for model access, invocations, changes, and data handling actions.
5. Resilience
-
Design the AI architecture for high availability and fault tolerance using cloud-native tools like failover, load balancers, and region redundancy.
-
Implement checkpointing and version control for AI models and training datasets to enable rollback and recovery.
-
Maintain disaster recovery plans that cover AI infrastructure, data loss scenarios, and operational continuity.
-
Conduct load and stress testing to understand system behavior under high inference or training demand.
-
Ensure operational excellence by monitoring system health, latency, accuracy, and throughput.
-
Adopt continuous improvement cycles, including regular retraining, patching, and security hardening, aligned with AWS Well-Architected Framework’s guidelines.
-