Last updated on July 22, 2025
Imagine a world where machines compose music, diagnose diseases, write code, drive cars, and even generate original artwork. That world isn’t the future, it’s now.
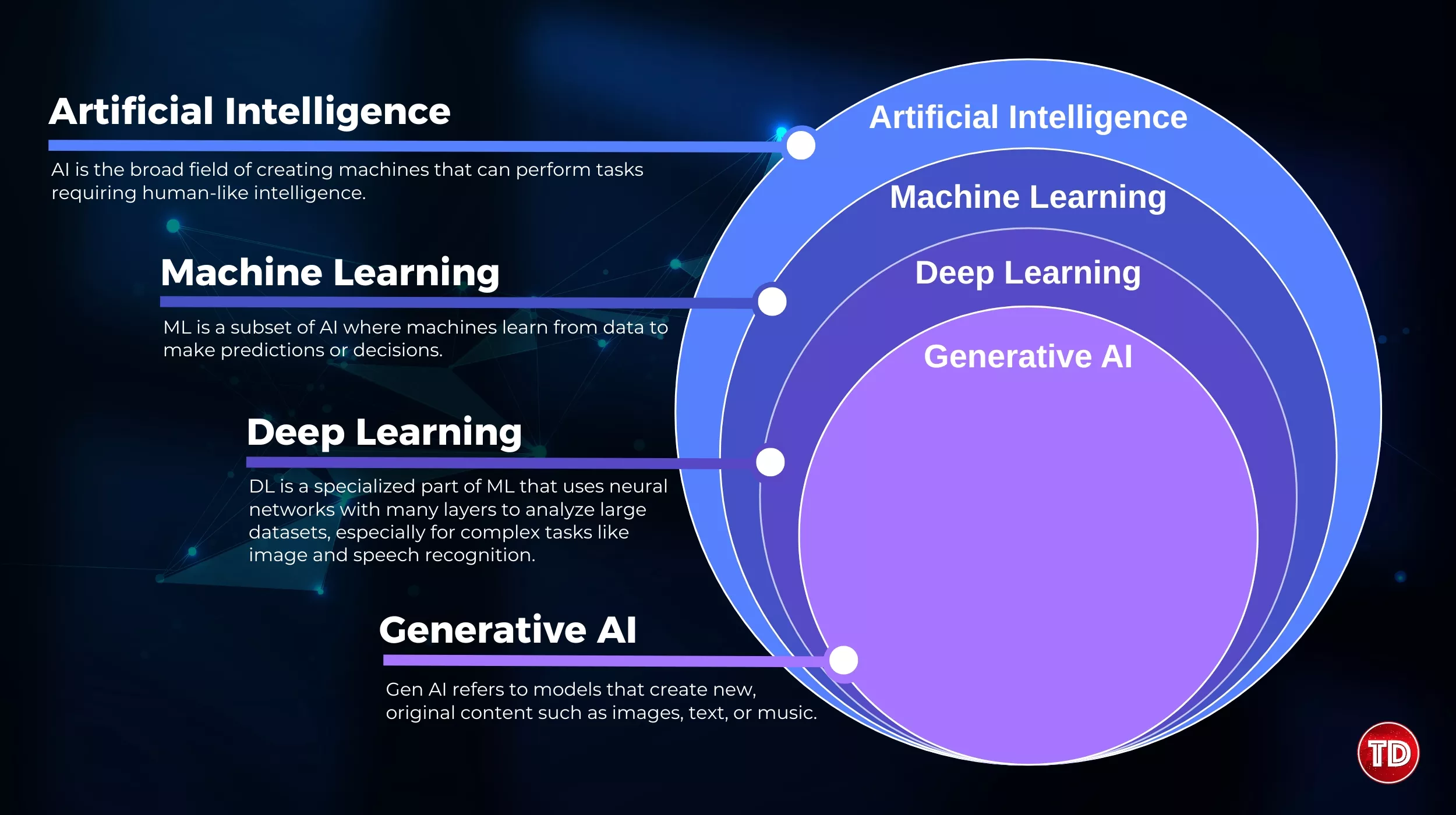
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a buzzword; it’s a driving force behind the most significant innovations of our time. But here’s the catch: while AI is everywhere, many still confuse its core components:
Understanding the differences between these technologies isn’t just helpful, it’s essential. Whether you’re a student, a tech professional, a business leader, or AI-curious, this guide will give you a crystal-clear breakdown of these foundational terms in 2025 and beyond.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the field of computer science focused on creating machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. It includes abilities such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making. AI systems are designed to simulate cognitive functions and improve performance over time through experience and data.
Types of AI:
- Narrow AI: Specialized for specific tasks (e.g., voice assistants, spam filters)
- General AI: Theoretical machines with human-level intelligence across any domain
Where You See AI:
- Intelligent assistants like Alexa or Siri
- Fraud detection systems in banks
- Autonomous drones
- AI-powered recommendation engines (Netflix, Amazon)
Skills Needed:
- Computer science and logic
- Programming (Python, R)
- Understanding of AI ethics
- Problem-solving and analytical thinking
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that allows machines to learn from data. Unlike traditional programming, ML models identify patterns in data and use them to make predictions or decisions. These models continuously improve their accuracy and performance as they are exposed to more data.
Types of ML:
- Supervised Learning: Trained on labeled data
- Unsupervised Learning: Discovers patterns in unlabeled data
- Reinforcement Learning: Learns by trial and error with feedback
Real-World Examples:
- Email spam detection
- Credit scoring
- Chatbot personalization
- Forecasting stock trends
Skills Needed:
- Statistics and data science
- ML libraries (scikit-learn, PyTorch, TensorFlow)
- Data preprocessing and model evaluation
What is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning (DL) is an advanced subset of Machine Learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to mimic the human brain’s structure. It enables systems to learn from vast amounts of data and enhance their performance autonomously. DL drives many of the most impressive AI innovations, including image recognition and natural language processing.
What Makes It Unique:
- Requires massive datasets
- Automates feature extraction
- Needs GPUs for training
- Excels at complex tasks like image or speech recognition
Use Cases:
- Facial recognition
- Self-driving cars
- Voice assistants
- Medical image analysis
- Language translation
Skills Needed:
- Neural network design
- Advanced math (linear algebra, calculus)
- GPU programming
- Deep learning frameworks (Keras, TensorFlow, PyTorch)
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a powerful subset of AI that generates new content, including text, images, music, and code. Unlike traditional AI, which analyzes or predicts, it creates original outputs. This technology drives advancements in art, entertainment, and software development.
Most modern Generative AI tools are built on transformer architectures, like GPT (used in ChatGPT) or DALL·E.
Key Difference:
- ML/DL: Focus on prediction and classification
- Generative AI: Focus on creation
Applications:
- AI writing assistants (blog posts, emails, books)
- Image generation (e.g., Midjourney, DALL·E)
- Code generation (e.g., GitHub Copilot)
- Video editing and animation
- Music and game design
- Synthetic data generation
Skills Needed:
- Prompt engineering
- Understanding of transformers
- Content evaluation techniques
- Fine-tuning and model alignment
AI Careers Are Booming
As AI expands, new roles are appearing that blend tech, creativity, and strategy:
| Role | Description |
|
AI Researcher |
Creates new algorithms and models |
|
ML Engineer |
builds and deploys ML systems |
|
DL Specialist |
Works on advanced neural network solutions |
|
Prompt Engineer |
Crafts prompts for Generative AI |
|
AI Product Manager |
Aligns AI products with business needs |
|
AI Ethics Specialist |
Ensures fair and responsible AI practices |
|
AI UX Designer |
Designs user experiences for AI tools |
Conclusions:
AI is no longer just a field for computer scientists; it’s a revolution affecting every industry. By understanding the difference between AI, ML, DL, and Generative AI, you equip yourself with the language and perspective to thrive in this new era.
So, whether you’re aiming for a career in AI, leading a business, or simply trying to stay informed, this knowledge is your superpower.