Last updated on November 25, 2025
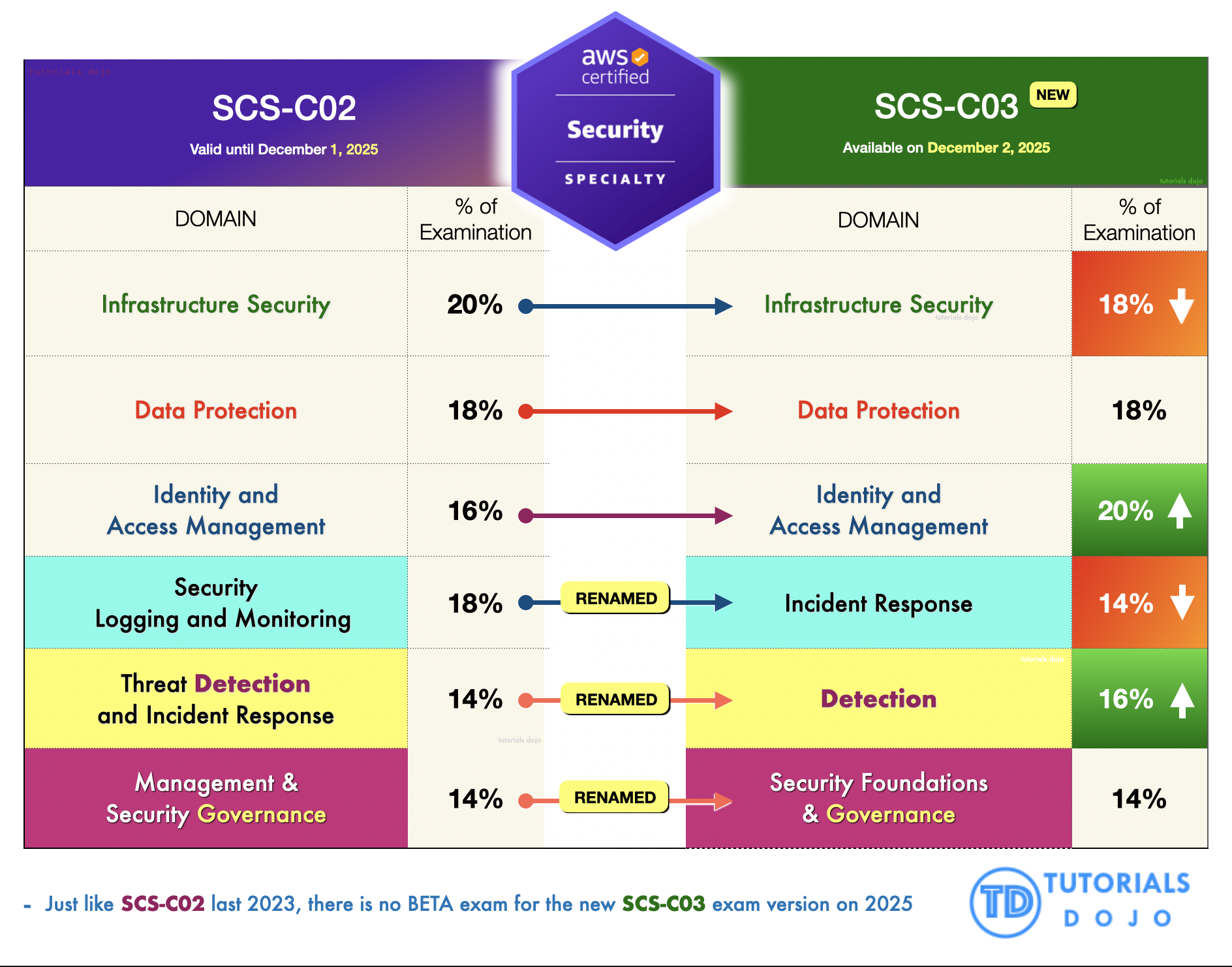
The AWS Certified Security Specialty exam, last updated on July 11, 2023, is set to undergo another official update. The AWS Training and Certification team is releasing a new version, with an exam code of SCS-C03, available on December 02, 2025. You can register for the latest updated SCS-C03 Certified Security Specialty exam as early as November 18, 2025. Take note that the last day that you can take the soon-to-be decommissioned SCS-C02 exam is on December 01, 2025, so make sure that you verify your exam schedule.
The New SCS-C03 Exam Domains
The updated AWS Certified Security Specialty (SCS-C03) exam introduces meaningful refinements to align with the current landscape of cloud security operations. Several domains have been restructured or renamed to better match real-world security responsibilities, threat-response workflows, and governance requirements across modern AWS environments.
Additionally, several existing exam domains have been renamed to better reflect evolving task objectives. For instance, the “Security Logging and Monitoring” domain is now called “Incident Response”, the “Threat Detection and Incident Response” domain has been renamed and refocused to “Detection”, and the “Management & Security Governance” domain is now called “Security Foundations & Governance”.
With the total number of six domains, the weighting distribution has also been adjusted accordingly:
-
“Infrastructure Security” domain decreased from 20% to 18%.
-
“Data Protection” domain remains the same at 18%.
-
“Identity and Access Management” domain increased from 16% to 20%, reflecting the growing importance of IAM in cloud security.
-
“Security Logging and Monitoring” domain has been renamed “Incident Response,” and its weighting has been reduced from 18% to 14%.
-
“Detection” domain, previously Threat Detection and Incident Response, increased from 14% to 16%
-
“Security Foundations & Governance” domain, previously Management & Security Governance, remains the same at 14%
Recommended AWS Certified Security Specialty SCS-C02 Exam Resources
- Official SCS-C03 Exam Guide
- Official AWS Certified Security – Specialty Official Practice Question Set SCS-C03
- AWS Certified Security – Specialty Practice Exams
What are the SCS-C03 Exam Topics and Questions that I need to prepare?
The SCS-C03 exam introduces new topics and broadens its scope to include additional AWS services and features. According to the official SCS-C03 Exam Guide, security is a critical consideration for all AWS services and components within your cloud infrastructure. While certain AWS services may not be explicitly covered in the exam, their security aspects are still relevant. For instance, questions related to securing machine learning workloads may address data protection, access control, and network security for AI/ML applications.
Remember that the exam is intended for experienced professionals who design, implement, and manage security in AWS environments. As a result, it emphasizes the service capabilities, configuration patterns, and architectural decisions that directly impact the security of workloads, identities, networks, and data across the cloud.
|
Analytics: Application Integration: Compute:
Developer Tools
Internet of Things
Machine Learning:
Management and Governance:
Networking and Content Delivery:
|
Security, Identity, and Compliance:
Storage and Data Management:
|
Let’s now dive deeper and check all the relevant SCS-C03 exam topics for the AWS Certified Security Specialty per Exam Domain. This wealth of information should be your ultimate guide when you start studying for the exam.
SCS-C03 Domain 1: Detection
Task 1.1: Design and implement monitoring and alerting solutions for an AWS account or organization.
-
Skill 1.1.1: Analyze workloads to determine monitoring requirements.
-
Skill 1.1.2: Design and implement workload monitoring strategies (for example, by configuring resource health checks).
-
Skill 1.1.3: Aggregate security and monitoring events.
-
Skill 1.1.4: Create metrics, alerts, and dashboards to detect anomalous data and events (for example, Amazon GuardDuty, Amazon Security Lake, AWS Security Hub, Amazon Macie).
-
Skill 1.1.5: Create and manage automations to perform regular assessments and investigations (for example, by deploying AWS Config conformance packs, Security Hub, AWS Systems Manager State Manager)
Task 1.2: Design and implement logging solutions.
-
Skill 1.2.1: Identify sources for log ingestion and storage based on requirements.
-
Skill 1.2.2: Configure logging for AWS services and applications (for example, by configuring an AWS CloudTrail trail for an organization, by creating a dedicated Amazon CloudWatch logging account, by configuring the Amazon CloudWatch Logs agent).
-
Skill 1.2.3: Implement log storage and log data lakes (for example, Security Lake) and integrate with third-party security tools.
-
Skill 1.2.4: Use AWS services to analyze logs (for example, CloudWatch Logs Insights, Amazon Athena, Security Hub findings).
-
Skill 1.2.5: Use AWS services to normalize, parse, and correlate logs (for example, Amazon OpenSearch Service, AWS Lambda, Amazon Managed Grafana).
-
Skill 1.2.6: Determine and configure appropriate log sources based on network design, threats, and attacks (for example, VPC Flow Logs, transit gateway flow logs, Amazon Route 53 Resolver logs).
Task 1.3: Troubleshoot security monitoring, logging, and alerting solutions.
-
Skill 1.3.1: Analyze the functionality, permissions, and configuration of resources (for example, Lambda function logging, Amazon API Gateway logging, health checks, Amazon CloudFront logging).
-
Skill 1.3.2: Remediate misconfiguration of resources (for example, by troubleshooting CloudWatch Agent configurations, troubleshooting missing logs).
SCS-C03 Domain 2: Incident Response
Here are the task statements and related SCS-C03 exam topics for Domain 2: Incident Response. In the previous version of the AWS Certified Security Specialty exam, many of these responsibilities were included under the broader “Security Logging and Monitoring” domain. In the updated SCS-C03 exam, these responsibilities have been reorganized and expanded to form a dedicated Incident Response domain, emphasizing the ability to investigate, contain, and remediate security events across AWS environments.
Task 2.1: Design and test an incident response plan.
-
Skill 2.1.1: Design and implement response plans and runbooks to respond to security incidents (for example, Systems Manager OpsCenter, Amazon SageMaker AI notebooks).
-
Skill 2.1.2: Use AWS service features and capabilities to configure services to be prepared for incidents (for example, by provisioning access, deploying security tools, minimizing the blast radius, and configuring AWS Shield Advanced protections).
-
Skill 2.1.3: Recommend procedures to test and validate the effectiveness of an incident response plan (for example, AWS Fault Injection Service, AWS Resiliency
Hub).
-
Skill 2.1.4: Use AWS services to automatically remediate incidents (for example, Systems Manager, Automated Forensics Orchestrator for Amazon EC2, AWS Step Functions, Amazon Application Recovery Controller, Lambda functions).
Task 2.2: Respond to security events.
-
Skill 2.2.1: Capture and store relevant system and application logs as forensic artifacts.
-
Skill 2.2.2: Search and correlate logs for security events across applications and AWS services.
-
Skill 2.2.3: Validate findings from AWS security services to assess the scope and impact of an event.
-
Skill 2.2.4: Respond to affected resources by containing and eradicating threats, and recover resources (for example, by implementing network containment controls, restoring backups).
-
Skill 2.2.5: Describe methods to conduct root cause analysis (for example, Amazon
Detective).
SCS-C03 Domain 3: Infrastructure Security
The following task statements and related SCS-C03 exam topics are for the third Exam Domain of the AWS Certified Security Specialty called “Infrastructure Security”. The previous version of the AWS Certified Security Specialty exam also had the exact “Infrastructure Security” domain, which was the largest at 20% coverage in the old SCS-C02 version. For the new SCS-C03 test, this domain has decreased to an exam weighting of only 18%. This domain now reflects broader, modernized coverage of cloud infrastructure security, including enhanced edge protections, secure workload configurations, hybrid connectivity, network segmentation, and guardrails for emerging generative AI applications.
Task 3.1: Design, implement, and troubleshoot security controls for network edge services.
-
Skill 3.1.1: Define and select edge security strategies based on anticipated threats and attacks.
-
Skill 3.1.2: Implement appropriate network edge protection (for example, CloudFront headers, AWS WAF, AWS IoT policies, protecting against OWASP Top 10 threats, Amazon S3 cross-origin resource sharing [CORS], Shield Advanced).
-
Skill 3.1.3: Design and implement AWS edge controls and rules based on requirements (for example, geography, geolocation, rate limiting, client fingerprinting).
-
Skill 3.1.4: Configure integrations with AWS edge services and third-party services (for example, by ingesting data in Open Cybersecurity Schema Framework [OCSF] format, by using third-party WAF rules).
Task 3.2: Design, implement, and troubleshoot security controls for compute workloads.
-
Skill 3.2.1: Design and implement hardened Amazon EC2 AMIs and container images to secure compute workloads and embed security controls (for example, Systems Manager, EC2 Image Builder).
-
Skill 3.2.2: Apply instance profiles, service roles, and execution roles appropriately to authorize compute workloads.
-
Skill 3.2.3: Scan compute resources for known vulnerabilities (for example, scan container images and Lambda functions by using Amazon Inspector, monitor compute runtimes by using GuardDuty).
-
Skill 3.2.4: Deploy patches across compute resources to maintain secure and compliant environments by automating update processes and by integrating continuous validation (for example, Systems Manager Patch Manager, Amazon Inspector).
-
Skill 3.2.5: Configure secure administrative access to compute resources (for example, Systems Manager Session Manager, EC2 Instance Connect).
-
Skill 3.2.6: Configure security tools to discover and remediate vulnerabilities within a pipeline (for example, Amazon Q Developer, Amazon CodeGuru Security).
-
Skill 3.2.7: Implement protections and guardrails for generative AI applications (for example, by applying GenAI OWASP Top 10 for LLM Applications protections).
Task 3.3: Design and troubleshoot network security controls.
-
Skill 3.3.1: Design and troubleshoot appropriate network controls to permit or prevent network traffic as required (for example, security groups, network ACLs, AWS Network Firewall).
-
Skill 3.3.2: Design secure connectivity between hybrid and multi-cloud networks (for example, AWS Site-to-Site VPN, AWS Direct Connect, MAC Security [MACsec]).
-
Skill 3.3.3: Determine and configure security workload requirements for communication between hybrid environments and AWS (for example, by using AWS Verified Access).
-
Skill 3.3.4: Design network segmentation based on security requirements (for example, north/south and east/west traffic protections, isolated subnets).
-
Skill 3.3.5: Identify unnecessary network access (for example, AWS Verified Access, Network Access Analyzer, Amazon Inspector network reachability findings).
SCS-C03 Domain 4: Identity and Access Management
The following task statements and related SCS-C03 exam topics are for the fourth Exam Domain of the AWS Certified Security Specialty, “Identity and Access Management.” The previous SCS-C02 exam included the same domain name and assigned it a 16% weighting. In the updated SCS-C03 exam, this domain has increased in emphasis and now represents 20% of the scored content. This domain focuses on designing, implementing, and troubleshooting authentication and authorization mechanisms that control access to AWS resources across human users, applications, and systems.
Task 4.1: Design, implement, and troubleshoot authentication strategies.
-
Skill 4.1.1: Design and establish identity solutions for human, application, and system authentication (for example, AWS IAM Identity Center, Amazon Cognito, multi-factor authentication [MFA], identity provider [IdP] integration).
-
Skill 4.1.2: Configure mechanisms to issue temporary credentials (for example, AWS Security Token Service [AWS STS], Amazon S3 presigned URLs).
-
Skill 4.1.3: Troubleshooting authentication issues (for example, CloudTrail, Amazon Cognito, IAM Identity Center permission sets, AWS Directory Service).
Task 4.2: Design, implement, and troubleshoot authorization strategies.
-
Skill 4.2.1: Design and evaluate authorization controls for human, application, and system access (for example, Amazon Verified Permissions, IAM paths, IAM Roles Anywhere, resource policies for cross-account access, IAM role trust policies).
-
Skill 4.2.2: Design attribute-based access control (ABAC) and role-based access control (RBAC) strategies (for example, by configuring resource access based on tags or attributes).
-
Skill 4.2.3: Design, interpret, and implement IAM policies by following the principle of least privilege (for example, permission boundaries, session policies).
-
Skill 4.2.4: Analyze authorization failures to determine causes or effects (for example, IAM Policy Simulator, IAM Access Analyzer).
-
Skill 4.2.5: Investigate and correct unintended permissions, authorizations, or privileges granted to a resource, service, or entity (for example, IAM Access Analyzer).
SCS-C03 Domain 5: Data Protection
The following task statements and related SCS-C02 exam topics are for the fifth Exam Domain of the AWS Certified Security Specialty called “Data Protection.” This domain emphasizes the design and implementation of controls to protect data, both at rest and in transit. You will be required to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and compliance with security policies.
Task 5.1: Design and implement controls for data in transit.
- Skill 5.1.1: Design and configure mechanisms to require encryption when connecting to connect to resources (for example, by configuring Elastic Load Balancing [ELB] security policies, by enforcing TLS configurations).
- Skill 5.1.2: Design and configure mechanisms for secure and private access to resources (for example, AWS PrivateLink, VPC endpoints, AWS Client VPN, AWS Verified Access).
- Skill 5.1.3: Design and configure inter-resource encryption in transit (for example, inter-node encryption configurations for Amazon EMR, Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service [Amazon EKS], SageMaker AI, Nitro encryption).
Task 5.2: Design and implement controls for data at rest.
-
Skill 5.2.1: Design, implement, and configure data encryption at rest based on specific requirements (for example, by selecting the appropriate encryption key service such as AWS CloudHSM or AWS Key Management Service [AWS KMS] or by selecting the appropriate encryption type such as client-side encryption or server-side encryption).
-
Skill 5.2.2: Design and configure mechanisms to protect data integrity (for example, S3 Object Lock, S3 Glacier Vault Lock, versioning, digital code signing, file validation).
-
Skill 5.2.3: Design automatic lifecycle management and retention solutions for data (for example, S3 Lifecycle policies, S3 Object Lock, Amazon Elastic File System [Amazon EFS] Lifecycle policies, Amazon FSx for Lustre backup policies).
-
Skill 5.2.4: Design and configure secure data replication and backup solutions (for example, Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager, AWS Backup, ransomware protection, AWS DataSync).
Task 5.3: Design and implement controls to protect confidential data, credentials, secrets, and cryptographic key materials.
-
Skill 5.3.1: Design management and rotation of credentials and secrets (for example, AWS Secrets Manager).
-
Skill 5.3.2: Manage and use imported key material (for example, by managing and rotating imported key material, by managing and configuring external key stores).
-
Skill 5.3.3: Describe the differences between imported key material and AWS-generated key material.
-
Skill 5.3.4: Mask sensitive data (for example, CloudWatch Logs data protection policies, Amazon Simple Notification Service [Amazon SNS] message data protection).
-
Skill 5.3.5: Create and manage encryption keys and certificates across a single AWS Region or multiple Regions (for example, AWS KMS customer-managed AWS KMS keys, AWS Private Certificate Authority).
SCS-C03 Domain 6: Security Foundations & Governance
Finally, here are the task statements and related SCS-C02 exam topics for the sixth and final Exam Domain of the AWS Certified Security Specialty, “Security Foundations & Governance.” In the previous SCS-C02 version, this domain appeared under the name “Management and Security Governance.” In SCS-C03, the domain has been updated and expanded to more clearly emphasize governance, organizational controls, compliance evaluation, and the management of security at scale across multi-account AWS environments.
Task 6.1: Develop a strategy to centrally deploy and manage AWS accounts.
-
Skill 6.1.1: Deploy and configure organizations by using AWS Organizations.
-
Skill 6.1.2: Implement and manage AWS Control Tower in new and existing environments, and deploy optional and custom controls.
-
Skill 6.1.3: Implement organization policies to manage permissions (for example, SCPs, RCPs, AI service opt-out policies, declarative policies).
-
Skill 6.1.4: Centrally manage security services (for example, delegated administrator accounts).
-
Skill 6.1.5: Manage AWS account root user credentials (for example, by centralizing root access for member accounts, managing MFA, designing break glass procedures).
Task 6.2: Implement a secure and consistent deployment strategy for cloud resources.
-
Skill 6.2.1: Use infrastructure as code (IaC) to deploy cloud resources consistently and securely across accounts (for example, CloudFormation stack sets, third-party IaC tools, CloudFormation Guard, cfn-lint).
-
Skill 6.2.2: Use tags to organize AWS resources into groups for management (for example, by grouping by department, cost center, environment).
-
Skill 6.2.3: Deploy and enforce policies and configurations from a central source (for example, AWS Firewall Manager).
-
Skill 6.2.4: Securely share resources across AWS accounts (for example, AWS Service Catalog, AWS Resource Access Manager [AWS RAM]).
-
Task 6.3: Evaluate the compliance of AWS resources.
-
Skill 6.3.1: Create or enable rules to detect and remediate noncompliant AWS resources and to send notifications (for example, by using AWS Config to aggregate alerts and remediate non-compliant resources, Security Hub).
-
Skill 6.3.2: Use AWS audit services to collect and organize evidence (for example, AWS Audit Manager, AWS Artifact).
-
Skill 6.3.3: Use AWS services to evaluate architecture for compliance with AWS security best practices (for example, AWS Well-Architected Framework tool).
Which AWS services are NOT included in the SCS-C03 exam?
This list is not exhaustive and serves only as a general overview of AWS services and features not covered on the SCS-C03 exam. However, it can give you an idea of the services you do not need to focus on for the AWS Certified Security Specialty exam.
-
Application Integration:
-
Amazon Managed Workflows for Apache Airflow (Amazon MWAA)
-
-
Security, Identity, and Compliance:
-
AWS Payment Cryptography
-