Last updated on November 10, 2025
AWS Disaster Recovery Cheat Sheet
- RTO (Recovery Time Objective) is the time it takes after a disruption to restore a business process to its service level.
- In simpler terms: “How long can we afford to be down?”
- RPO (Recovery Point Objective) is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time before the disaster occurs.
- In simpler terms: “How much data can we afford to lose?”
Disaster Recovery With AWS
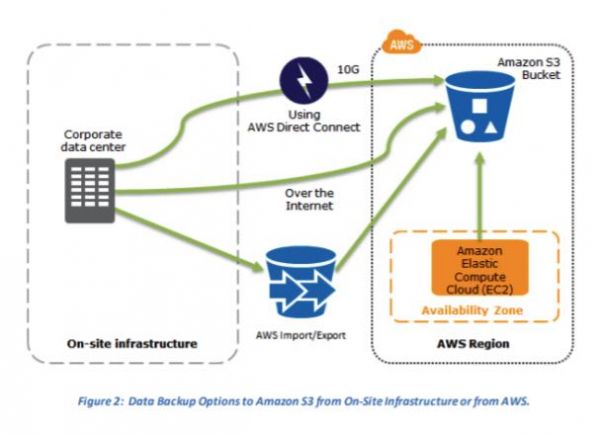
Backup and Restore – Storing backup data on S3 and recovering data quickly and reliably.
- This method is the most cost-effective Disaster Risk strategy but has the longest RTO/RPO.
- Modern Services: AWS Backup is a fully managed service that centralizes and automates data backup across AWS services (such as EBS, RDS, DynamoDB, and S3) and on-premises environments. Backups can be copied across regions for protection.
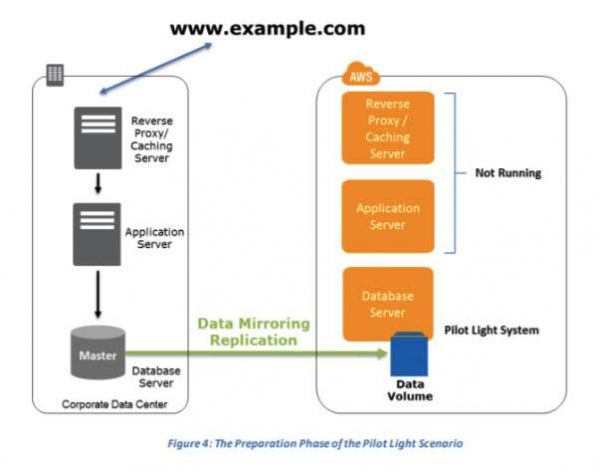
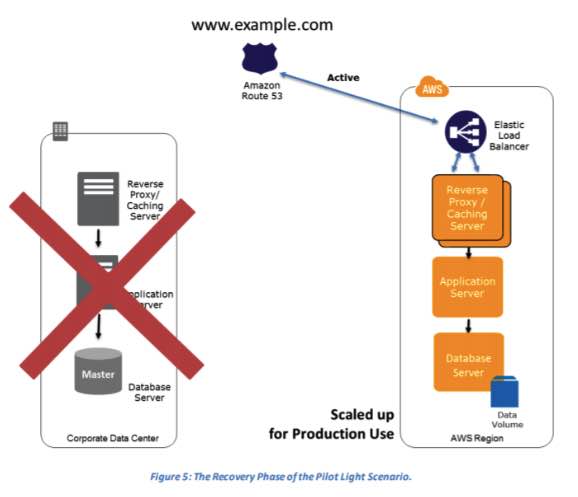
Pilot Light for Quick Recovery into AWS – This approach offers a quicker recovery time than backup and restore, as core system components are already running and continually kept up to date.
- How it works: Core infrastructure (like databases) is kept running in the DR region, while application servers are turned off. In a disaster, the application servers are quickly launched (e.g., from a pre-built AMI) and traffic is routed.
- Modern services, such as Amazon RDS Read Replicas or Amazon Aurora Global Databases, can serve as the “pilot light” database, ready for promotion and scaling.
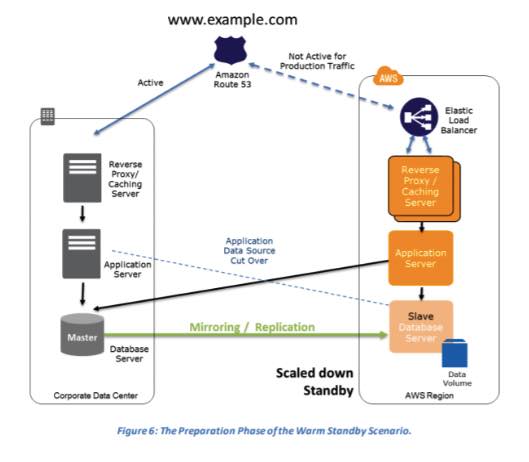
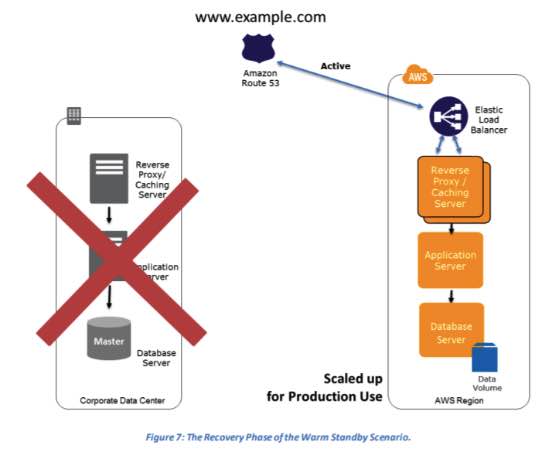
Warm Standby Solution – A scaled-down version of a fully functional environment is always running in the cloud.
- How it works: This strategy runs a minimal version of your production environment (e.g., one EC2 instance instead of ten). During a disaster, this environment is scaled up using services like Auto Scaling, and Route 53 fails over traffic to it.
- Provides a faster RTO (minutes) than Pilot Light.
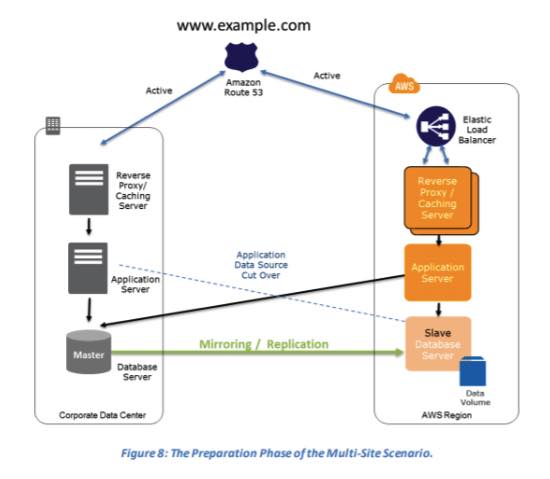
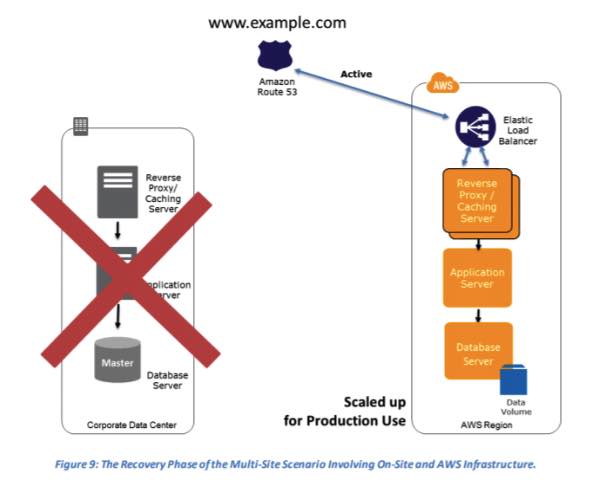
Multi-Site Solution – Run your infrastructure on another site in an active-active configuration.
- How it works: This is the most resilient (and most expensive) strategy. It runs a full-scale production environment in two or more AWS Regions, with traffic load-balanced between them.
- If one region fails, traffic is directed to the other healthy regions.
- Modern Services: This strategy leverages services designed for global distribution, including Amazon DynamoDB Global Tables, Amazon Aurora Global Databases, and AWS Global Accelerator.
-
- AWS Production to an AWS DR Solution Using Multiple AWS Regions – take advantage of AWS’ multiple availability zones
Services
- S3 as a destination for backup data that might be needed quickly to perform a restore.
- Import/Export for transferring very large data sets by shipping storage devices directly to AWS.
- Glacier for longer-term data storage where retrieval times of several hours are adequate.
- Server Migration Service for performing agentless server migrations from on-premises to AWS.
- Database Migration Service and Schema Conversion Tool for moving databases from on-premises to AWS and automatically converting SQL schema from one engine to another.
- Storage Gateway copies snapshots of your on-premises data volumes to S3 for backup. You can create local volumes or EBS volumes from these snapshots.
- Preconfigured servers bundled as Amazon Machine Images (AMIs).
- Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) for distributing traffic to multiple instances.
- Route 53 for routing production traffic to different sites that deliver the same application or service.
- Elastic IP address for static IP addresses.
- Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) for provisioning a private, isolated section of the AWS cloud.
- Direct Connect for a dedicated network connection from your premises to AWS.
- Relational Database Service (RDS) for scale of a relational database in the cloud.
- DynamoDB for a fully managed NoSQL database service to store and retrieve any amount of data and serve any level of request traffic.
- Redshift for a petabyte-scale data warehouse service that analyzes all your data using existing business intelligence tools.
- CloudFormation for creating a collection of related AWS resources and provision them in an orderly and predictable fashion.
- Elastic Beanstalk is a service for deploying and scaling web applications and services developed.
- OpsWorks is an application management service for deploying and operating applications of all types and sizes.
AWS Disaster Recovery Cheat Sheet Reference:
https://www.slideshare.net/AmazonWebServices/disaster-recovery-options-with-aws