AWS Fault Injection Service Cheat Sheet
A fully managed chaos engineering service that help you improve the resilience and performance of your AWS applications by injecting controlled faults into your environment.
It allows you to simulate real-world failures such as instance interruptions, pod crashes, network issues, and service throttling.
Features
- No infrastructure maintenance required as it is a managed chaos engineering platform.
- Provides pre-built fault actions for EC2, EKS, ECS, RDS, DynamoDB, EBS, ELB, and many others.
- Uses experiment templates for repeatable, automated resilience tests.
- Supports tag-based targeting and granular resource selection.
- Has built-in guardrails: stop conditions, minimum/maximum duration, and controlled blast radius.
- Integrates with Amazon CloudWatch, CloudTrail, IAM, EventBridge, and Systems Manager.
- You can create custom fault actions via SSM Automation or SSM commands.
Key Concepts
- Experiment: A single run of a chaos test. Specifies the actions, targets, stop conditions, and duration.
- Experiment Template: A reusable configuration that defines how faults are injected. Can be version-controlled and automated.
- Actions
- Defines the fault to be injected. Such as:
- Stopping or rebooting EC2 instances
- Inducing CPU/memory stress on EC2/EKS/ECS
- Killing ECS tasks or Kubernetes pods
- Adding network latency, packet loss, or blackhole traffic
- Triggering RDS failover
- Throttling DynamoDB
- Injecting EBS I/O latency or volume degradation
- Defines the fault to be injected. Such as:
- Targets
- Specifies the AWS resources affected by actions. Can be defined using:
- Tags (most common)
- ARNs
- Resource property filters
- Specifies the AWS resources affected by actions. Can be defined using:
- Stop Conditions
- CloudWatch Alarms that automatically halt experiments when thresholds are breached. Prevents uncontrolled failures.
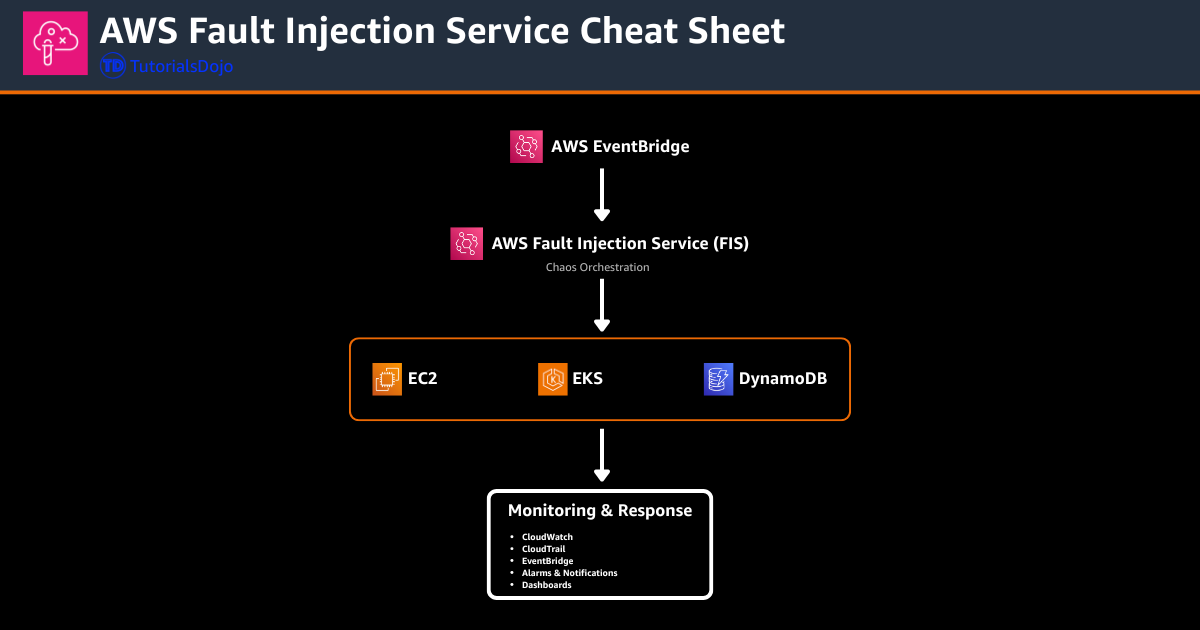
Example High-Level Architecture Diagram
Experiment Structure Overview
- Actions: The specific faults to be injected (e.g., reboot instance, kill pod, add network delay).
- Targets: The selected AWS resources identified by tags, ARNs, or filters.
- Stop Conditions: CloudWatch alarms that halt the experiment if system health declines too far.
- Duration & Timing: Defines how long the fault occurs and ensures controlled test windows.
- Experiment Templates: A reusable definition that packages all actions, targets, and guardrails into a single configuration.
Monitoring & Observability
- CloudWatch provides real-time metrics to observe system degradation and recovery during experiments.
- CloudTrail logs all experiment runs, template changes, and user actions for auditing.
- EventBridge can trigger notifications, automate workflows, or start follow-up tests after an experiment completes.
- Logs and experiment output can be routed to S3, CloudWatch Logs, or third-party monitoring tools.
- Alarms tied to stop conditions ensure observability-driven safety mechanisms.
Best Practices
- Use tags to precisely control which resources can be targeted by FIS.
- Always include stop conditions based on meaningful health metrics.
- Start with a small blast radius and expand gradually.
- Run experiments first in staging before applying them in production.
- Version your experiment templates for repeatability and rollback.
- Combine FIS with Auto Scaling, load balancers, and multi-AZ setups for meaningful resilience tests.
Security
- IAM policies controls access, determining who can create or run experiments.
- Supports resource-level permissions to restrict which AWS resources FIS can target.
- All FIS activity is logged in CloudTrail.
- Includes built-in safety controls: time limits, stop conditions, and controlled targeting.
- Logs and sensitive data can be encrypted using AWS KMS.
Pricing
- An experiment charges per minute that it runs
- Based on the specific fault actions used, pricing varies
- No charge for creating or storing experiment templates
- No charge for canceled or failed experiment runs
- AWS resources affected by the experiment incurs cost
References
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/fis/latest/userguide/what-is.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/fis/latest/userguide/fis-actions-reference.html
https://aws.amazon.com/fis/faqs/