AWS Strands Agents Cheat Sheet
- AWS Strands Agents is an open-source SDK that enables developers to build, test, and deploy AI agents by simply defining a prompt and a list of tools in code. True to its name, inspired by the two strands of DNA, Strands connects the agent’s two core components: the Model and the Tools.
- The framework uses the model’s advanced reasoning capabilities to plan the agent’s next steps and execute tools autonomously. It scales effortlessly from simple local prototypes to complex, cloud-deployed agent systems, offering deep customization for advanced use cases.
Key Features of Strands Agents
-
Foundation-Driven Intelligence:
- Built on the principle that the Foundation Model (FM) acts as the primary engine for decision-making, driving autonomous planning rather than following rigid, pre-scripted paths.
-
Standardized Tooling Protocol:
- Native support for the Model Context Protocol (MCP) ensures a consistent, portable way to connect LLMs with external data and tools.
-
Native AWS Ecosystem:
- Provides deep, out-of-the-box connectivity with Amazon Bedrock, AWS Lambda, and AWS Step Functions, enabling the creation of comprehensive autonomous workflows entirely within AWS.
-
Flexible Model Selection:
- Offers the freedom to choose from a wide range of models, including Anthropic Claude and the Amazon Nova family on Amazon Bedrock, allowing optimization for specific reasoning tasks.
-
LLM API integration:
- Designed to support multiple LLM interfaces, such as Amazon Bedrock and OpenAI, making it effortless to switch providers for production deployments.
-
Multi-Format Processing:
- Natively handles diverse data inputs, including text, speech, and images, creating richer and more natural agent interactions.
-
Extensible Tool Library:
- Includes a robust set of pre-built tools for AWS services while allowing developers to easily plug in custom tools to expand agent capabilities.
Use Cases
- AWS-Native Workflows:
- For organizations that need seamless integration with AWS services to automate tasks.
- Enterprise Production:
- For teams requiring robust security, scalability, and compliance in their autonomous systems.
- Model Flexibility:
- For projects needing to choose or switch between multiple foundation models for specialized needs.
- Complex Orchestration:
- For scenarios involving intricate coordination with AWS resources to automate multi-step processes.
Implementation Approach for Strands Agents
- Select your foundation model on Amazon Bedrock, such as Amazon Nova (Premier, Pro, Lite, or Micro), based on your business needs.
- Define custom tools that connect to enterprise systems and data sources.
- Create prompts that outline the agent’s persona, tasks, and behavioral rules.
- Enable agents to process multiple modalities, including text, images, and speech.
- Deploy agents that can autonomously respond to business queries and perform tasks.
Real World Examples of Strands Agents
- AWS teams deploy Strands Agents in production environments, such as with the VPC Reachability Analyzer.
- In this scenario, Strands autonomously diagnoses complex network connectivity issues in AWS VPCs. By leveraging tools to inspect security groups, route tables, and network ACLs, the agent identifies root causes and recommends remediation—demonstrating Strands’ ability to perform secure, multi-step reasoning and automated problem solving without human intervention.
Agents
-
Agents:
-
The primary abstraction encapsulating the model, tools, and instructions.
-
-
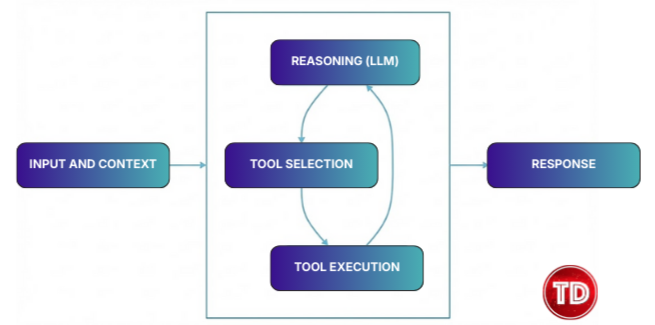
Agent Loop:
- The internal cycle (Think → Act → Observe) where the agent processes input, decides on tools, executes actions, and refines its response.
-
-
- At its core, the agent loop works as follows:
- Receives user input and context
- Processes input with a language model (LLM)
- Determines whether to use tools to access external data or perform actions
- Executes tools and gathers results
- Reasons for new information
- Produces a final response or repeats the cycle as needed
- The agent loop can be executed multiple times within a single interaction, enabling complex, multi-step reasoning and fully autonomous task execution.
- At its core, the agent loop works as follows:
-
-
State:
- Strands agents maintain state in several forms:
-
Conversation History: The sequence of messages between the user and the agent.
-
Agent State: Stateful information outside of conversation context, maintained across multiple requests.
- Request State: Contextual information maintained within a single request.
-
- Strands agents maintain state in several forms:
-
Session Management:
- Mechanisms to handle long-running interactions and persist state across different user sessions.
-
Prompts:
- System Prompts: System prompts set clear guidance for the model’s role, capabilities, and behavioral boundaries, establishing how it should act throughout the conversation. Effective system prompts are essential for shaping model responses and ensuring consistent, reliable behavior.
-
Structured Output:
- Structured output constrains model responses to a defined schema (e.g., Pydantic), ensuring outputs are always properly formatted and type-safe—eliminating the need for manual parsing or validation.
-
Conversation Management:
- Conversation management in the SDK is handled by the
ConversationManagerinterface, which lets you define strategies for storing and reducing conversation history. Implementapply_managementto manage history after each loop, andreduce_contextto trim history when the model’s context window is exceeded.
- Conversation management in the SDK is handled by the
Tools
-
Tools:
- Functions or APIs the agent invokes to perform actions.
-
Model Context Protocol (MCP):
- An open protocol that lets agents securely connect to external tools, services, and other agents. MCP enables seamless communication and the expansion of capabilities for Strands Agents.
Model Providers
- Amazon Bedrock
- Anthropic
- LiteLLM
- LlamaAPI
- Ollama
- OpenAI
- Custom Providers:
- The Strands Agents SDK supports custom model providers, enabling you to integrate private or specialized LLMs into your agent workflows.
Streaming
-
Streaming:
- Delivers tokens as they are generated to reduce perceived latency.
-
Async Iterators:
- Use
stream_asyncfor real-time streaming of agent responses in async environments (like web servers or APIs).
- Use
-
Callback Handlers:
- Intercept and process events during agent execution for real-time monitoring, custom output, or system integration.
Multi-Agent
-
Agent2Agent (A2A):
- Protocol for agents to send messages or delegate tasks to each other.
-
Agents as Tools:
- Specialized agents are wrapped as callable tools, allowing an orchestrator agent to delegate domain-specific tasks to them. This enables modular, hierarchical workflows where agents can call other agents as needed.
-
Multi-Agent Systems and Swarm Intelligence:
- An agent swarm is a collection of autonomous AI agents that collaborate to solve complex problems.
-
Graph:
- An agent graph is a network of specialized AI agents that collaborate on complex tasks, each serving a unique function and communicating through defined pathways.
-
Workflow:
- An agent workflow coordinates tasks across multiple specialized AI agents, assigning each agent a defined role within a sequence. This approach breaks down complex problems, manages dependencies, and ensures reliable execution for multi-step processes.
Safety & Security
-
Responsible AI:
- Safeguards and best practices for ethical, transparent, and safe AI operation. Learn more about Responsible AI here: Responsible AI
-
Guardrails:
- Define boundaries for AI behavior and content generation to help prevent harmful outputs. Integrated with Amazon Bedrock Guardrails for robust content filtering.
-
Prompt Engineering:
- Essential for optimizing Strands Agents and protecting against LLM-related security risks.
-
PII Redaction:
- Automated detection and redaction of sensitive data.
Observability & Evaluation
-
Observability:
- Track system behavior and performance to monitor and troubleshoot.
-
Metrics:
- Monitor key data such as tokens, latency, and errors to evaluate agent performance and optimize resource usage.
-
Traces:
- Detailed execution paths of model and tool calls.
-
Logs
-
Strands SDK uses Python’s standard
loggingmodule to help monitor and debug agent operations.
-
-
Evaluation:
-
Assess agent performance and progress to maintain quality and drive continual improvement.
-
Strands Agents vs. Strands Agents SOPs
- Strands Agents (SDK):
- A code-first Python library for developers needing full programmatic control.
- Strands Agents SOPs:
- A configuration-driven tool using natural language “Standard Operating Procedures” for strict workflow adherence.
- For more information, see the AWS Strands Agent SOPs.
Pricing
- Strands Agents is free and open-source. Costs are incurred for:
- Model Inference: Token usage from providers (e.g., Amazon Bedrock).
- Infrastructure: AWS compute (Lambda, EC2) and storage used to run agents.
AWS Strands Agents Cheat Sheet References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/prescriptive-guidance/latest/agentic-ai-frameworks/strands-agents.html
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/opensource/introducing-strands-agents-an-open-source-ai-agents-sdk/