GitHub Models Cheat Sheet
GitHub Models is a comprehensive suite of developer tools designed to lower the barrier to enterprise-grade AI adoption. It embeds AI development directly into familiar GitHub workflows, helping developers move beyond isolated experimentation. The platform provides tools to test large language models (LLMs), refine prompts, evaluate outputs, and make data-driven decisions using structured metrics—all without requiring separate API keys or complex authentication.
Current Status: GitHub Models for organizations and repositories are in public preview and subject to change. The service is designed for learning, experimentation, and proof-of-concept activities with built-in rate limiting to ensure fair access across all users.
Core Purpose and Capabilities
GitHub Models serves as a workspace where developers can experiment with AI model capabilities through interactive testing and evaluation. Users build understanding by adjusting model settings and sending prompts through an intuitive chat interface, and can also interact directly with models via SDKs when ready for integration.
The platform bridges the gap between initial experimentation and production deployment by providing:
- Model Catalog Access –Free experimentation with industry-leading models from OpenAI, Meta, Mistral, Microsoft, and DeepSeek.
- Prompt Management – Version-controlled prompt storage as
.prompt.ymlfiles in repositories. - Quantitative Evaluations –Structured metrics to compare model performance objectively.
- Seamless Integration – Direct connection to GitHub Actions, SDKs, and REST API for production use.
When interacting with any AI model, users should remember they are experimenting with AI technology, where mistakes in content are possible. GitHub Models is explicitly designed to allow for learning, experimentation, and proof-of-concept activities. The feature is subject to various limits, including requests per minute, requests per day, tokens per request, and concurrent requests, and is not designed for production use cases without upgrading to paid tiers.
Key Features of GitHub Models
Prompt Development
GitHub Models provides a structured editor that supports system instructions, test inputs, and variable configuration. Developers start their AI development directly in this editor, defining how models should behave and testing various scenarios. The editor allows for sophisticated prompt engineering with support for multi-turn conversations and dynamic variable substitution using the {{variable_name}} syntax.
Model Comparison
The platform enables side-by-side testing of multiple models with identical prompts and inputs. This comparison capability is essential for understanding how different models respond to the same queries, allowing developers to evaluate trade-offs between quality, speed, cost, and capabilities before committing to a specific model.
Built-in Evaluators
GitHub Models includes sophisticated scoring metrics to analyze outputs and track performance across multiple dimensions:
- Similarity: Measures how closely model output matches expected or reference answers (0-1 scale, higher is better)
- Fluency: Evaluates linguistic quality including grammar, coherence, and readability
- Coherence: Measures logical flow and consistency within responses
- Relevance: Checks whether responses actually address the original query
- Groundedness: Validates factual accuracy against source material
- String Check: Custom string matching with options for startsWith, endsWith, contains, and equals
- Custom LLM-as-Judge: Use another LLM to evaluate outputs based on custom criteria
Prompt Configurations
All prompt, model, and parameter settings can be saved as .prompt.yml files within repositories. This approach enables review, collaboration, and reproducibility across teams. Each prompt file can include the model identifier, configuration parameters, system and user messages, test data with expected outputs, and evaluator definitions for automated quality assessment.
Production Integration
Once prompts are refined and tested, developers can use their saved configurations to build AI features through multiple integration paths. The GitHub Models REST API provides programmatic access for automation and enterprise workflows. SDKs are available for multiple languages, and GitHub Actions can be leveraged to incorporate AI capabilities directly into CI/CD pipelines.
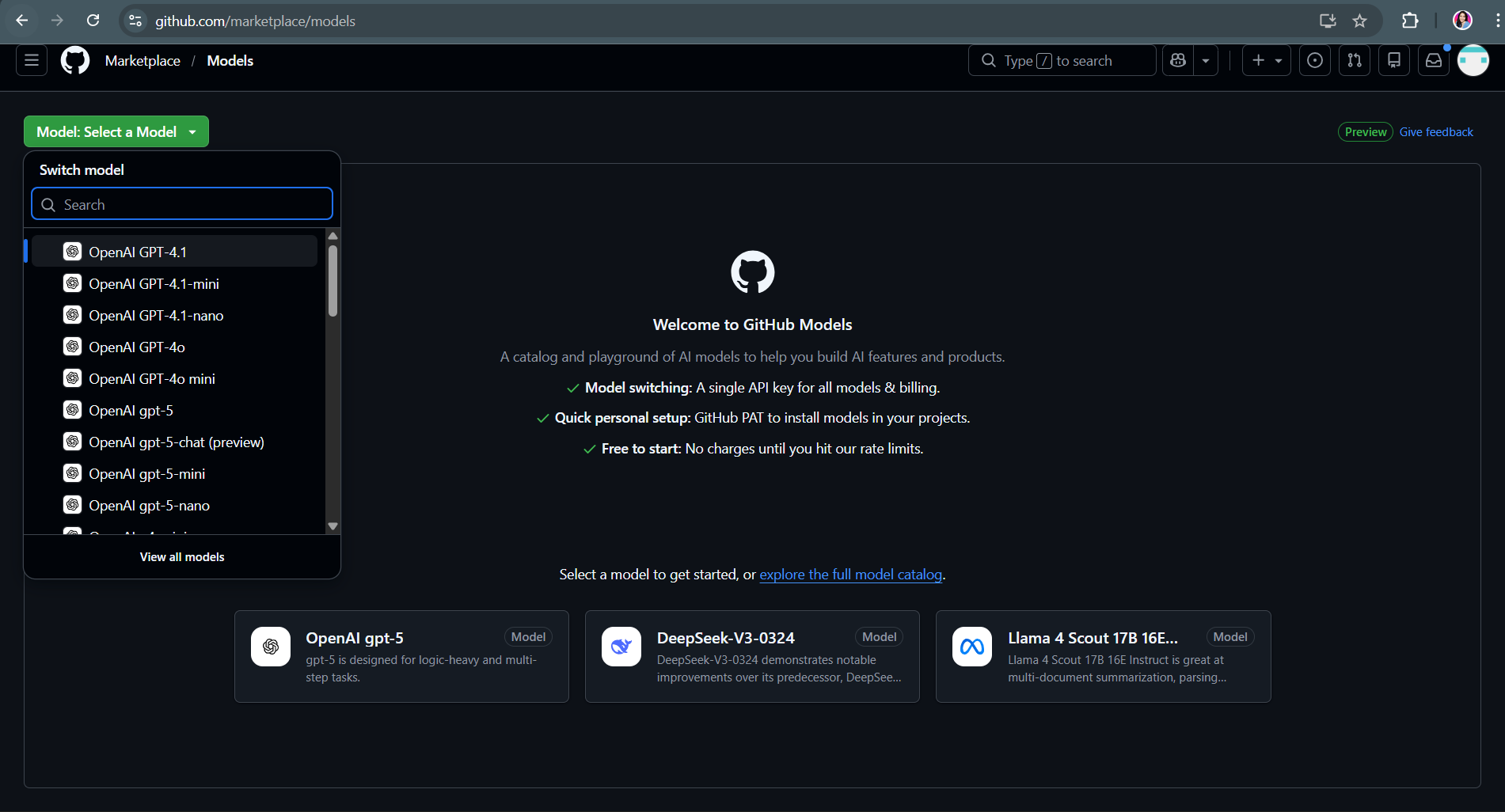
The Playground
The Playground is a free, interactive resource that lets developers adjust model parameters and submit prompts to see how models respond in real time. It’s ideal for early experimentation, helping users understand a model’s behavior, capabilities, and response style without writing any code. Access requires only a GitHub account—no API keys, no setup, and no configuration files needed.
Accessing the Playground
Developers can access the Playground by navigating to github.com/marketplace/models and selecting a model from the dropdown menu. Alternatively, they can click “View all models” to browse the complete catalog in GitHub Marketplace, then click the Playground button on any model card to begin testing immediately.
Playground Capabilities
The Playground supports several key activities:
- Interactive Testing: Type prompts and receive immediate responses in a chat-style interface
- Parameter Adjustment: Modify temperature, max tokens, top_p, and other model-specific settings to see how they affect outputs
- Side-by-Side Comparison: Test two models simultaneously with mirrored prompts to evaluate differences in quality and performance
- Code Generation: Switch to the Code tab to get production-ready code snippets in various programming languages
- Preset Management: Save and share configurations including parameters, prompts, and chat history for reproducible experiments
Rate Limiting in the Playground
The Playground is rate-limited to ensure fair access for all users. Limits are enforced on requests per minute, requests per day, tokens per request, and concurrent requests. When rate limits are reached, users must wait for the limit to reset before making additional requests. These limits vary by model type, with low and high models having different thresholds, while embedding models have a single threshold.
Prompt Management and Version Control
Storing Prompts in Repositories
GitHub Models enables developers to store prompts as YAML files with the .prompt.yml or .prompt.yaml extension. These files can be located anywhere in the repository and contain all necessary configuration including the model identifier, parameters, messages, test data, and evaluators. This approach integrates AI development into standard GitHub workflows, making prompts first-class citizens in version control.
Benefits of Prompt Version Control
Storing prompts in repositories provides several significant advantages:
- Change Tracking – Every modification to prompts is tracked through Git commits, providing a complete history of what changed, when, and why.
- Collaboration – Team members can review and discuss prompt changes through pull requests before merging to production.
- Reproducibility – Anyone can check out a specific prompt version and reproduce the exact model behavior.
- Consistency – Organizations can establish prompt libraries and enforce standards through review processes.
- Integration – Prompts stored in repositories are automatically available in the prompt editor and evaluation tooling.
Prompt File Structure
Each prompt file follows a standardized YAML structure that includes:
- name – Descriptive identifier for the prompt.
- description – Explanation of what the prompt does.
- model – Identifier for the AI model (e.g.,
openai/gpt-4o-mini). - modelParameters – Configuration settings like temperature, max_tokens.
- messages – Array of role-based messages (system, user, assistant) that define the conversation.
- testData – Optional test cases with inputs and expected outputs.
- evaluators – Optional automated checks to validate prompt performance.
Using Variables in Prompts
Prompts can include dynamic variables using double curly brace syntax {{variable_name}}. This allows the creation of reusable templates that substitute specific values at runtime. Variables can appear in both system and user messages, enabling flexible prompt designs that adapt to different contexts without requiring multiple hardcoded versions.
Evaluation and Testing
The Comparisons View
GitHub Models provides a Comparisons view designed for structured evaluation of multiple prompt configurations across different models. In this view, each row represents a test case with specific input and expected output, while each column represents a different prompt configuration. This grid layout enables systematic comparison of how various models or prompt styles perform against the same test data.
Creating and Running Evaluations
Developers use the Comparisons view by adding rows of test data that represent realistic use cases for their application. Each test case includes an input that simulates real user queries and an expected output that represents the ideal response. After defining test cases, developers can add multiple prompt columns to compare different models or prompt variations side by side. Running the evaluation processes on all test cases across all configurations and displays results with evaluator scores.
Command Line Evaluation
For developers who prefer terminal workflows or need to integrate evaluations into CI/CD pipelines, GitHub Models supports command-line evaluation through the gh models eval command. This command uses the same evaluators as the web UI—including string match, similarity, and custom LLM-as-judge evaluators—allowing developers to test their .prompt.yml files locally or in automated pipelines.
Evaluation Metrics
GitHub Models helps developers optimize their prompts and model selection by tracking key metrics during evaluation:
- Latency: Response time from submission to completion, critical for user-facing applications
- Token Usage: Input and output token counts, which directly affect API costs
- Quality Scores: Numerical ratings from evaluators measuring aspects like similarity and relevance
- Pass/Fail Status: Binary results from string check or custom evaluators
Refining Based on Results
Model behavior can vary widely based on prompt phrasing, input characteristics, or parameter configuration. GitHub Models helps developers test and compare multiple LLMs across realistic use cases, optimize prompt phrasing and parameters, and evaluate outputs using structured, repeatable metrics. The evaluation workflow is designed to be iterative—developers run tests, identify areas for improvement, refine their prompts or parameters, and run tests again to measure progress.
Enterprise and Organization Features
Centralized Model Management
GitHub Models allows enterprises to maintain control over which AI models and providers are available to developers across the organization. This centralized approach ensures consistency, simplifies onboarding, and makes it easier to enforce compliance requirements. Organization owners can enable or disable GitHub Models, specify which models or publishers are allowed, and integrate custom models using their own API keys.
Enabling GitHub Models in Organizations
For organizations to use GitHub Models, an enterprise owner must first enable the feature at the enterprise level. After enterprise approval, organization owners can configure specific settings including access permissions and model availability. This two-tier authorization ensures appropriate governance while giving organizations flexibility in implementation.
Model Access Control
Organizations can choose from several permission models:
- All Publishers – Default option allowing models from all current and future publishers in the GitHub Models catalog
- Only Select Models – Allows definition of specific enabled or disabled lists of models and publishers
- Custom Combinations – Organizations can specify both enabled and disabled lists for fine-grained control
Limiting available models helps control spending, meet governance requirements, and prevent teams from inadvertently using models that don’t meet organizational standards.
Custom Model Integration (BYOK)
Organization owners can integrate their preferred external LLMs by providing their own API keys (BYOK). This capability gives organizations greater flexibility and control over available models while keeping aligned with existing payment methods, credits, and provider relationships. When using BYOK, billing and usage are managed directly through the provider account, such as an Azure Subscription ID.
Governance and Compliance
GitHub Models provides comprehensive governance features for enterprises:
- Usage Monitoring – Track model usage across the organization to understand consumption patterns.
- Compliance Controls – Ensure all AI usage complies with regulatory requirements such as GDPR, SOC 2, and ISO 27001.
- Audit Logs – Maintain records of who accessed or modified models and prompts for accountability.
- Data Persistence Control – Specify policies around whether prompts and outputs should be logged.
- Change Management – All prompt and model changes go through standard Git commit and pull request workflows.
Security-Focused Architecture
A critical feature for enterprise adoption is GitHub Models’ security architecture. All data remains within GitHub and Azure infrastructure and is not shared with model providers. This ensures sensitive business information, proprietary code, and confidential data stay protected within the organization’s security perimeter.
Cost Optimization at Scale
As adoption of AI-powered applications grows, enterprises need tools to manage costs effectively. GitHub Models helps organizations evaluate the cost and performance of different models and model updates, select the most cost-effective options, and manage expenses as usage scales across multiple teams. By limiting access to expensive models and monitoring consumption, organizations can avoid unexpected costs while still providing developers with powerful AI capabilities.
Collaboration Through Standard Workflows
Development teams can share prompts and results using standard GitHub development practices. As teams create effective prompts, they save them as YAML files and share them for review using pull requests. Committed prompts are accessible to other teams and workflows and can be kept consistent with company standards. This version-control approach ensures everyone knows when and why prompts change, making it easy to collaborate and maintain quality over time.
API and SDK Integration
GitHub Models REST API
The platform provides a REST API for programmatic access to all features. Organizations can use this API to automate and integrate with enterprise workflows, manage and update organization settings across multiple teams, list and retrieve prompts for monitoring and auditing, and run model inference requests with specific parameters.
SDK Support
GitHub Models supports the Azure AI Inference SDK as the recommended option for developers who want to easily switch between models. Some models also support additional SDKs for more specialized use cases. The Azure AI Inference SDK provides a consistent interface across different model providers, reducing the code changes needed when experimenting with or switching models.
Authentication
For API usage, developers need a GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT) with the models scope. This token provides authentication for all API requests and enables higher rate limits compared to unauthenticated access. When using GitHub Actions, workflows can use the built-in GITHUB_TOKEN with appropriate permissions to make model inference requests.
Rate Limits and Scaling
Free Tier Limitations
The free rate limits in the Playground and API usage are intended to help users get started with experimentation. The service is subject to various limits, including:
- Requests per minute – Controls burst traffic
- Requests per day – Cumulative daily cap
- Tokens per request – Varies by model but typically restricted below the model’s theoretical maximum
- Concurrent requests – Limits on simultaneous API calls
Moving Beyond Free Limits
When ready to move beyond the free offering for experimentation, users have two options:
- Option 1 – Paid Usage for GitHub Models: Organizations can opt in to paid usage, accessing increased rate limits, larger context windows, and additional features. This option provides production-grade capabilities while maintaining the same familiar interface and integration points.
- Option 2 – Bring Your Own API Keys (BYOK): Organizations with existing OpenAI or Azure subscriptions can bring their own API keys to access custom models. This approach keeps billing and usage management directly through the provider account while leveraging GitHub Models’ interface and workflow integration.
Best Practices for Organizations
Review Available Models
Before rolling out GitHub Models, organizations should review and compare available AI models against company governance, data security, and compliance requirements. This review can be done in any Models-enabled repository or through the GitHub Models catalog in the Marketplace. Key considerations include:
- Governance and Security – Examine each model’s compliance with standards and regulations, ensure data is not persisted outside the organization unless explicitly logged with consent
- Model Performance – Run benchmark evaluations on internal datasets to assess reasoning, context retention, and hallucination rates
- Cost-Benefit Analysis – Compare token costs across models for typical workloads to understand total cost of ownership
- Capability Alignment – Verify models support required features like multimodal inputs, function calling, or specific context lengths
Prompt Development Workflow
Organizations should establish a systematic approach to prompt development:
- Experimentation Phase – Developers use the Playground and prompt editor to create and refine prompts in a non-production environment. The visual interface allows non-technical stakeholders to contribute alongside developers, democratizing AI development.
- Evaluation Phase – Teams use lightweight evaluation tools to compare results across common metrics such as latency, relevance, and groundedness. Custom evaluators can be created to ensure results meet specific organizational standards or contain required keywords.
- Review and Approval – As teams create effective prompts, they save them as YAML files and share them for review using pull requests. This ensures prompts go through the same quality checks and approval processes as code.
- Deployment – Once reviewed and merged, prompts become available to anyone in the repository. They can be called through APIs, used in GitHub Actions workflows, or integrated into applications through SDKs.
Leverage API for Automation
Organizations should leverage the GitHub Models REST API to manage resources efficiently across teams. This includes programmatically updating model access permissions and governance settings to ensure consistency and compliance, listing and retrieving prompts used by different teams to monitor usage and maintain best practices, and running inference requests with standardized parameters and configurations.
Responsible Use Guidelines
Understanding Limitations
GitHub Models is designed for learning, experimentation, and proof-of-concept activities. Users should remember that when interacting with any model, content mistakes are possible. The platform is not designed for production use cases without appropriate upgrades and safeguards.
Key Limitations to Consider
- Rate Limiting – The service is subject to various limits on requests per minute, per day, tokens per request, and concurrent requests
- Availability – As a public preview service, features and availability may change
- Content Accuracy – AI models can generate incorrect information, hallucinate facts, or produce biased content
- Scope – GitHub Models focuses on experimentation and development, not production deployment at scale
Best Practices for Responsible Use
Organizations and developers should:
- Validate Outputs: Always review and verify AI-generated content before using it in production or making decisions based on it
- Test Thoroughly: Use the evaluation tools to systematically test prompts across diverse inputs including edge cases
- Monitor Performance: Track metrics over time to identify degradation or unexpected behavior changes
- Provide Context: Give models sufficient context in system prompts to generate appropriate responses
- Respect Limits: Work within rate limits and upgrade to paid tiers when experimentation transitions to production
- Document Usage: Maintain records of which models and prompts are used where for troubleshooting and compliance
Data Handling
While GitHub Models maintains strong security practices (data remains within GitHub and Azure, not shared with model providers, not used for training), organizations should still implement their own data handling policies. This includes avoiding sending sensitive PII unless necessary, implementing client-side filtering for user inputs, using synthetic data in testing when possible, and maintaining compliance with relevant data protection regulations.
Model Catalog and Search
Browsing Available Models
GitHub Models provides access to a diverse catalog of AI models from multiple providers. Users can browse the catalog at github.com/marketplace?type=models and filter by various criteria including model name, publisher, programming language support, modality (text, image, etc.), and other characteristics.
Model Information
Each model in the catalog includes:
- README Tab – Comprehensive information about the model including capabilities, limitations, training data, and use cases
- Getting Started Tab – Instructions on how to use the model through SDKs or API
- Playground Access – Direct link to test the model interactively
- Rate Limit Information – Details about token limits and request constraints
- Model Type – Classification as low, high, or embedding model affecting rate limits
Searching and Filtering
The search functionality allows developers to quickly find models that meet specific requirements. Filters can be applied by publisher, capability, language support, or custom criteria. This helps teams narrow down options when evaluating which models to use for particular use cases.
Billing and Production Deployment
Free Tier for Prototyping
GitHub Models provides free access for prototyping and experimentation. This free tier includes access to the Playground, API usage with rate limits, and all evaluation and collaboration features. The goal is to remove financial barriers during the learning and development phase.
Transitioning to Production
When ready to bring applications to production, organizations should opt in to paid usage. This transition provides:
- Production-Grade Rate Limits – Significantly higher capacity to support real user traffic
- Larger Context Windows – Ability to process longer inputs and maintain more conversation history
- Additional Features – Access to advanced capabilities not available in the free tier
- SLA Guarantees – Service level agreements for availability and performance
- Support – Access to enterprise support channels
Integration with GitHub Environment
GitHub Actions Integration
GitHub Models integrates seamlessly with GitHub Actions, allowing developers to incorporate AI capabilities directly into CI/CD pipelines. Workflows can trigger model inference on events like issue creation, pull request submission, or scheduled intervals. Common use cases include automatically summarizing issues, generating documentation, analyzing code changes, and running prompt evaluations in continuous integration.
Repository Integration
By enabling GitHub Models in repository settings, teams gain access to the Models tab in their repository navigation. This tab provides access to the prompt editor, evaluation tools, and model catalog without leaving the repository context. All prompts stored as .prompt.yml files in the repository automatically appear in this interface.
Codespaces Integration
GitHub Models works with Codespaces to provide a zero-friction development environment. From the Playground, developers can click “Run codespace” to launch a cloud-based environment with pre-configured credentials and sample code. This eliminates local setup requirements and enables immediate experimentation.