Last updated on April 8, 2023
In this day and age, your site speed performance is an important factor when it comes to user experience. It is widely recommended for websites to have an average load time of 3 seconds as users tend to abandon the site if a page takes longer than 3 seconds to load. According to Amazon, just 100 milliseconds of extra load time cost them 1% in sales. Indeed, every second counts in our fast-paced digital world.
Amazon Web Services has always been the global leader in Cloud Computing with its speed, performance, and reliability. With its breadth of services, AWS gives us numerous solutions that we can take advantage of to make our businesses better.
In this article, we will be discussing the purpose and differences between Amazon CloudFront and AWS Global Accelerator. The common denominator with these two services is that they use Edge Locations and they are data centers with the main purpose of reducing latency. There are currently over 200 Edge Locations in the world that are situated strategically in major cities.
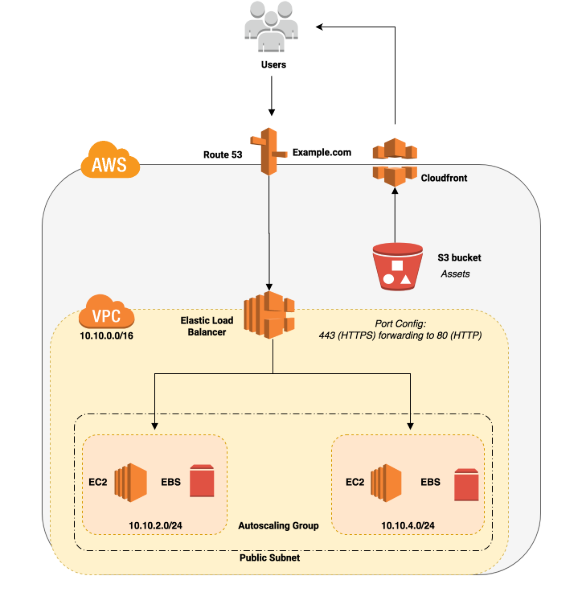
Amazon CloudFront is a Content Delivery Network (CDN) like Cloudflare and Akamai. CloudFront is used to deliver static assets (such as videos, images, and files) securely to various devices around the globe with low latency.
To put this into perspective, let us say you have a streaming website with thousands of videos in your repository. It is inefficient to serve these videos uniquely whenever a user requests for it as this will lead to high bandwidth requirements and high CPU/Memory/disk utilization, which in turn results in frequent downtimes, endless video buffering, and irritated users who are trying to load their favorite shows. Speeding up the website is as simple as offloading the videos, thumbnails, and any static assets from your server to Amazon S3, and using CloudFront to serve and cache these assets.
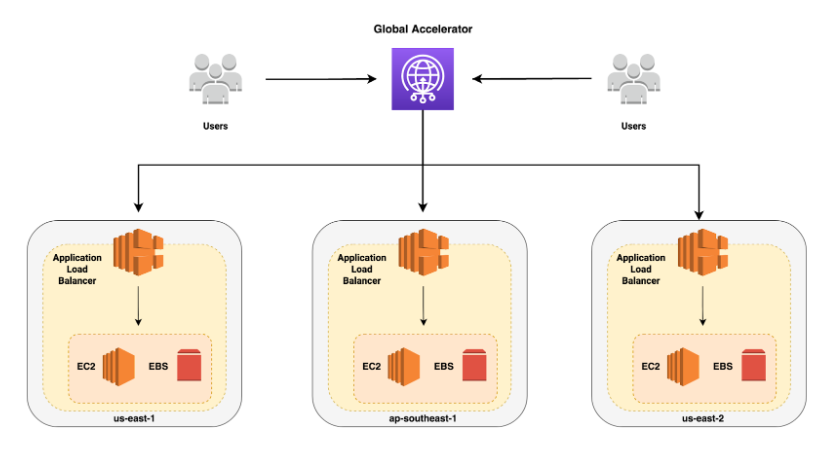
AWS Global Accelerator is a service that uses edge locations to look for the optimal pathway from your users to your applications.
For example, you have a banking application that is scattered through multiple AWS regions and low latency is a must. Global Accelerator will route the user to the nearest edge location then route it to the nearest regional endpoint where your applications are hosted.
The differences between CloudFront and Global Accelerator are:
- CloudFront uses multiple sets of dynamically changing IP addresses while Global Accelerator will provide you a set of static IP addresses as a fixed entry point to your applications.
- CloudFront pricing is mainly based on data transfer out and HTTP requests while Global Accelerator charges a fixed hourly fee and an incremental charge over your standard Data Transfer rates, also called a Data Transfer-Premium fee (DT-Premium).
- CloudFront uses Edge Locations to cache content while Global Accelerator uses Edge Locations to find an optimal pathway to the nearest regional endpoint.
- CloudFront is designed to handle HTTP protocol meanwhile Global Accelerator is best used for both HTTP and non-HTTP protocols such as TCP and UDP.
Note: If you are studying for the AWS Certified Advanced Networking Specialty exam, we highly recommend that you take our AWS Certified Advanced Networking – Specialty Practice Exams and read our Advanced Networking Specialty exam study guide.
Resources:
https://www.gigaspaces.com/blog/amazon-found-every-100ms-of-latency-cost-them-1-in-sales/
https://www.forbes.com/sites/steveolenski/2016/11/10/why-brands-are-fighting-over-milliseconds/#4d8e3b344ad3
https://aws.amazon.com/global-accelerator/
https://aws.amazon.com/cloudfront/