Last updated on January 8, 2026
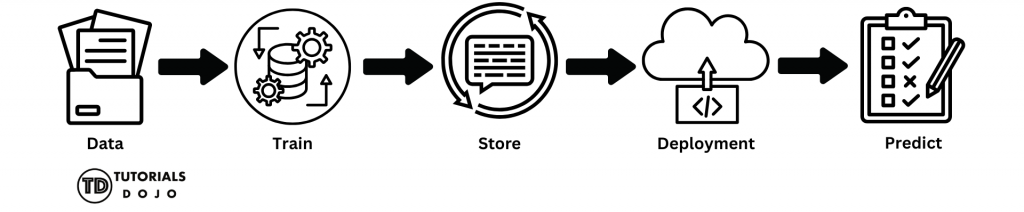
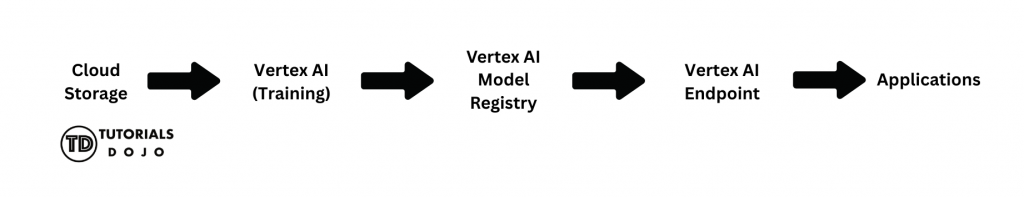
When people hear the term “machine learning,” they often imagine complex math, advanced algorithms, or mysterious “AI magic” happening behind the scenes. In reality, machine learning on the cloud is far more practical and structured than it may sound. At its core, an ML pipeline is a series of steps that transform raw data into useful predictions. Think of it like a typical software workflow: An ML pipeline follows the same idea, just with different building blocks. Instead of starting with source code, you begin with data. Instead of compiling an app, you train a model. Instead of deploying a web service, you deploy a model endpoint. On Google Cloud Platform (GCP), each step in this process is handled by a specific cloud resource. There’s no single “ML button” you press. Instead, you connect managed services, and each service does one job well. That’s why it’s helpful to think of machine learning on GCP not as a black box, but as a pipeline of cloud resources working together. In the sections that follow, we’ll walk through this pipeline step by step—from storing data to training a model and making predictions—using simple language and beginner-friendly examples—no machine learning background required. By the end of this article, you should have a clear, high-level understanding of how a basic machine learning pipeline works on Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Specifically, you will learn: This article focuses on concepts and architecture, not implementation details. You won’t be writing code or training real models—but you will gain the mental model needed to understand how ML workloads are handled on GCP. This article is designed to be beginner-friendly, and no prior machine learning experience is required. That said, you’ll benefit the most if you have: You do not need: If you’re new to machine learning but curious about how it works in a cloud environment, this article is a great place to start. Before diving into individual services, it is helpful to take a step back and examine the entire machine learning pipeline from start to finish. At a high level, every ML workflow—no matter how advanced—follows the same basic pattern: This sequence doesn’t change. What changes is how much automation and complexity you add on top of it. On GCP, this simple flow maps cleanly to specific cloud resources: Let’s briefly walk through what this means—without getting into details yet. At this stage, you don’t need to understand how each service works internally. What matters is recognizing that machine learning on GCP is a connected pipeline, where each resource plays a clear role. In the next sections, we’ll break down each step of this pipeline one by one, starting with how and where your data is stored. Every machine learning pipeline starts with data. Think of data as the “ingredients” you’ll use to train your model. Without good data, even the most innovative model won’t make accurate predictions. On GCP, the service that handles this is Cloud Storage. Cloud Storage is Google Cloud’s place to store files in the cloud. You can think of it like Google Drive, but designed to hold datasets, model files, or anything else you need for ML. It’s secure, scalable, and accessible from other GCP services, such as Vertex AI. Once your data is safely stored in Cloud Storage, the next step in the ML pipeline is training a model. Training is the process by which a machine learning model learns patterns from your data so it can make predictions later. Don’t worry—you don’t need to understand complex algorithms to get the big picture. On GCP, the service that handles training is Vertex AI. Vertex AI is a fully managed service, which means GCP handles all the servers, scaling, and infrastructure for you. You need to provide your data and select some basic settings. There are two beginner-friendly ways to train models on Vertex AI: After your model is trained in Vertex AI, the next step is to save it and keep track of its versions. This ensures you can reuse your models, improve them over time, and avoid mistakes from overwriting important work. GCP provides the Vertex AI Model Registry, a service that acts like a library for all your trained models. Each time you train a new model, you can save it here, along with metadata like: This way, you always know which version is the best, and you can roll back to an older model if needed. While Vertex AI handles versioning, it’s also a good idea to store a copy of your model in Cloud Storage. This serves as a safe backup, making it easy to transfer models between projects or environments. Once your model is trained and saved, it’s time to deploy it. Deployment is the step that transforms a static model file into a functioning service that applications can utilize to make predictions. On GCP, the service used for deployment is the Vertex AI Endpoint. Think of it as a web address (URL) for your model. Once deployed, the model can receive data from applications and automatically return predictions. Key points about deployment: When deploying a model for the first time: Now that your model is deployed to a Vertex AI Endpoint, it’s ready to do what it was trained to do: make predictions. Making predictions is simply sending new data to the deployed model and receiving an output. For example: The model does not retrain during this step—it only applies what it learned during training. The Vertex AI Endpoint provides a secure HTTPS URL that your applications can use to interact with the model. All requests and responses are handled automatically, so you don’t have to manage servers or scale manually. Once your ML model is trained, saved, deployed, and making predictions, it’s important to control who can access it. Security ensures that only authorized users or applications can interact with your data or model. On GCP, access control is managed with Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Service Accounts: Once your ML pipeline is running—data stored, model trained, deployed, and serving predictions—it’s essential to monitor its usage and manage costs. Even simple pipelines can incur charges if endpoints or training jobs are left running. In this article, we walked through a beginner-friendly machine learning pipeline on Google Cloud Platform (GCP). By following these steps, you can understand how data turns into predictions using cloud resources—even without any coding or advanced ML knowledge. Here’s a recap of the pipeline steps: So far, we’ve created a basic ML pipeline on GCP: storing data, training a model, saving and versioning it, deploying it, making predictions, securing access, and monitoring usage. This is everything a beginner needs to understand the core workflow. But in real-world projects, ML pipelines can become more complex. That’s where MLOps comes in. MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) is the practice of automating and managing ML pipelines at scale. It combines ideas from software engineering, DevOps, and ML to make pipelines: Vertex AI Tutorials & Hands‑On Guides — Step‑by‑step tutorials for training and deploying models on GCP. GCP Machine Learning & AI Training Paths — Google official training courses and paths for ML & Vertex AI.
Objectives
Prerequisites
The Simplest ML Pipeline on GCP
Storing Your Data
What is Cloud Storage?
How Data Fits Into the Pipeline
Why This Matters for ML
Training a Model
Vertex AI: The Beginner-Friendly Training Tool
What Happens During Training?
Saving and Versioning the Model
Vertex AI Model Registry: Your Model Library
Why Versioning Matters
Cloud Storage Backup
Deploying the Model
Vertex AI Endpoint: Making Your Model Accessible
Why Deployment Matters
Quick Beginner Checklist
Making Predictions
How Predictions Work
GCP Resource: HTTPS Endpoint
Securing the Pipeline
GCP Resource: IAM and Service Accounts
Beginner-Friendly Rules
Monitoring and Cost Awareness
GCP Resources for Monitoring
Why This Matters
Summary
Key Takeaways for Beginners
Next Steps
What is MLOps?
Supplementary Resources
References