AWS App Runner Cheat Sheet
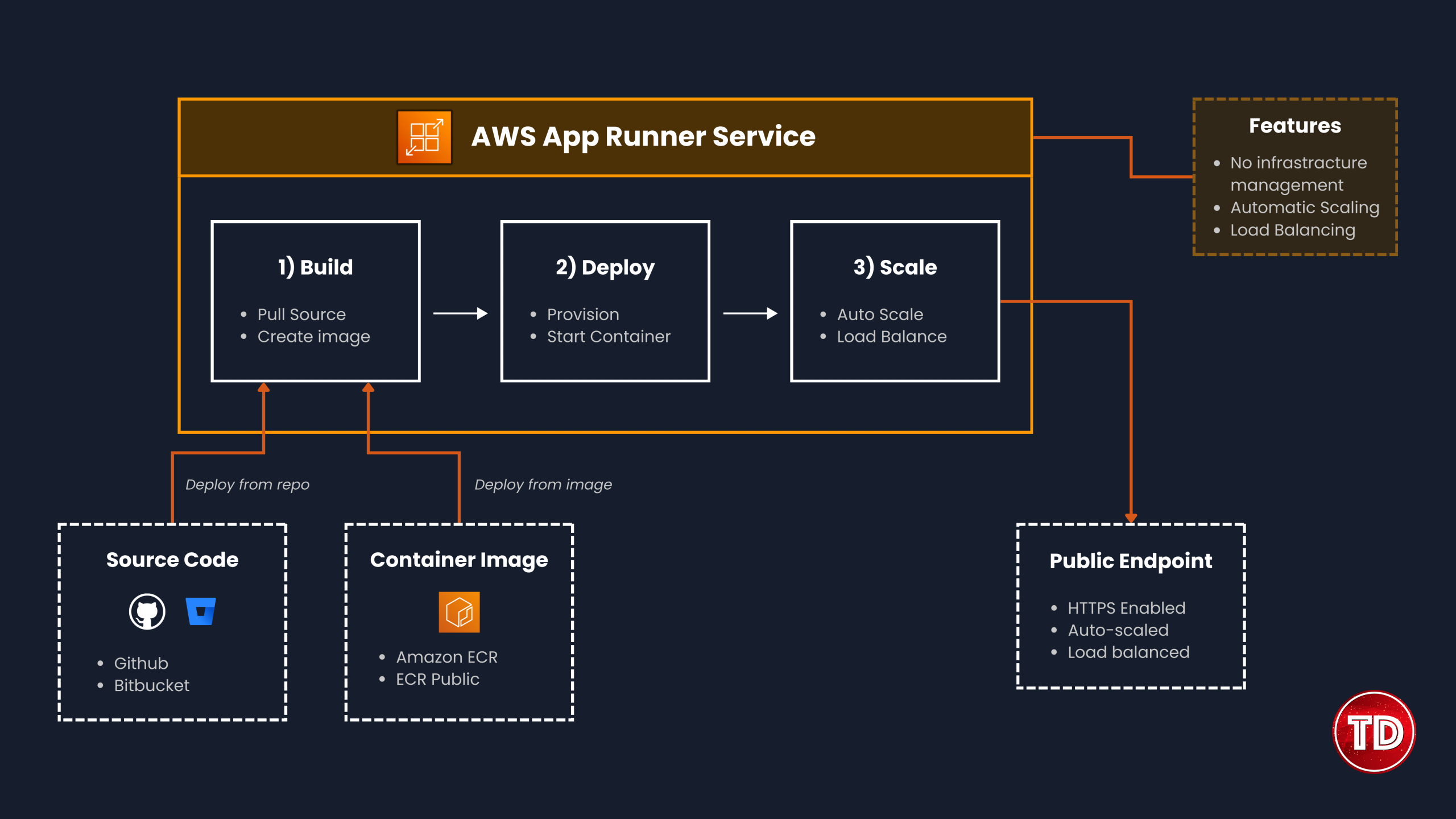
- A fully managed container application service that enables you to build, deploy, and run scalable and secure web applications or API services directly from source code or container images in the AWS Cloud without requiring prior infrastructure or container experience.
- It supports full-stack development for both frontend and backend applications using the HTTP and HTTPS protocols, making it ideal for deploying websites, backend services, and APIs.
- For developers and operations teams, App Runner simplifies deploying new versions of code or images and enables automatic deployments triggered by commits or new container image versions.
Key Concepts
- App Runner service – An AWS resource that deploys and manages your application based on its source code repository or container image.
- Source type – The type of source repository you provide for deploying your App Runner service: Source code – App Runner builds and deploys from your code repository (GitHub/Bitbucket).
- Source image – App Runner deploys a pre-built container image from Amazon ECR or ECR Public.
- Repository provider – The repository service that contains your application source (for example, GitHub, Bitbucket, or Amazon ECR).
- Runtime – A base image for deploying a source code repository. App Runner provides a variety of managed runtimes for different programming platforms and versions.
- Deployment – An action that applies a version of your source repository (code or image) to an App Runner service.
AWS App Runner Source Options
1. Source Code Repository
- App Runner can retrieve your source code from either a Bitbucket or GitHub repository.
- App Runner supports container images, runtimes, and web frameworks, including Node.js and Python.
2. Container Image Repository
- App Runner supports Amazon ECR (Amazon Elastic Container Registry) for storing private images in your AWS account, and Amazon ECR Public for storing publicly readable images.
- When providing container images, you are responsible for regularly updating and patching these images.
- To deploy your image to an App Runner service from a private repository, App Runner needs permission to read your image from Amazon ECR.
AWS App Runner Deployment Methods
App Runner allows you to set deployment behavior through the following interfaces:
- Console – When creating a new service or updating an existing one, go to the Deployment settings in the Source and deployment configuration page and select Manual or Automatic.
- API or AWS CLI – In a CreateService or UpdateService call, set SourceConfiguration.AutoDeploymentsEnabled to False for manual deployment or True for automatic deployment.
1. Automatic Deployment
- Use automatic deployment for continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD): whenever you push a new image version to your image repository or a new commit to your code repository, App Runner automatically deploys it.
- For code repositories, whenever you push a new commit that makes changes in the source directory, App Runner deploys your entire repository.
- Source directory set to root (default): All commits trigger deployment
- Source directory set to specific path: Only commits within that path trigger deployment
- App Runner doesn’t support automatic deployment for Amazon ECR Public images and for images in an Amazon ECR repository that belongs to a different AWS account.
2. Manual Deployment
- Use manual deployment when you want to control and initiate each service deployment yourself.
- In a manual deployment, App Runner uses the entire repository as the source.
AWS App Runner Auto Scaling
- App Runner automatically scales the number of containers up or down to meet the application needs you specify.
- App Runner maintains auto-scaling settings in a shareable resource called AutoScalingConfiguration.
- Auto Scaling Settings:
-
- Max concurrency: The maximum number of concurrent requests that an instance processes. If concurrent requests exceed this limit, App Runner scales up the service.
- Max size: The maximum number of instances that a service scales up to. At most, MaxSize instances actively serve traffic for your service.
- Min size: The minimum number of instances that App Runner provisions for a service.
AWS App Runner Networking and Security
VPC for Outgoing Traffic
- You can configure your App Runner service with a custom VPC connector for outbound traffic, which may experience a two to five-minute one-time startup latency. Reusing the same VPC connector for another service avoids the startup latency.
- A VPC connector configuration is based on a security group and subnet combination, and the underlying Hyperplane ENIs are shared across your App Runner services.
Private Endpoints for Incoming Traffic
- After you enable a Private endpoint, your service is only accessible from your VPC and can’t be accessed from the internet.
- VPC interface endpoint: an AWS PrivateLink resource that connects an Amazon VPC to an endpoint service.
App Runner doesn’t support VPC endpoint policies. By default, the VPC interface endpoint allows full access to App Runner. To control traffic, you can attach a security group to the endpoint’s network interfaces.
AWS App Runner Pricing
- You only pay for compute and memory resources that your App Runner service consumes.
- Automated deployments: Monthly fee per application that covers all automated deployments for that month.
- Deploying from source code: Build fee for the time it takes App Runner to build a container from your source code.
AWS App Runner Supported Runtimes
- App Runner provides managed runtimes for various programming environments, including Python, Node.js, .NET, PHP, Ruby, and Go.
- When a managed language runtime version reaches End of Life (EOL) officially, App Runner declares the version status to be End of Support.
- Existing services will continue to run and serve traffic even if they use a runtime that has reached End of Support, but they will run on unsupported runtimes that no longer receive updates, security patches, or technical support.
- If your service is based on a source image, no further action is required.
- If your service is based on source code, update the service configuration to use a supported runtime version.
AWS App Runner Service Management
Custom Domains
- A domain that you associate with your App Runner service, so users can use this domain to access your web service instead of the default App Runner subdomain.
- The *.awsapprunner.com domain is registered in the Public Suffix List (PSL) to augment security of your App Runner applications.
- Root domain: You cannot use CNAME for the root domain (e.g., example.com). Use a Route 53 alias record, which supports root domains, is more flexible, and incurs no DNS query charges.
- Subdomain: For login.example.com or www.example.com, use either CNAME or alias record.
- Wildcard: *.example.com covers all immediate subdomains but not the root domain. Must be used alone and only at the first subdomain level.
Maintenance
-
- An activity that App Runner occasionally performs on the infrastructure that runs your App Runner service.
- During this time, the service status changes to OPERATION_IN_PROGRESS for a few minutes, and actions like deployment, config updates, pause/resume, or deletion are temporarily blocked.
AWS App Runner Best Practices
- For high availability, configure MinSize to spread service instances across multiple AZs.
- Select at least three subnets across different AZs when configuring VPC access.
- Use automatic deployments for CI/CD workflows.
- Regularly update and patch container images when using source image deployments.
- Use private subnets (not public) for VPC connectors.
- Monitor auto scaling metrics to optimize MaxConcurrency and instance counts.
- Use custom auto scaling configs depending on goals (high availability vs low cost)
- Implement monitoring – Use AWS tools to track reliability, security, availability, and performanceMonitor Amazon CloudWatch metrics and set alarms.
- Review AWS CloudTrail logs for actions affecting availability (e.g., PauseService, DeleteConnection).
- Scan images for vulnerabilities using Amazon ECR’s image scanning APIs.
AWS App Runner Cheat Sheet References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apprunner
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apprunner/latest/dg/architecture.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apprunner/latest/dg/
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apprunner/latest/dg/service-source-code.html#service-source-code.managed-platforms.eos