Last updated on November 21, 2025
AWS Fargate Cheat Sheet
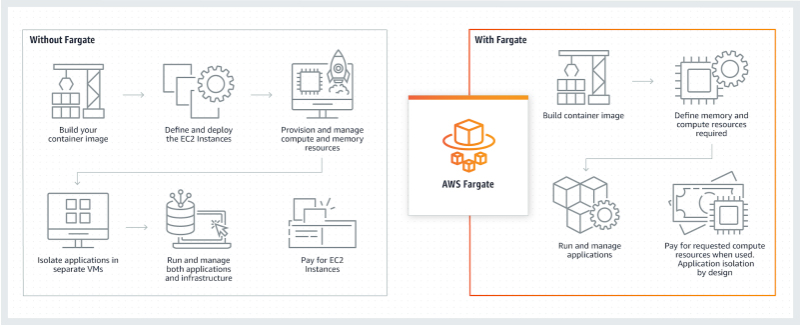
- A serverless compute engine for containers that works with both Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
- It removes the need to provision, configure, and scale clusters of virtual machines to run containers. You define your application’s requirements (CPU, memory), and Fargate manages the underlying infrastructure.
How It Works
Use Case
-
- Launching containers without having to provision or manage EC2 instances.
- If you want a managed service for container cluster management.
- Configurations
- Amazon ECS task definitions for Fargate require that you specify CPU and memory at the task level.
- Operating Systems & Architecture: Supports Linux (X86_64 and ARM64/Graviton2) and Windows Server (X86_64) workloads.
- Resource Limits: Supports the
ulimitsparameter to define resource limits for a container. - Logging: Supports
awslogs,splunk,firelens, andfluentdlog drivers. - Storage:
- Default Ephemeral Storage: When provisioned, each Fargate task receives 20 GiB of ephemeral storage by default (consolidated for images, logs, and scratch work).
- Configurable Storage: You can increase the ephemeral storage to up to 200 GiB for workloads that require more data processing space.
- Persistent Storage: Fargate tasks can mount Amazon EFS file systems for persistent, shared storage.
- Updates:
- If you have a service with running tasks and want to update its platform version, you can update your service, specify a new platform version, and choose Force new deployment. Your tasks are redeployed with the latest platform version.
- If your service is scaled up without updating the platform version, those tasks receive the platform version specified in the service’s current deployment.
- Amazon ECS Exec is a way for customers to execute commands in a container running on Amazon EC2 instances or AWS Fargate. ECS Exec gives you interactive shell or single command access to a running container.
AWS Fargate Network
-
- Amazon ECS task definitions for Fargate require that the network mode is set to
awsvpc. Theawsvpcnetwork mode provides each task with its own elastic network interface. - Requires the
awsvpcnetwork mode, providing each task with its own elastic network interface (ENI) and private IP address.
- Amazon ECS task definitions for Fargate require that the network mode is set to
AWS Fargate Compliance
-
- PCI DSS Level 1, ISO 9001, ISO 27001, ISO 27017, ISO 27018, SOC 1, SOC 2, SOC 3, and HIPAA
AWS Fargate Pricing
-
- You pay for the amount of vCPU and memory resources your containerized application requests.
- Billing Granularity: Usage is calculated per second, with a 1-minute minimum, from when your container image is pulled until the task terminates.
- Cost Factors: Rates vary depending on the Operating System (Linux vs. Windows) and CPU Architecture (x86 vs. ARM/Graviton) you select.
- Storage: Each task comes with 20 GiB of ephemeral storage at no additional cost. You only pay for storage configured above this default amount.
- Ways to Save:
- Fargate Spot: Offers significant discounts for fault-tolerant workloads using spare AWS capacity.
- Compute Savings Plans: Provides lower prices in exchange for a flexible commitment to a consistent amount of usage (e.g., 1 or 3 years).
Note: If you are studying for the AWS Certified Security Specialty exam, we highly recommend that you take our AWS Certified Security – Specialty Practice Exams and read our Security Specialty exam study guide.
AWS Fargate Cheat Sheet References:
https://aws.amazon.com/fargate/
https://aws.amazon.com/fargate/faqs/
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/developerguide/AWS_Fargate.html
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/aws-fargate/
Deep dive into AWS Fargate