Last updated on December 12, 2025
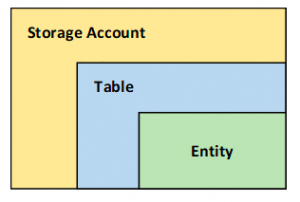
Azure Table Storage Cheat Sheet
- A NoSQL key-value store for large semi-structured datasets.
- Supports flexible data schema.
- Query using a subset of the OData protocol and filter on the PartitionKey and RowKey properties for fast, indexed lookups. Azure Cosmos DB for Table offers enhanced query capabilities.
Important Update (2024): Microsoft’s strategic direction for table storage is Azure Cosmos DB for Table. This offering provides the Azure Table Storage API with significant enhancements: guaranteed single-digit millisecond latency, automatic global distribution, dedicated throughput, and a comprehensive SLA. For all new development, Microsoft recommends using Azure Cosmos DB for Table. The classic Azure Storage Tables service is being maintained but is not the focus for new feature development.
Features
- Allows you to store and query huge sets of structured, non-relational data. And as demand grows, your tables will scale-out.
- Supports transactional batch operations (Entity Group Transactions) for atomic updates of up to 100 entities within the same partition.
- Scale-up without having to manually shard your dataset.
- The data is replicated three times within a region using geo-redundant storage. Analytical Store (Preview): Enables large-scale analytics on table data using tools like Apache Spark and Synapse Analytics without impacting transactional performance.
- An entity has a limit of 1MB in size.
- Store data sets that do not require complex joins, foreign keys, or stored procedures, and can be denormalized for fast access.
- Table storage is used to store flexible data sets such as user data for web applications, device information, or other types of metadata the service requires.
- You can store any number of entities in a table, up to the storage account’s capacity limit.
- Throughput Management: Azure Cosmos DB for Table offers provisioned throughput (RU/s) with autoscale options, providing predictable performance and cost for demanding workloads.
Performance and Pricing Models
-
Standard Azure Table Storage: Offered in General-purpose v2 (GPv2) storage accounts. Billed based on storage capacity, transaction operations, and data transfer.
-
Azure Cosmos DB for Table: Offers two capacity modes:
-
Provisioned Throughput: Reserve throughput (Request Units/sec) billed hourly. Best for steady, predictable workloads.
-
Serverless: Pay only for consumed Request Units. Ideal for intermittent, unpredictable traffic with bursts.
-
Validate Your Knowledge
Question 1
Question Type: Matrix Sorting Choice
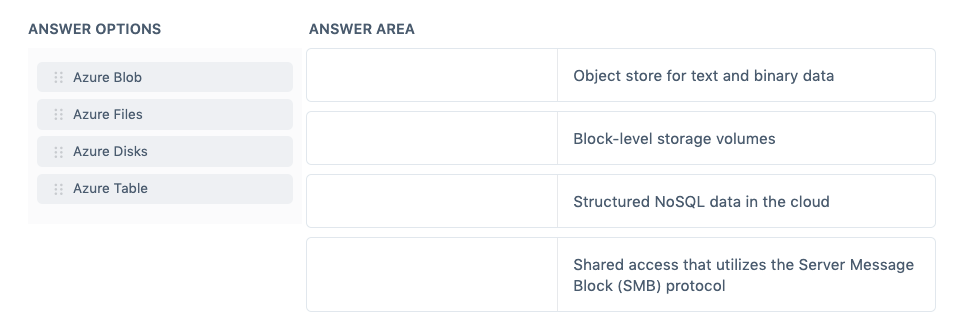
Match the Azure Storage service to its correct description.
Instructions: To answer, drag the appropriate Azure service from the column on the left to its description on the right. Each correct match is worth one point.
For more Azure practice exam questions with detailed explanations, check out the Tutorials Dojo Portal:
Azure Table Storage Cheat Sheet Resources:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/storage/tables/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/tables/table-storage-overview