Last updated on February 13, 2026
GitHub Desktop Cheat Sheet
GitHub Desktop is an application that enables you to interact with GitHub using a visual interface instead of the command line. It extends and simplifies your Git workflow using a transparent and accessible graphical user interface.
Key Concepts
- Repository: A project folder that is tracked by Git, containing all files and their version history.
- Clone: The act of creating a complete local copy of a repository that exists on GitHub.com.
- Commit: A snapshot of the changes you have staged, saved permanently to your local repository’s history.
- Branch: An independent line of development within a repository.
- Pull Request (PR): A request to merge the changes from one branch into another, facilitating code review and discussion on GitHub.com.
- Remote: The common version of your repository hosted on GitHub.com (typically named
origin)
Core Workflows
Getting a Repository
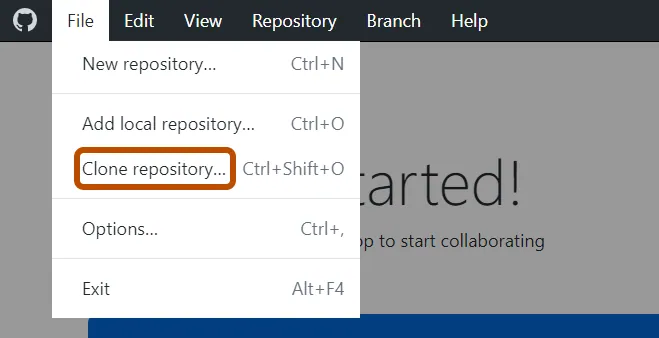
- Clone an existing repository
- Use File > Clone Repository.
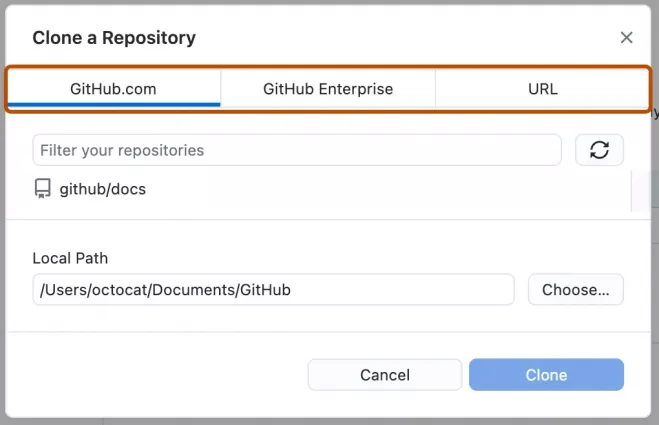
- Select a repository from your GitHub.com list or enter its URL directly.
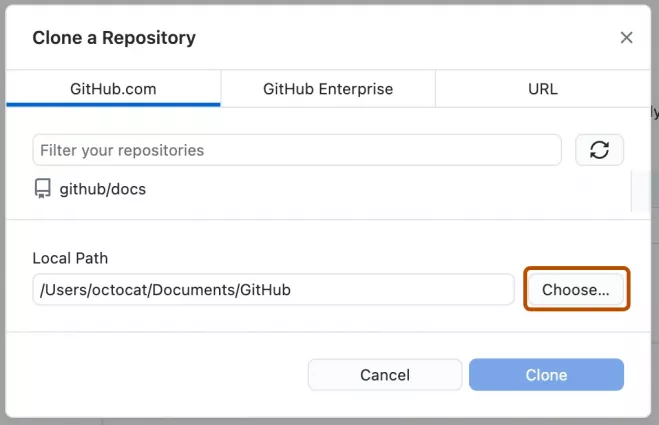
- Choose a local path and click Clone.
- Use File > Clone Repository.
- Create a new repository
- Use File > New Repository.
- Enter a name, optional description, and choose a local path.
- You can choose to initialize the repository with a README file.
- Add an existing local repository
- Use File > Add Local Repository.
- Navigate to the folder on your computer that already contains a
.gitsubdirectory.
Making and Saving Changes
-
Make Changes: Edit files in your configured external editor.
-
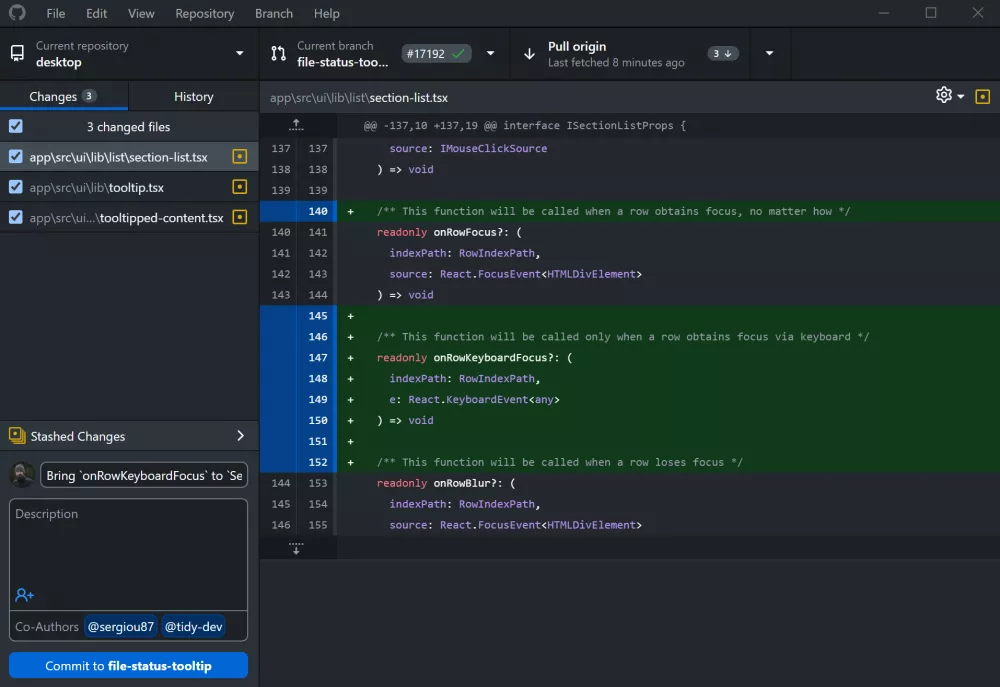
View Changes: All modified files are listed in the Changes tab in the left sidebar. Click a file to see a line-by-line diff.
-
Stage Changes: Select the checkbox next to individual files you wish to commit.
-
Create a Commit:
-
-
Write a mandatory summary and an optional extended description.
-
Click Commit to
[branch-name]to save the snapshot to your current branch.
-
Branching
- Create a new branch: Click Current Branch in the toolbar, then click New Branch. Name the branch and select which existing branch to base it on.
- Switch branches: Click Current Branch in the toolbar and select any available local branch.
- Merge a branch:
- Switch to the branch you want to merge into (e.g.,
main). - Click Current Branch, then Choose a branch to merge into
main. - Select the branch containing the changes you want to integrate (e.g.,
feature-branch).
- Switch to the branch you want to merge into (e.g.,
Synchronizing with GitHub
- Push: To upload your local commits to the remote repository on GitHub, click Push origin.
- Pull: To download and integrate changes from the remote repository into your current local branch, click Pull origin.
- Fetch: To check for new changes on the remote without merging them, use Repository > Fetch.
Working with Pull Requests
- Publish a branch: After committing to a new branch, click Publish branch to push it to GitHub. A button to create a pull request will appear.
- Create a Pull Request: Click Create Pull Request to open GitHub.com in your browser and finalize the pull request.
- View open pull requests: Check the Pull Requests list tab to see open requests and checkout their associated branches locally.
Troubleshooting
| Problem | Likely Cause | Solution |
| Authentication failed | Expired or missing credentials. | Re-authenticate your account in File > Options > Accounts. |
| Can’t push or pull | Your local history diverges from the remote, often causing a merge conflict. | You must first pull the remote changes. GitHub Desktop will guide you to resolve any conflicts. |
| Repository not found | Incorrect URL or lack of permissions. | Verify the repository URL and your access permissions on GitHub.com. |
| Changes not appearing in the list | Files are not tracked by Git, possibly due to a .gitignore rule. |
Ensure the files are not listed in your .gitignore file. |
| Merge conflict | Git cannot automatically merge changes from different branches. | The application will list conflicted files. You must open them, resolve the conflicts manually, mark them as resolved, and then commit. |
Best Practices
- Make focused, atomic commits with clear messages.
- Always create a new branch for any feature or bug fix.
- Regularly pull changes from the upstream
mainbranch into your feature branches. - Review the diff of your changes in the Changes tab before every commit.
- Use the History tab to examine past commits and revert changes if necessary.