Last updated on December 21, 2025
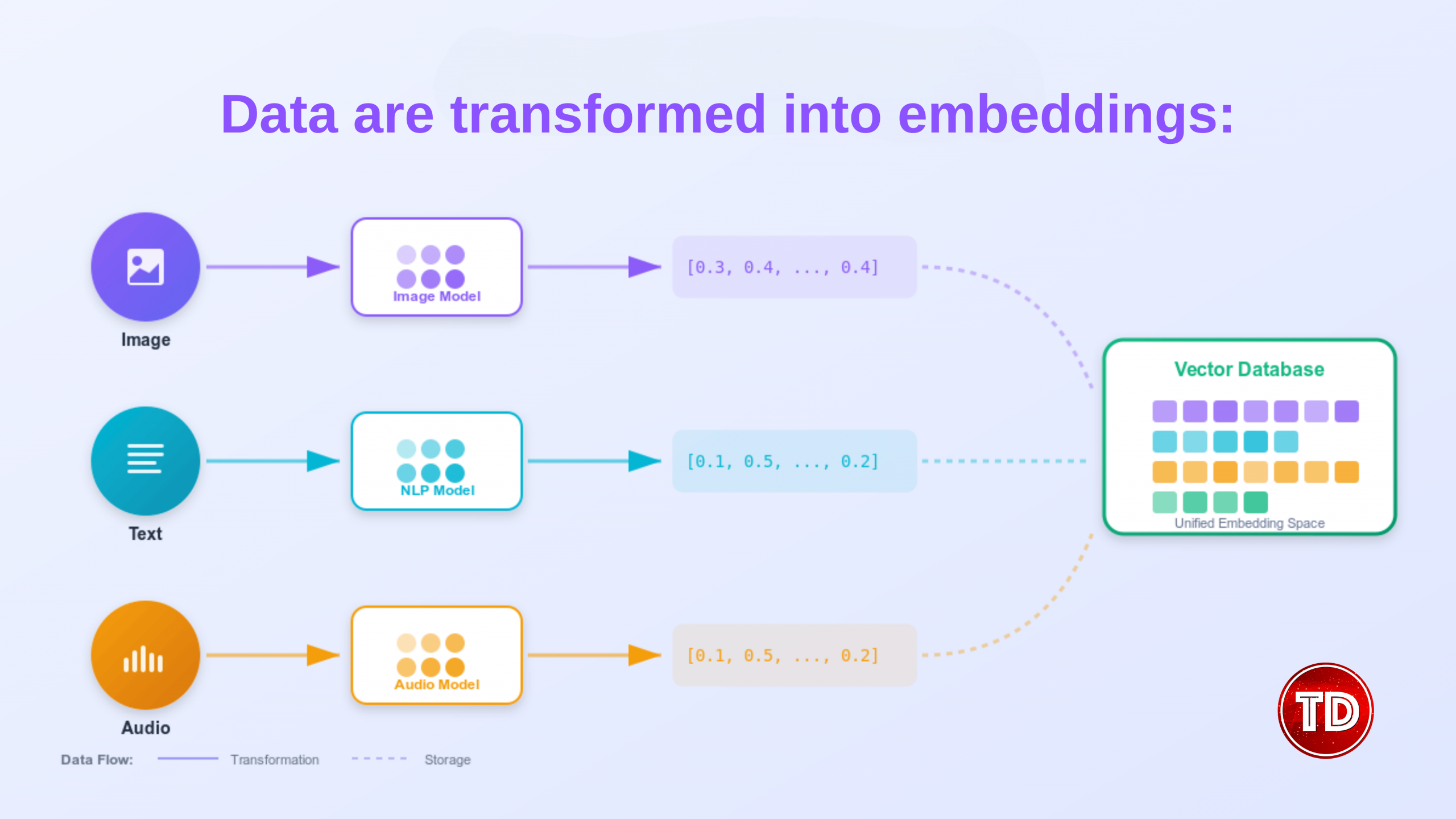
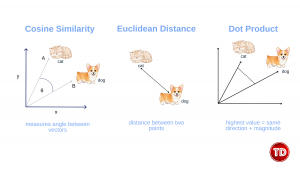
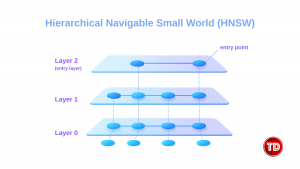
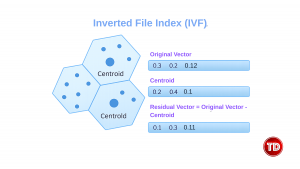
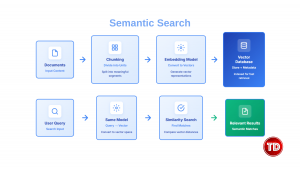
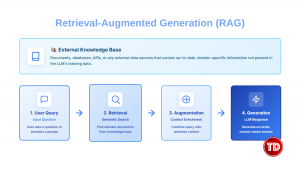
The generative AI (GenAI) revolution has transformed how organizations extract value from their data. While large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities in understanding and generating human-like text, their true enterprise potential is unlocked only when they can access proprietary, domain-specific information. This necessity has propelled vector databases from a specialized niche into an essential pillar of modern AI infrastructure. A vector database, as its name suggests, is a type of database designed to store, index, and efficiently search vector embeddings. These vectors are high-dimensional points that represent meaning. At its core, a vector database is designed to provide several capabilities beyond simple storage: efficient nearest-neighbor search algorithms, sophisticated indexing structures optimized for high-dimensional data, fault tolerance and durability guarantees, authentication and access control mechanisms, and query engines that support complex filtering alongside similarity search. Embeddings are number arrays that capture the meaning of text, images, or audio. When text, images, audio, or other content passes through an embedding model, it is transformed into a dense vector where each dimension contributes to representing some aspect of the content’s meaning. Consider a practical example: the words “king,” “queen,” “prince,“ and “princess“ would occupy neighboring regions in the embedding space because they share semantic relationships around royalty. Similarly, “Paris“ and “France“ would be closer to each other than either would be to “Tokyo“ or “Japan,“ yet all four would share some relationship as capital-country pairs. This geometric representation of meaning enables machines to understand relationships that would be impossible to capture solely through keyword matching. Traditional databases rely on exact matching. For example, if I search for “y2k tops for women,“ the products returned to me will include the specific words: “y2k”, “top”, and “women.“ Vector search operates on an entirely different principle: it finds items whose vector representations are closest to the query vector in the embedding space, regardless of the specific words used. This capability enables semantic search. When I search for “y2k tops for women,“ a vector-powered system understands my intent and retrieves trendy tops that match the Y2K aesthetic, even if the product descriptions never use that exact phrase. The system accomplishes this by converting the query into a vector embedding using the same model that generated the product embeddings, then finding the query’s nearest neighbors in the database. Vector search typically relies on distance metrics to quantify similarity between vectors: To speed up similarity search, vector databases use algorithms such as: Vector databases are the backbone of two significant AI capabilities today: semantic search and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Both applications leverage the ability to find contextually relevant information based on meaning rather than keywords, but they serve different purposes and operate in other contexts. Semantic search lets users ask questions using natural language. Instead of matching keywords, it searches by meaning. Example: If someone searches for “heart attack symptoms,“ they would find documents that discuss “myocardial infarction“ or “cardiac arrest“ because the embedding model will understand that these concepts are related. This works by: LLMs sometimes produce incorrect answers, also known as hallucinations. RAG addresses this challenge by grounding LLM responses in evidence retrieved from trusted data sources. How it works: As a result, the adoption of RAG in enterprises has accelerated dramatically. AWS provides a range of vector database services built into its existing platforms. Rather than forcing a one-size-fits-all approach, you can pick the service that best matches your needs and keep your data close to where you use it. What It Does: Why Use It: What Makes It Different: Why Use It: What Makes It Different: How It Works: What It Provides: Simplifies Work: Storage Options: New Capabilities: To summarize, here is a table explaining when to use the service and its strengths: Service When to Use Main Strength Aurora PostgreSQL + pgvector You already use PostgreSQL or need both normal and vector search Familiar database, powerful flexibility Amazon OpenSearch Large searches, complex queries, mixing keywords with semantic search Hybrid search (keywords + meaning) Amazon MemoryDB Instant responses matter (AI chat, recommendations, fraud detection) Fastest search possible Neptune Analytics Questions need answers from multiple connected sources Understands relationships Amazon DocumentDB MongoDB users, documents + vectors together MongoDB compatibility Knowledge Bases for Bedrock Want AI search working quickly with minimal setup Completely managed, turn-key solution To build strong and scalable semantic search systems: Vector databases are now essential for modern AI. They help LLMs access accurate, relevant, and meaningful information, which leads to better results for users and organizations. AWS strengthens this approach by adding vector features directly into its core services. Because of this, developers can choose the right tool for their existing systems, whether they need relational storage, fast search, or a complete RAG solution. In the end, this means faster development, higher accuracy, and AI systems that are ready to scale with your business.
But First, What Are Vector Databases?
Embeddings (Vectors)
Vector Search
Indexing and Algorithms
The GenAI Imperative: Semantic Search and RAG
Semantic Search
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
AWS Vector Database Services: A Simple Overview
PostgreSQL with Vector Search (pgvector) using Amazon Aurora and Amazon RDS
Amazon OpenSearch Service
Amazon Memory DB
Amazon Neptune Analytics
Amazon DocumentDB
Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases
Quick Recap
Conclusion
Resources: