Last updated on January 23, 2026
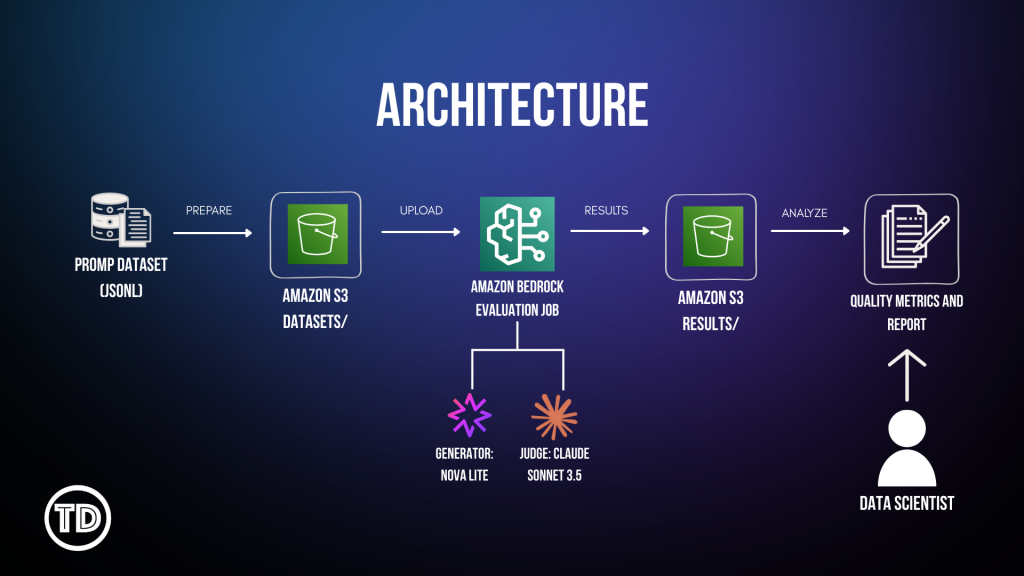
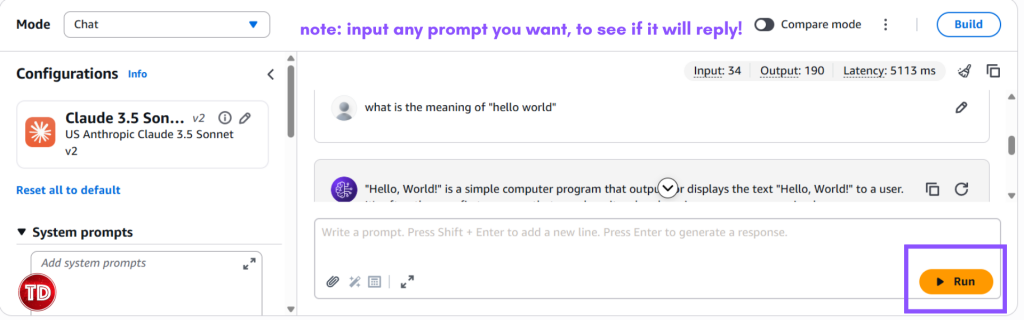
Evaluating your LLM’s quality should not cost you too much money or even weeks of your time. You’re probably stuck in a limbo of choosing between two options that have their own drawbacks: Automated metrics like BLEU, ROUGE and accuracy scores? Sure, they are quite fast and cheap, but they ultimately fall short in judging real conversations. Since they simply match word patterns, they’re not a good fit for open ended responses simply because they can’t tell if they actually understood the question or its tone. As for human reviewers, they do get it right. They captured the context/subtlety and spot tone issues much better than the tools earlier. The problem though is that it’s costly and super time consuming. Imagine the time consumed in testing responses that are over a thousand. Your budget’s wont like it for sure. So as an alternative, there’s another technique that will make your LLM judging-life easier…. It’s called LLM-as-a-judge! From the name itself, LLM- as a-judge uses one AI model to assess another’s output. Amazon Bedrock now offers this feature that is up to par with the human preference by 80% for a much cheaper and faster way! In this guide, you will learn how to set up LLM-as-a-judge using Amazon Nova Lite (the model you’re testing) and Claude (the judge). You’ll automate quality checks, lower cost, and finally scale your testing. LLM-as-a-judge is a process where one LLM evaluates another LLM’s quality of generated output based on guidelines you’ve created. Instead of the manual approach using human evaluators (which takes a lot of effort and time!), you speed up model evaluation by automating it. You might be thinking that out of all the available models to use, why choose Nova Lite? Well, simply because it’s an overachiever in so many things! Not only is it cheap, but it’s also good. Like real good. Amazon Nova Lite (the model being evaluated) has a balanced and consistent performance in all dimensions: problem identification, communication clarity, logical coherence and empathy. This means that you could confidently deploy your AI system with an assurance knowing that Nova Lite is reliable and smart. Claude 3.5 Sonnet (the judge) is your evaluator. It’s one of the best models at assessing quality, catching nuance, and providing consistent scores. When you need an AI to judge another AI’s work, Claude is the model you want. With that said, let’s get to work and automate! Before we start, I assume you already have an AWS account and access to Bedrock. Let’s start by setting up our resources and IAM configurations. You’ll need the following: Policy #1: Bedrock Model Access Paste this and name it: BedrockEvaluationModelAccessPolicy Note: Replace YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID with your AWS account ID. Policy #2: Amazon S3 Access First, create the Amazon S3 bucket: Secondly, create folders: This is where you’ll be putting our input dataset and the result of the evaluation of your generator. Thirdly, configure Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS): Enabling this allows you to upload files to Amazon S3 through the Bedrock console. Click Edit and paste:
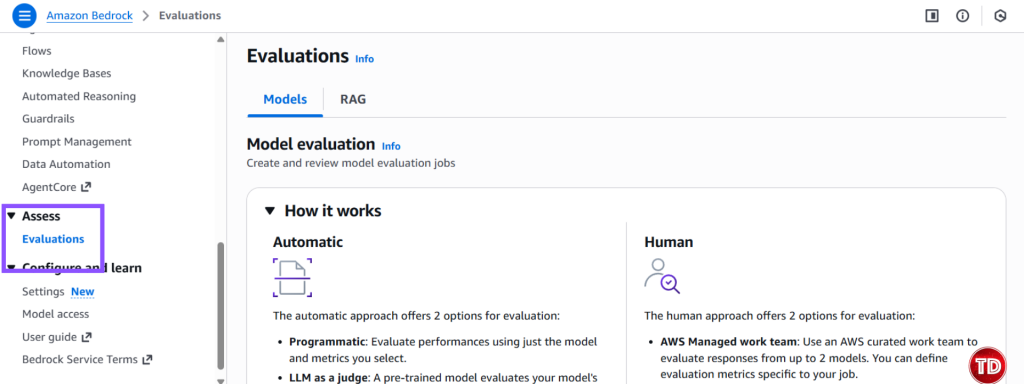
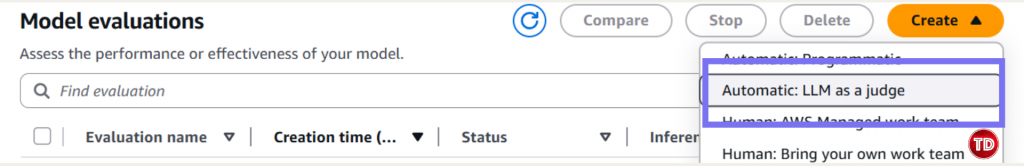
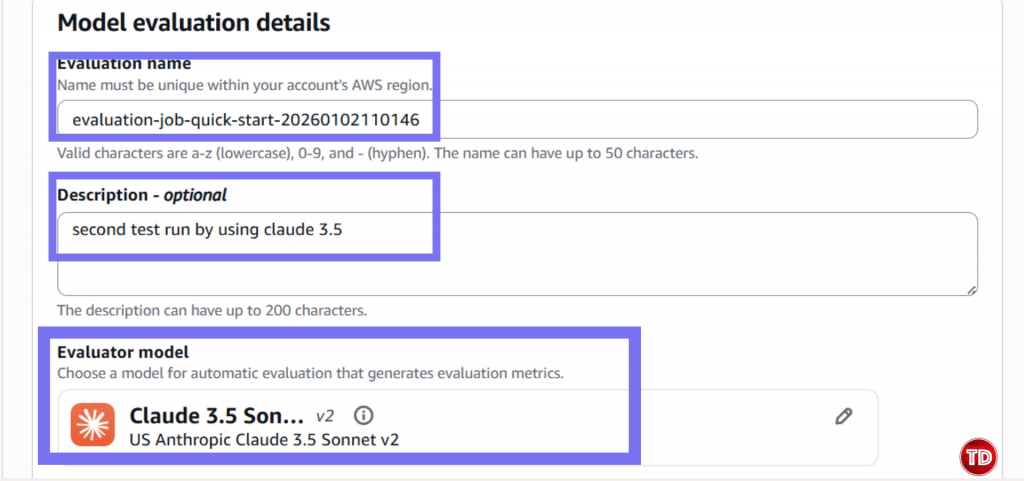
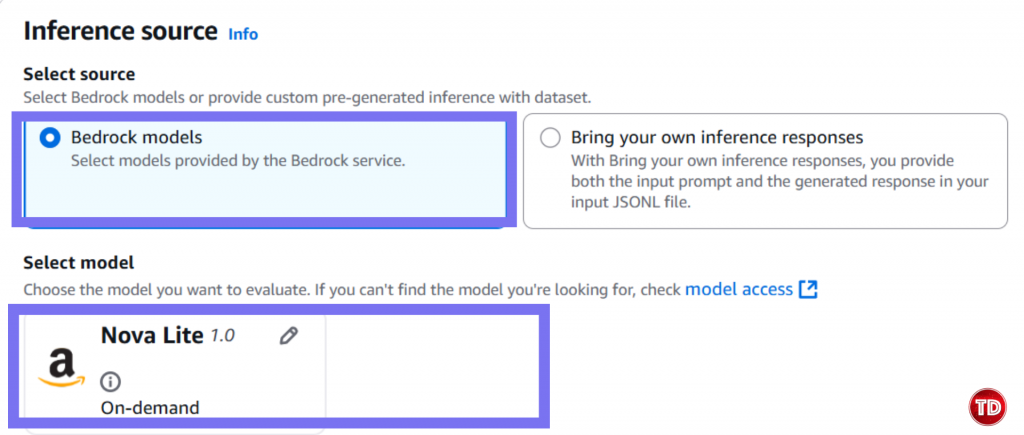
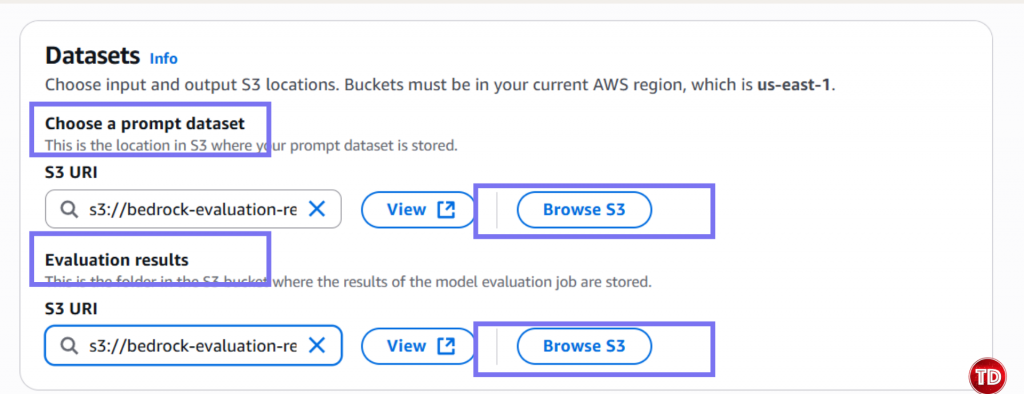
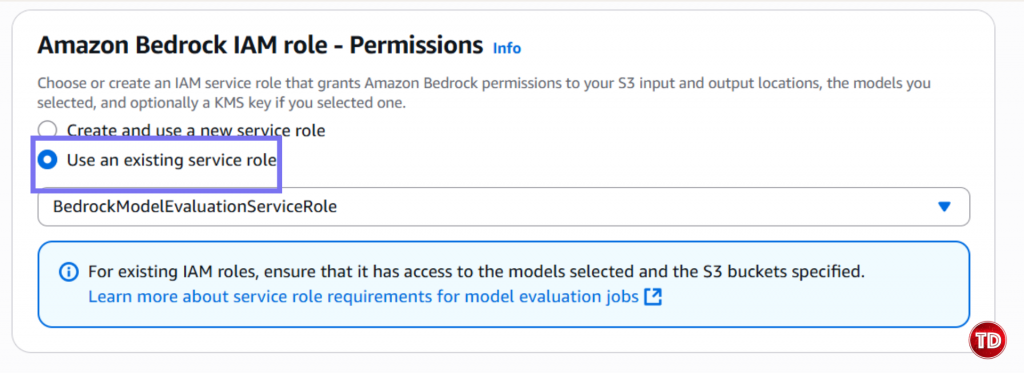
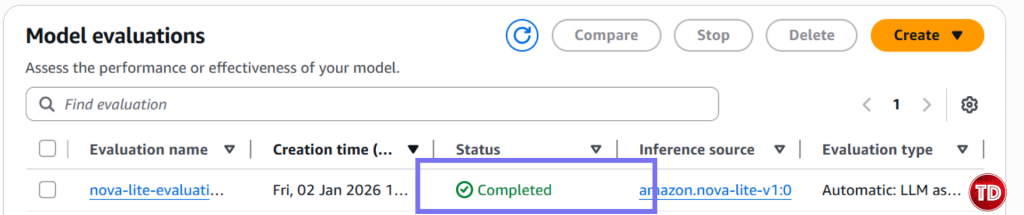
Now, we need to create a policy. 1.Go to IAM -> Policies -> Create Policy Note: Replace YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID and update bucket name if its different. Policy #3: Console User Access Next, we’ll edit our IAM policy to grant access to our models for generator and evaluator. Paste this and name it BedrockConsoleUserPolicy Note: Replace YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID in all 3 places (S3 bucket ARNs and service role ARN). Now you need to create a service role where you will attached the 2 policies created earlier (BedrockEvaluationModelAccess and BedrockEvaluationS3AccessPolicy) Note: Don't forget to replace YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID with your own aws account id! Now you’re done setting up the Prerequisites! Quite lengthy isn't it? Next we’re moving forward to set access for the models, namely the Claude 3.5 Sonnet and Amazon Nova Lite. You have to verify if you can access the Claude Sonnet 3.5 and Amazon Nova Lite Moving on, we now create prompts that the Amazon Nova Lite will respond to. You can create your own dataset by having: Create a file called evaluation-dataset.jsonl: 1. Go to Bedrock Console → Evaluations (under Assess section) 2. Click Create. 3. Select Automatic: LLM-as-a-judge 4. Enter evaluation name and fill in description. Select Claude 3.5 Sonnet. For Prompt Dataset, click your jsonl file while for the evaluation results, click your results folder. Yay that’s it, you're done! You now learned how to set up an automatic model that used Claude Sonnet 3.5 to judge your Amazon Nova Lite outputs. All free from manual review and costly evaluation. Still not convinced to use llm-as-a-judge? Check out this AWS documentation showing how LLM-as-a-judge compares to other alternative options.
What is LLM-as-a-Judge?
Why Amazon Nova Lite + Claude?
Prerequisites
Step 1: Create IAM Policies
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "BedrockModelInvoke",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"bedrock:InvokeModel",
"bedrock:CreateModelInvocationJob",
"bedrock:StopModelInvocationJob"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:bedrock:*::foundation-model/*",
"arn:aws:bedrock:*:YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID:inference-profile/*",
"arn:aws:bedrock:us-east-1:YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID:provisioned-model/*",
"arn:aws:bedrock:us-east-1:YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID:imported-model/*"
]
}
]
}
[
{
"AllowedHeaders": [
"*"
],
"AllowedMethods": [
"GET",
"PUT",
"POST",
"DELETE"
],
"AllowedOrigins": [
"*"
],
"ExposeHeaders": [
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin"
]
}
]
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "FetchAndUpdateOutputBucket",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:GetBucketLocation",
"s3:AbortMultipartUpload",
"s3:ListBucketMultipartUploads"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::bedrock-evaluation-results-YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID",
"arn:aws:s3:::bedrock-evaluation-results-YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID/*"
]
}
]
}
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "BedrockConsole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"bedrock:CreateEvaluationJob",
"bedrock:GetEvaluationJob",
"bedrock:ListEvaluationJobs",
"bedrock:StopEvaluationJob",
"bedrock:GetCustomModel",
"bedrock:ListCustomModels",
"bedrock:CreateProvisionedModelThroughput",
"bedrock:UpdateProvisionedModelThroughput",
"bedrock:GetProvisionedModelThroughput",
"bedrock:ListProvisionedModelThroughputs",
"bedrock:GetImportedModel",
"bedrock:ListImportedModels",
"bedrock:ListFoundationModels",
"bedrock:GetFoundationModel",
"bedrock:ListTagsForResource",
"bedrock:UntagResource",
"bedrock:TagResource"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "AllowConsoleS3Access",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:GetBucketCORS",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:ListBucketVersions",
"s3:GetBucketLocation"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::bedrock-evaluation-results-YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID",
"arn:aws:s3:::bedrock-evaluation-results-YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID/*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "AllowPassingServiceRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:PassRole",
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID:role/BedrockModelEvaluationServiceRole",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"iam:PassedToService": "bedrock.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}
Step 2: Create Service Role
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [{
"Sid": "AllowBedrockToAssumeRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "bedrock.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"aws:SourceAccount": "YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID"
},
"ArnEquals": {
"aws:SourceArn": "arn:aws:bedrock:us-east-1:YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID:evaluation-job/*"
}
}
}]
}
Step 4: Enable Model Access
Step 5. Prepare your Input Dataset
{"prompt": "Write a professional email declining a meeting request politely.", "referenceResponse": "A professional decline should thank the sender, briefly explain you're unavailable, and suggest an alternative time or delegate if possible. Keep the tone friendly and respectful.", "category": "professional_writing"}
{"prompt": "Explain the difference between machine learning and deep learning.", "referenceResponse": "Machine learning is when computers learn from data to make predictions. Deep learning is a type of machine learning that uses neural networks with many layers, similar to how the human brain processes information.", "category": "technical"}
{"prompt": "What are three tips for improving work-life balance?", "referenceResponse": "Set clear work hours and stick to them. Make time for hobbies and activities you enjoy. Learn to say no to extra commitments when you're already busy.", "category": "productivity"}
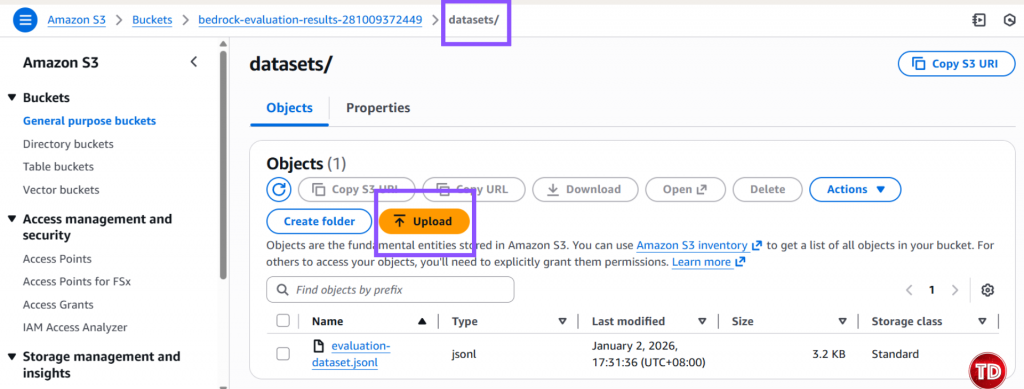
Step 6. Upload Dataset to Amazon S3
Step 7: Create Your First Evaluation Job
References: