Last updated on February 10, 2026
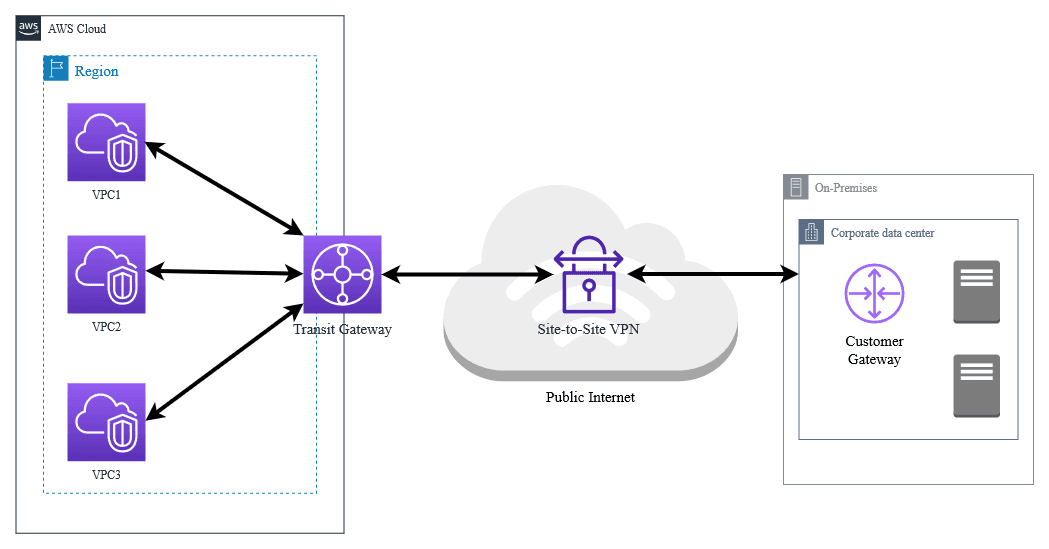
AWS Direct Connect vs VPN are two ways to securely connect your on-premises network to AWS, but they offer very different experiences. Think of AWS VPN as taking a secure highway through city traffic, while AWS Direct Connect is like having your own private express lane straight into AWS. Both options get your data to the cloud safely, but performance, reliability, and scalability vary depending on your workloads. On the public highway, you’ll occasionally hit congestion, unexpected slowdowns, and fluctuating speeds. That’s AWS VPN: reliable and encrypted, yes—but ultimately limited by the unpredictability of the internet. Direct Connect, by contrast, gives you a dedicated private lane. Traffic flows smoothly, latency stays low, throughput is consistent, and performance scales with your growing workloads. For small workloads or temporary projects, VPN can be enough. But as applications become data-heavy, latency-sensitive, or mission-critical, the wrong connection can quietly slow performance, drive up costs, and create bottlenecks in your hybrid cloud architecture. Many organizations discover the hard way that what worked in testing fails under production loads. In this article, we’ll explore AWS Direct Connect vs AWS VPN in depth. You’ll learn how they differ under the hood, when each is appropriate, and how enterprises combine both to create a fast, resilient, and future-proof connection to the cloud. By the end, you’ll know exactly which path will keep your workloads running efficiently—and your business ahead of the competition. AWS Direct Connect provides a dedicated, private network connection between your data center or office and AWS. It bypasses the public internet for faster, more consistent, and secure network performance. Key Advantages: Low Latency & High Throughput: Ideal for workloads needing real-time response. Reliable Performance: Less affected by internet congestion. Cost-Efficient for Large Transfers: Data transfer rates are often cheaper than over the internet. Hybrid Cloud Ready: Connect multiple AWS VPCs via Transit Gateway for enterprise setups. Example Use Cases: Moving large datasets to AWS S3 or Redshift. Running latency-sensitive applications (e.g., ERP, VoIP, streaming). Connecting multiple cloud environments with on-premises data centers. AWS VPN establishes a secure, encrypted connection over the public internet between your on-premises network and AWS using IPsec tunnels. Key Advantages: Quick Setup: No physical infrastructure required. Cost-Effective for Small Workloads: Pay only for VPN endpoints and data transfer. Flexible & Portable: Works anywhere with internet connectivity. Example Use Cases: Connecting small remote offices to AWS. Backup connection for Direct Connect. Short-term cloud migration or testing environments. Direct Connect is ideal when your organization needs consistent, high-speed, and reliable connectivity. Indicators Direct Connect is Right for You: Large Data Transfers: Regularly moving terabytes of data between on-premises and AWS. Latency-Sensitive Applications: Video conferencing, VoIP, or real-time analytics. Hybrid or Multi-Cloud Architecture: Connecting multiple VPCs, regions, or on-prem data centers. Predictable Costs: Direct Connect allows you to calculate fixed monthly costs for high-volume data. Best Practices: Implement redundant connections using multiple Direct Connect links for high availability. Pair Direct Connect with a VPN as backup to ensure business continuity. Use Private Virtual Interfaces (VIFs) for sensitive workloads and Public VIFs for internet-bound traffic. AWS VPN is ideal for flexibility, cost-efficiency, and quick deployment. Indicators VPN is Right for You: Small Offices or Teams: Low-volume workloads connecting to AWS. Temporary or Short-Term Needs: Cloud migration testing, temporary connections. Backup for Direct Connect: VPN can act as a failover when Direct Connect is unavailable. Quick Deployment Needs: No waiting for physical connections or provider scheduling. Best Practices: Monitor VPN connections using CloudWatch metrics to detect flaps or latency spikes. Combine with Direct Connect for hybrid redundancy in production environments. Ensure strong encryption policies and rotate keys periodically for security. Scenario: Option 1 – Direct Connect: Provides a dedicated 10 Gbps connection for predictable transfer speeds, enabling a seamless migration and real-time analytics. Option 2 – VPN: Could handle small-scale testing or remote access, but performance may fluctuate during peak hours. Optimal Approach: Use Direct Connect as the primary connection and VPN as a backup, combining reliability, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Direct Connect Costs: Port fee (1–100 Gbps). Reduced data transfer charges. Additional costs for cross-region data transfers. VPN Costs: VPN endpoint charges. Data transfer over the internet. Cost-effective for low-volume workloads but can be higher at scale. Pro Tip: For large data volumes, Direct Connect often becomes cheaper than VPN despite the initial setup cost. Direct Connect → Best for high-speed, reliable, and predictable workloads. VPN → Best for quick, flexible, and cost-effective connections. Hybrid Approach → Use Direct Connect as primary and VPN as backup for enterprise setups. Evaluate based on data volume, latency sensitivity, budget, and deployment timeline. Choosing between AWS Direct Connect and VPN isn’t just a technical decision, it’s a strategic one. The way your organization connects to the cloud can directly impact performance, reliability, cost, and ultimately, business success. Think of your network as the foundation of your cloud journey: a strong, fast, and reliable connection empowers innovation, accelerates data-driven decisions, and keeps your teams productive. Direct Connect offers unmatched speed and consistency for mission-critical workloads, while VPN provides the flexibility and agility for smaller or temporary needs. The real power comes when you combine both leveraging Direct Connect for primary workloads and VPN as a backup to build a network that is resilient, scalable, and future-proof. By understanding your business needs, evaluating workloads, and aligning them with the right connectivity option, you’re not just connecting to AWS, you’re unlocking the full potential of the cloud. Your network can become a true competitive advantage, enabling faster innovation, seamless collaboration, and limitless possibilities. The right connection is more than infrastructure—it’s your bridge to the future of your business.
1. Understanding the Basics
What is AWS Direct Connect?
What is AWS VPN?
2. Direct Connect vs VPN: Detailed Comparison
Feature
AWS Direct Connect
AWS VPN
Connection Type
Dedicated private network
Encrypted tunnels over Internet
Latency
Very low and consistent
Higher, depends on internet
Throughput
High (1–100 Gbps options)
Limited by internet connection
Reliability
Highly reliable
Internet-dependent, less predictable
Cost Structure
Fixed port fee + data transfer savings
Pay-per-use endpoint & transfer fees
Setup Complexity
Physical setup, longer lead time
Quick, software-based setup
Security
Private network, optional encryption
Encrypted traffic over internet
Best Suited For
Large-scale, high-performance workloads
Small or temporary connections, failover
3. When to Choose AWS Direct Connect
4. When to Choose AWS VPN
5. Real-World Example: Hybrid Connectivity
A company with offices in Manila and Cebu wants to migrate a 10TB database to AWS.
6. Cost Considerations
7. Choosing the Right Strategy
Strategy Type
When to Use
Pros
Cons
Direct Connect only
Large workloads, high-speed needs
Fast, reliable, secure
Higher setup cost, longer lead time
VPN only
Small workloads, temporary needs
Quick setup, low cost
Internet-dependent, variable speed
Hybrid (Direct Connect + VPN)
Enterprise-grade, critical workloads
Reliable, redundant, flexible
Slightly higher management complexity
8. Key Takeaways
Making the Right Connection for Your Cloud Journey
References